Abstract
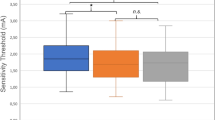
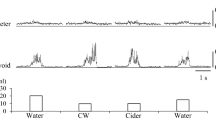
Cold stimulation of the oropharyngeal mucosa, including the faucial pillar region, is used as a specific technique for the treatment of swallowing disorders. The physiological mechanisms underpinning this clinical technique are unclear. Thermal (cold), chemical (saline, glucose and water), mechanical (light touch) and feigned stimulation of the faucial pillar were assessed for their effects on the latency to swallow and the repetitive frequency of swallowing. There was no significant difference between these variables following light stimulation of the faucial pillar with a metal probe warmed to body temperature compared with feigned stimulation. However, cold touch stimulation evoked a significant increase in swallowing latency and repetitive frequency compared to feigned stimulation. The results suggest the existence of thermo-sensitive receptors in the faucial pillars that evoke swallowing when stimulated by cold touch. The clinical and physiological importance of these findings are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Logemann J: Evaluation and Treatment of Swallowing Disorders. San Diego: College Hill Press, 1983
Lazzara G, Lazarus C, Logemann JA: Impact of thermal stimulation on the triggering of the swallowing reflex. Dysphagia 1:73–77, 1986
Rosenbek JC, Robbins J, Fishback B, Levine RL: Effects of thermal application on dysphagia after stroke. J Speech Hear Res 34:1257–1268, 1991
Selinger M, Prescott TE, Hoffman I: Temperature acceleration in cold oral stimulation. Dysphagia 9:83–87, 1994
Chi-Fishman G, Capra NF, McCall GN: Thermomechanical facilitation of swallowing evoked by electrical nerve stimulation in cats. Dysphagia 9:149–155, 1994
Wassilieff N: Wo wird der Schluckreflex ausgelöst? Zeitschrift für Biologie 24:24–46, 1888
Miller FR, Sherrington CS: Some observations on the buccopharyngeal stage of reflex deglution in the cat. Q J of Exp Physiol 9:147–186, 1916
Pommerenke WT: A study on the sensory areas of eliciting the swallowing reflex. Am J Physiol 84:36–41, 1928
Doty RW: Influence of stimulus pattern on reflex deglutition. Am J Physiol 166:142–158, 1951
Lalonde E, Eglitis J: Number and distribution of taste buds on the epiglottis, pharynx, larynx, soft palate and uvula in a human newborn. Anat Rec 140:91–95, 1961
Perlman AL, Liang H: Frequency response of the Fourcin electroglottograph and measurement of temporal aspects of laryngeal movement during swallowing. J Speech Hear Res 34:791–795, 1991
Perlman AL, Grayhack JP: Use of the electroglottograph for measurement of temporal aspects of the swallow: preliminary observations. Dysphagia 6:88–93, 1991
Kahrilas PJ, Dent J, Dodds WJ, Hogan WT, Arndorfer RC: A method for continuous monitoring of upper esophageal sphincter pressure. Dig Dis Sci 32(2):121, 1987
Grossman RC: The implications of the distribution of sensory nerve endings in the oral mucous membrane. In: Bosma J (ed.): Symposium on Oral Sensation and Perception. CC Thomas: Springfield, IL, 1967, pp 5–62
Larsson H, Carlsson-Nordlander B, Lindbland LE, Norbeck O, Svanborg E: Temperature thresholds in the oropharynx of patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis 146:1246–1249, 1992
Jebeles JA, Reilly JS, Gutierrez JF, Bradley EL, Kissen I: The effect of preincisional infiltration of tonsils with bupivacaine on the pain following tonsillectomy under general anesthesia. Pain 47:305–308, 1991
Hamilton I: Die Nervenausbreitungen in der Uvula. Acta Anat (Basel) 31:66–75, 1957
Zotterman Y: Touch, pain and tickling: an electrophysiological investigation on cutaneous sensory nerves. J Physiol (Lond) 95:1–28, 1939
Sant' Ambrogio G, Mathew OP, Sant' Ambrogio FB, Fisher JT: Laryngeal cold receptors. Respir Physiol 59:35–44, 1985
Basner RC, Ringler J, Berkowitz S, Schwartzstein RM, Weinberger SE, Sparrow D, Weiss JW: Effect of inspired air temperature on genioglossus activity during nose breathing in awake humans. J App Physiol 69(3):1098–1103, 1990
Salata A, Verbalis JG, Robinson AG: Cold water stimulation of oropharyngeal receptors in man inhibits release of vasopressin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 65(3):561–567, 1987
Thomas WC: Diabetes insipidus. J Endocrinol Metab 17:565–582, 1957
Kapotos G, Gold RW: Tongue cooling during drinking: a regulator of water intake in rats. Science 176:685–686, 1972
