Abstract
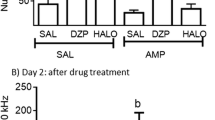
Male albino guinea pigs were treated for 3 weeks with methadone, morphine, haloperidol, or saline. One week and 5 weeks following termination of treatment they were challenged with the directly acting dopaminergic agonist apomorphine. At the week 1 test the haloperidol and saline groups did not differ, but behavioral supersensitivity was apparent in significantly elevated mean stereotypy scores of the methadone and morphine groups relative to the saline group. The source of differences in mean scores was a higher peak score rather than increased duration of action. At the week 5 test the scores of the methadone group were even higher, the morphine group's scores were equivalent to the saline group's, and the haloperidol group's scores were significantly depressed. This study indicates that a 3-week treatment period with methadone or morphine is sufficient to induce dopaminergic supersensitivity and suggests that there may be different time courses for the retention or expression of supersensitivity following these narcotics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahtee, L.: Catalepsy and stereotypies in rats treated with methadone: relation to striatal dopamine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 27, 221–230 (1974)
Andén, N.-E., Rubenson, A., Fuxe, K., Hokfelt, T.: Evidence for dopamine receptor stimulation by apomorphine. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 19, 627–629 (1967)
Carlson, K. R., Almasi, J.: Sensitivity to apomorphine in the guinea pig as a function of age and body weight. Psychopharmacology 57, 279–282 (1978)
Carlson, K. R., Eibergen, R. D.: Susceptibility to amphetamine-elicited dyskinesias following chronic methadone treatment in monkeys. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 281, 336–349 (1976)
Costall, B., Naylor, R. J.: On catalepsy and catatonia and the predictability of the catalepsy test for neuroleptic activity. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 34, 233–241 (1974)
Crane, G. E., Paulson, G.: Involuntary movements in a sample of chronic mental patients and their relation to the treatment with neuroleptics. Int. J. Neuropsychiatry 3, 286–291 (1967)
Creese, I., Burt, D. R., Snyder, S. H.: Dopamine receptor binding predicts clinical and pharmacological potencies of antischizoprenic drugs. Science 192, 481–483 (1976)
Eibergen, R. D., Carlson, K. R.: Behavioral evidence for dopaminergic supersensitivity following chronic treatment with methadone or chlorpromazine in the guinea pig. Psychopharmacology 48, 139–146 (1976a)
Eibergen, R. D., Carlson, K. R.: Dyskinesias in monkeys: interaction of methamphetamine with prior methadone treatment. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 5, 175–187 (1976b)
Eidelberg, E., Erspamer, R.: Dopaminergic mechanisms of opiate actions in brain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 192, 50–57 (1975)
Ernst, A. M.: Mode of action of apomorphine and dexamphetamine on gnawing compulsion in rats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 10, 316–323 (1967)
Fjalland, B., Moller-Nielsen, I.: Enhancement of methylphenidate-induced stereotypies by repeated administration of neuroleptics. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 34, 105–109 (1974)
Gerlach, J., Reisby, N., Randrup, A.: Dopaminergic hypersensitivity and cholinergic hypofunction in the pathophysiology of tardive dyskinesia. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 34, 21–35 (1974)
Gianutsos, G., Hynes, M. D., Puri, S. K., Drawbaugh, R. B., Lal, H.: Effect of apomorphine and nigrostriatal lesions on aggression and striatal dopamine turnover during morphine with-drawal: evidence for dopaminergic supersensitivity in protracted abstinence. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 34, 37–44 (1974)
Klawans, H. L., Jr., Rubovits, R.: An experimental model of tardive dyskinesia. J. Neural Trans. 33, 235–246 (1972)
Kreek, M. J., Gutjahr, C. L., Garfield, J. W., Bowen, D. V., Field, F. H.: Drug interactions with methadone. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 281, 350–371 (1976)
Lal, S., Feldmuller, F.: Effect of amphetamine and apomorphine on brain monoamines and behavior in the immature and young adult rat. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. 218, 239–251 (1975)
Moffett, A. D., Soloway, I. H., Glick, M. X.: Post-treatment behavior following ambulatory detoxification. In: Methadone: experiences and issues, C. D. Chambers and L. Brill, eds., pp. 215–227. New York: Behavioral Publications 1973
Perez-Cruet, J., Di Chiara, G., Gessa, G. L.: Accelerated synthesis of dopamine in the rat brain after methadone. Experientia 28, 926 (1972)
Puri, S. K., Lal, H.: Effect of dopaminergic stimulation or blockade on morphine-withdrawal aggression. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 32, 113–120 (1973)
Puri, S. K., Reddy, C., Lal, H.: Blockade of central dopaminergic receptors by morphine: effect of haloperidol, apomorphine or benztropine. Res. Commun. Chem. Path. Pharmacol. 5, 389–401 (1973)
Sasame, H. A., Perez-Cruet, J., Di Chiara, G., Tagliamonte, A., Tagliamonte, P., Gessa, G. L.: Evidence that methadone blocks dopamine receptors in the brain. J. Neurochem. 19, 1953–1957 (1972)
Sayers, A. C., Burki, H. R., Ruch, W., Asper, H.: Neuroleptic-induced hypersensitivity of striatal dopamine receptors in the rat as a model of tardive dyskinesias. Effects of clozapine, haloperidol, loxapine and chlorpromazine. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 41, 97–104 (1975)
Srimal, R. C., Dhawan, B. N.: An analysis of methylphenidate induced gnawing in guinea pigs. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 18, 99–107 (1970)
Tarsy, D., Baldessarini, R. J.: Behavioral supersensitivity to apomorphine following chronic treatment with drugs which interfere with the synaptic function of catecholamines. Neuropharmacology 13, 927–940 (1974)
Tarsy, D., Baldessarini, R. J.: The tardive dyskinesia syndrome. In: Clinical neuropharmacology, vol. 1, H. L. Klawans Jr., ed., pp. 29–61. New York: Raven Press 1976
Teiger, D. G.: A test for antinociceptive activity of narcotic and narcotic antagonist analgesics in the guinea pig. J. Pharm. Exp. Ther. 197, 311–316 (1976)
Ungerstedt, U., Butcher, L. L., Butcher, S. G., Andén, N.-E., Fuxe, K.: Direct chemical stimulation of dopaminergic mechanisms in the neostriatum of the rat. Brain Res. 14, 461–471 (1969)
Winer, B. J.: Statistical principles in experimental design, 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill 1971
York, D. H.: Dopamine receptor blockade—a central action of chlorpromazine on striatal neurons. Brain Res. 37, 91–99 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carlson, K.R., Almasi, J. Behavioral supersensitivity to apomorphine following chronic narcotic treatment in the guinea pig. Psychopharmacology 57, 273–277 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00426750
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00426750