Abstract
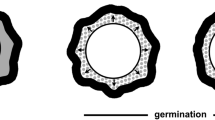
At the end of heat activation the distribution of spore plasma membrane particles between the two fracture faces (PF and EF) is drastically changed. While in dormant spores the particle number ratio of PF/EF was about 1:1, it increased up to 9:1 in heat activated spores, indicating a subtle change in plasma membrane properties. The permeability of spores increased within 30 min following heat activation as determined by efflux measurements of radioactively labelled spores. At the onset of swelling this efflux was accelerated. During germination the osmotically active material within the spores increased, part of which could be recovered from the supernatant. The combined experiments point to the plasma membrane as possible target site of heat activation in this system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Branton, D., Bullivant, N., Gilula, N. B., Karnovsky, M. J., Moor, H., Mühlethaler, K., Northcote, D. H., Packer, L., Satir, B., Satir, P., Staehelin, L. A., Steere, R. L., Weinstein, R. S.: Freeze-etching nomenclature. Science 190, 54–56 (1975)
Cochrane, J. C., Rado, T. A., Cochrane, V. W.: Synthesis of macromolecules and polyribosome formation in early stages of spore germination in Fusarium solani. J. Gen. Microbiol. 65, 45–55 (1971)
Cotter, D. A.: Spore germination in Dictyostelium discoideum. I. Thermodynamics of reversible activation. J. Theoret. Biol. 41, 41–51 (1973)
Cotter, D. A.: Spores of the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. In: Spores, Vol. VI (P. Gerhardt, R. N. Costilow, H. L. Sadoff, eds.), pp. 61–72. Washington: American Soc. Microbiol. 1975
Cotter, D. A., George, R. P.: Germination and mitochondrial damage in spores of Dictyostelium discoideum following supraoptimal heating. Arch. Microbiol. 103, 163–168 (1975)
Cotter, D. A., Miura-Santo, L. Y., Hohl, H. R.: Ultrastructural changes during germination of Dictyostelium discoideum spores. J. Bacteriol. 100, 1020–1026 (1969)
Cotter, D. A., Raper, K. B.: Spore germination in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., U.S.A. 56, 880–887 (1966)
Cotter, D. A., Raper, K. B.: Factors affecting the rate of heatinduced spore germination in Dictyostelium discoideum. J. Bacteriol. 96, 86–92 (1968)
Daly, J. M., Knoche, H. W., Wiese, M. V.: Carbohydrate and lipid metabolism during germination of uredospores of Puccinia graminis tritict. Plant Physiol. 42, 1633–1642 (1967)
Edidin, M.: Rotational and translational diffusion in membranes. Ann. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng 3, 179–201 (1974)
Gould, G. W., Hurst, A.: The bacterial spore. London: Academic Press 1969
Harris, E. J.: Transport and accumulation in biological systems. London: Butterworth 1960
Hemmes, D. E., Kojima-Buddenhagen, E. S., Hohl, H. R.: Structural and enzymatic analysis of the spore wall layers in Dictyostelium discoideum. J. Ultrastructure Res. 41, 406–417 (1972)
Hohl, H. R.: Myxomycetes: Acrasiomycetes. In: The fungal spore: form and function (D. J. Weber, W. M. Hess, eds.), pp. 463–500. New York: Wiley 1976
Hollomon, D. W.: Biochemistry of germination in Peronospora tabacina (Adam) conidia: Evidence for the existence of stable messenger RNA. J. Gen. Microbiol. 55, 267–274 (1969)
Jones, J. P., Snow, J. P.: Amino acids released during germination of 35S-labelled crown rust spores. Phytopathol. 55, 499–500 (1965)
Malhotra, S. K., Tewari, J. P.: Molecular alterations in the plasma membrane of sporangiospores of Phycomyces related to germination. Proc. Roy. Soc. (Lond.) B, 184, 207–216 (1973)
Moor, H.: Freeze-etching. Internat. Rev. Cytol. 25, 391–412 (1969)
O'Day, D. H.: Acid protease activity during germination of microcysts of the cellular slime mold Polysphondylium pallidum. J. Bacteriol. 125, 8–13 (1976)
Reinert, J. C., Steim, J. M.: Calorimetric detection of a membranelipid phase transition in living cells. Science 168, 1580–1582 (1970)
Sussman, A. S.: Activators of fungal spore germination. In: The fungal spore: form and function (D. J. Weber, W. M. Hess, eds.), pp. 101–137, New York: Wiley 1976
Taupin, Ch., Dvolaitzky, M., Sauterey, C.: Osmotic pressure induced pores in phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry 14, 4771–4775 (1975)
Thompson, T. E., Huang, C.: The water permeability of lipid bilayer membranes. Annals N.Y. Acad. Sci. 137, 740–744 (1966)
Verkeleij, A. J., Ververgaert, P. H. J. Th.: The architecture of biological and artificial membranes as visualized by freeze etching. Ann. Rev. Phys. Chem. 26, 101–122 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hohl, H.R., Bühlmann, M. & Wehrli, E. Plasma membrane alterations as a result of heat activation in Dictyostelium spores. Arch. Microbiol. 116, 239–244 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00417846
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00417846