Sant' Ambrogio G, Brambilla-Sant' Ambrogio F, Mathew OP: Effect of cold air on laryngeal mechanoreceptors in the dog. Respir Physiol 64:45–56, 1986
Davis PJ, Nail BS: The sensitivity of laryngeal epithelial receptors to static and dynamic forms of mechanical stimulation. In: Fujimura O (ed.): Vocal Fold Physiology: Voice Production, Mechanism and Functions. New York:Raven Press, 1988, pp 1–18
Shingai T, Miyaaoka Y, Ikarashi R, Shimada K: Swallowing reflex elicited by water and taste solutions in humans. Am J Physiol 256:R822–826, 1989
Yamamoto T, Matsuo R, Kiyomitsu Y, Kitamura R: Sensory inputs from the oral region to the cerebral cortex in behaving rats: an analysis of unit responses in cortical somatosensory and taste areas during ingestive behaviour. J Neurophysiol 60(4): 1303–1321, 1988
Nail BS, Sterling GM, Widdicombe JG: Epipharyngeal receptors responding to mechanical stimulation. J Physiol (Lond) 204:91–98, 1969
Hensel H, Zotterman Y: The response of mechanoreceptors to thermal stimulation. J Physiol115:16–24, 1951
Fujiu M, Toleikis R, Logemann JA, Larson CR: Glossopharyngeal evoked potential in normal subjects following mechanical stimulation of the anterior faucial pillar. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 92:183–195, 1994
Sinclair WJ: Initiation of reflex swallowing forms the naso-and oropharynx. Am J Physiol 218(4):956–959, 1970
Logemann JA, Lazarus C: Letters to the editor. Dysphagia 2:56–57, 1987
Storey AT: Laryngeal initiation of swallowing. Exp Neurol 20: 359–365, 1968
Shingai T, Shimada K: Reflex swallowing elicited by water and chemical substances applied in the oral cavity, pharynx and larynx of the rabbit. Jpn J Physiol 26:455–469, 1976
Shingai T: Ionic mechanism of water receptors in the laryngeal mucosa of the rabbit. Jpn J Physiol 27:27–42, 1977
Henkin RI, Christiansen RL: Taste localization on the tongue, palate, and pharynx of normal man. J Appl Physiol 22(2):316–320, 1967
Collings VB: Human taste as a function of the locus of stimulation on the tongue and soft palate. Percept Psychophys 16(1):169–174, 1974
Pangborn RM, Chrisp RB, Bertolero LL: Gustatory, salivary, and oral thermal responses to solutions of sodium chloride at four temperatures. Percept Psychophy 8(2):69–75, 1970
McBurney DH, Collings VB, Glanz LM: Temperature dependence of human taste responses. Physiol Behav 11: 89–94, 1973
Larsen G: Rehabilitation for dysphagia paralytica. J Speech Hear Dis 37:187–193, 1972
Hargrove R: Feeding the severely dysphagic patient. J Neurosurg Nurs 12(2):102–107 1980
West CJ, Crowley MF: Nutrition Principles and Application in Health Promotion. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott Co, 1984
Winstein C: Neurogenic dysphagia. Phys Ther 63:1992–1997, 1983
Selley WG: Swallowing difficulties in stroke patients: a new treatment. Age Ageing 14:361–365, 1985
Martin AW: Dietary management of swallowing disorders. Dysphagia 6:129–134, 1991
Miglietta OE: Evaluation of cold in spasticity. Am J Phys Med 41:148–151, 1962
Goff B: Excitatory cold. Physiotherapy 11:467–468, 1969a
Goff B: Appropriate afferent stimulation. Physiotherapy 1:9–17, 1969b
Chambers R: Clinical uses of cryotherapy. Phys Ther 49(3):245–249, 1969
Carr J, Shepherd R: Physiotherapy and Disorders of the Brain. London: Heineman, 1980
Kabat H, Knot M: Proprioceptive facilitation techniques for treatment of paralysis. Phys Ther Rev 33:53–64, 1953
Kuehn DP, Templeton PJ, Maynard JA: Muscle spindles in the velopharyngeal musculature of humans. J Speech Hear Res 33: 488–493, 1990
Ludlow CL, Connor NP: Dynamic aspects of phonatory control in spasmodic dysphonia. J Speech Hear Res 30:197–206, 1987
Sorin R, McClean MD, Ezerzer F, Meissner-Fishbein B: Electroglottographic evaluation of the swallow. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 68:232–235, 1987
Martin BJM: Treatment of dysphagia in adults. In: Cherney L (ed.): Clinical Management of Dysphagia in Adults and Children. Gaithersburg, MD: Aspen Publishers Inc
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaatzke-McDonald, M.N., Post, E. & Davis, P.J. The effects of cold, touch, and chemical stimulation of the anterior faucial pillar on human swallowing. Dysphagia 11, 198–206 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00366386
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00366386