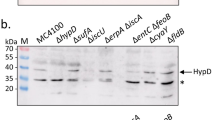
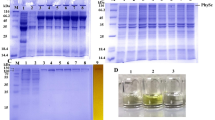
Abstract
Total protein of Alcaligenes eutrophus was analyzed by two-dimensional protein map. Cells grown at 30° C expressed hydrogen-oxidizing (Hox) ability mediated by a soluble (Hos) and a particulate hydrogenase (Hop). Hox ability was not expressed at 37° C (HoxTs). The six subunits of the two hydrogenases were identified. Besides these six subunits eight peptides were not or hardly detected at 37° C. The mutant HF117 which expressed Hox ability at 37° C (HoxTr), formed the hydrogenase peptides and five of the eight peptides. These peptides designated B, C, E, F, and H were characterized by their isoelectric point and molecular mass (M r); their M r were 18 800, 45 400, 41 900, 39 400, and 40 600, respectively. The five peptides were not formed in regulatory Hox− mutants, and not formed in mutants cured of plasmid pHG1, carrying the genetic information for hydrogenase formation. Strain HF160, carrying a Tn5 insertion in a gene essential for Hos expression specifically did not form the B-peptide. All peptides were found in the soluble fraction of cell extracts, the F-peptide was also detected in the particulate fraction. The function of the new Hox-peptides is presently unknown.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PAGE:
-
polyacrylamide gelelectrophoresis
- SDS:
-
sodium dodecylsulfate
- Hox:
-
hydrogen oxidizing ability
References
Aggag M, Schlegel HG (1973) Studies on a Gram-positive hydrogen bacterium Nocardia opaca 1b. I. Description and physiological characterization. Arch Microbiol 88:299–318
Dixon RA (1984) The genetic complexity of nitrogen fixation J Gen Microbiol 130:2745–2755
Friedrich CG (1982) Derepression of hydrogenase during limitation of electron donors and derepression of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase during carbon-limitation of Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol 149:203–210
Friedrich CG, Friedrich, B (1982) Regulation of hydrogenase formation is temperature sensitive and plasmid coded in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol 153:176–181
Friedrich B, Hogrefe C (1984) Genetics of lithoautotrophic metabolism in Alcaligenes eutrophus. In: Crawford RL, Hanson RS (eds) Microbial growth on C1 compounds, Proc 4th Intern Symp. Am Soc Microbiol, Washington D. C., pp 244–247
Friedrich CG, Bowien B, Friedrich B (1979) Formate and oxalate metabolism in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Gen Microbiol 115:185–192
Friedrich B, Heine E, Finck A, Friedrich CG (1981a) Nickel requirement for active hydrogenase formation in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol 145:1144–1149
Friedrich B, Hogrefe C, Schlegel HG (1981b) Naturally occurring genetic transfer of hydrogen-oxidizing ability between strains of Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol 147:198–205
Friedrich CG, Schneider K, Friedrich B (1982) Nickel in the catalytically active hydrogenase of Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol 152:42–48
Friedrich CG, Suetin S, Lohmeyer M (1984) Nickel and iron incorporation into soluble hydrogenase of Alcaligenes eutrophus. Arch Microbiol 140:206–211
Harker AR, Xu L-S, Hanus, FJ, Evans HJ (1984) Some properties of the nickel containing hydrogenase of chemolithotrophically grown Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol 159:850–856
Haugland RA, Cantrell MA, Beaty JS, Hanus FJ, Russel SA, Evans HJ (1984) Characterization of Rhizobium japonicum hydrogen uptake genes. J Bacteriol 159:1006–1012
Hogrefe C, Römermann D, Friedrich B (1984) Alcaligenes eutrophus hydrogenase genes (Hox). J Bacteriol 158:43–48
Im DS, Friedrich CG (1983) Fluoride, hydrogen, and formate activate ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase formation in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol 154:803–808
Lambert GR, Cantrell MA, Hanus FJ, Russel SA, Haddad KR, Evans HJ (1985) Intra- and interspecies transfer and expression of Rhizobium japonicum hydrogen uptake genes and autotrophic growth capability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:3232–3236
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Merberg D, O'Hara EB, Maier RJ (1983) Regulation of hydrogenase in Rhizobium japonicum: Analysis of mutants altered in regulation by carbon substrates and oxygen. J Bacteriol 156:1236–1242
Neidhardt FC, VanBogelen RA (1981) Positive regulatory gene for temperature-controlled proteins in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 100:894–900
Neidhardt FC, Vaughn V, Phillips TA, Bloch PL (1983) Geneprotein index of Escherichia coli K-12. Microbiol Rev 47:231–284
O'Farrell PH (1975) High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem 250:4007–4021
Pfitzner J (1974) Ein Beitrag zum H2−O2-Oxidoreductasesystem von Hydrogenomonas eutropha Stamm H16: Hydrogenasedefekte Mutanten. Zentralbl Bakteriol Parasitenkd Infektionskr Hyg Abt 1 Orig Reihe A 228:121–127
Sammons DW, Adams LD, Nishizawa EE (1981) Ultrasensitive silver-based color staining of polypeptides in polyacrylamide gels. Electrophoresis 2:135–141
Schink B, Schlegel HG (1978) Mutants of Alcaligenes eutrophus defective in autotrophic metabolism. Arch Microbiol 117:123–129
Schink B, Schlegel HG (1979) The membrane-bound hydrogenase of Alcaligenes eutrophus. I. Solubilisation, purification, and biochemical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta 567:315–324
Schlegel HG, Kaltwasser H, Gottschalk G (1961) Ein Submersverfahren zur Kultur wasserstoffoxidierender Bakterien: Wachstumsphysiologische Untersuchungen. Arch Mikrobiol 38:209–222
Schlesier M, Friedrich B (1982) Effect of molecular hydrogen on histidine utilization by Alcaligenes eutrophus. Arch Microbiol 132:260–265
Schneider K, Piechulla B (1986) Isolation and immunological characterization of the four non-identical subunits of the soluble, NAD-linked hydrogenase from Alcaligenes eutrophus H16. Biochimie 68:5–13
Schneider K, Schlegel HG (1976) Purification and properties of soluble hydrogenase from Alcaligenes eutrophus H16. Biochim Biophys Acta 452:66–80
Srivastava S, Urban M, Friedrich B (1982) Mutagenesis of Alcaligenes eutrophus by insertion of the drug resistance transposon Tn5. Arch Microbiol 131:203–207
Trah TJ, Schleyer M (1982) Formaldehyde fixation of proteins and small polypeptides after isoelectric focusing in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 127:326–329
Yates MG, Robson RL (1985) Mutants of Azotobacter chroococcum defective in hydrogenase activity. J Gen Microbiol 131:1459–1466
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kärst, U., Friedrich, C.G. Identification of new peptides synthesized under the hydrogenase control system of Alcaligenes eutrophus . Arch. Microbiol. 147, 346–353 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00406131
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00406131