Abstract
Rats treated with DSP-4 [N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-ethyl-2-bromobenzylamine], a selective noradrenergic neurotoxin, showed no differences compared to control rats in the number of head dips, a measure of exploratory behavior. Since a previous neurochemical investigation had demonstrated that DSP-4 rats have supersensitive α2 and β-adrenergic receptors in certain regions of the central nervous system, the behavior of these animals was also examined after the injection of clonidine, an α2 agonist, and clenbuterol, a β agonist. These drugs reduced, in a dose-dependent manner, the head-dipping of both control and DSP-4 rats. However, this effect was of greater magnitude in DSP-4 animals. Control experiments suggested that the response to clonidine and clenbuterol was mediated centrally by α2 and β receptors, respectively. Other behavioral experiments with agonists of the dopaminergic and serotoninergic systems indicated that these neurotransmitter systems were unchanged in DSP-4 animals. The results are discussed in terms of the selective action of DSP-4 and the responsiveness of DSP-4 rats to adrenergic agonists. The DSP-4-treated rat may constitute a new model of functional supersensitivity to adrenergic agonists.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cavero I, Depoortere H, Lefevre-Borg F (1980) Pharmacological studies on para-aminoclonidine. Br J Pharmacol 69:295P-296P
Costall B, Marsden CD, Naylor RJ, Pycock CJ (1977) Stereotyped behaviour patterns and hyperactivity induced by amphetamine and apomorphine after discrete 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of extrapyramidal and mesolimbic nuclei. Brain Res 123:89–111
Dausse J-P, Quan-Bui KHL, Meyer P (1982) 5-1 in rat cerebral cortex: effects of neonatal treatment with 6-hydroxydopamine. Eur J Pharmacol 78:15–20
Delini-Stula A, Baumann P, Büch O (1979) Depression of exploratory activity by clonidine in rats as a model for the detection of relative pre- and postsynaptic central noradrenergic receptor selectivity of α-adrenolytic drugs. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 307:115–122
Dooley DJ, Bittiger H, Hauser KL, Bischoff SF, Waldmeier PC (1983a) Alteration of central α2- and β-adrenergic receptors in the rat after DSP-4, a selective noradrenergic neurotoxin. Neuroscience 9:889–898
Dooley DJ, Hauser KL, Bittiger H (1983b) Differential decrease of the central β-adrenergic receptor in the rat after subchronic infusion of desipramine and clenbuterol. Neurochem Int 5:333–338
Drew GM, Gower AJ, Marriott AS (1979) 5-3 mediate clonidine-induced sedation in the rat. Br J Pharmacol 67:133–141
Goldstein A (1964) Biostatistics: An Introductory Text. MacMillan, New York
Jaim-Etcheverry G, Zieher LM (1980) DSP-4: a novel compound with neurotoxic effects on noradrenergic neurons of adult and developing rats. Brain Res 188:513–523
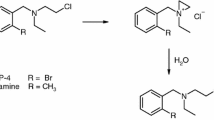
Jonsson G, Hallman H, Ponzio F, Ross S (1981) DSP-4 [N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-ethyl-2-bromobenzylamine] — a useful denervation tool for central and peripheral noradrenaline neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 72:173–188
Leclerc G, Rouot B, Schwartz J, Velly J, Wermuth CG (1980) Studies on some para-substituted clonidine derivatives that exhibit an α-adrenoceptor stimulant activity. Br J Pharmacol 71:5–9
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
McCleary PE, Leander JD (1981) Clonidine analgesia and suppression of operant responding: dissociation of mechanism. Eur J Pharmacol 69:63–69
Mogilnicka E (1982) The effects of acute and repeated treatment with salbutamol, a β-adrenoceptor agonist, on clonidine-induced hypoactivity in rats. J Neural Transm 53:117–126
Mogilnicka E, Dooley DJ, Boissard CG, Delini-Stula A (1983) Altered hindlimb extension in the rat after DSP-4: a useful marker of central noradrenergic depletion. Eur J Pharmacol 87:345–347
Noble W, Delini-Stula A (1976) Effect of oxprenolol on some fear-induced behavioral responses and hyperthermia in rats subjected to inescapable shocks. Psychopharmacology 49:17–22
Olpe H-R, Laszlo J, Dooley DJ, Heid J, Steinmann MW (1983) Decreased activity of locus coeruleus neurons in the rat after DSP-4 treatment. Neurosci Lett, in press
Omura T, Sato R (1964) The carbon monoxide-binding pigment of liver microsomes. J Biol Chem 239:2370–2378
Ortmann R, Waldmeier PC, Radeke E, Felner A, Delini-Stula A (1980) The effects of 5-HT uptake- and MAO-inhibitors on l-5-HTP-induced excitation in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 311:185–192
Ross SB (1976) Long-term effects of N-2-chloroethyl-N-ethyl-2-bromobenzylamine hydrochloride on noradrenergic neurones in the rat brain and heart. Br J Pharmacol 58:521–527
Schmid K, Schweizer W, Staubli W, Waechter F (1980) Studies on the effect of 2-(2′-hydroxy-5′-methylphenyl)benzotriazole on rat liver. Fd Cosmet Toxicol 18:245–252
Waldmeier PC, Baumann P, Maitre L (1979) CGP 6085 A, a new, specific inhibitor of serotonin uptake: neurochemical characterization and comparison with other serotonin uptake blockers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 211:42–49
Zieher LM, Jaim-Etcheverry G (1980) Neurotoxicity of N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-ethyl-2-bromobenzylamine hydrochloride (DSP 4) on noradrenergic neurons is mimicked by its cyclic aziridinium derivative. Eur J Pharmacol 65:249–256
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dooley, D.J., Mogilnicka, E., Delini-Stula, A. et al. Functional supersensitivity to adrenergic agonists in the rat after DSP-4, a selective noradrenergic neurotoxin. Psychopharmacology 81, 1–5 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00439263
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00439263