Abstract
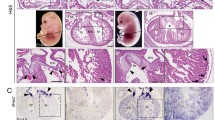
XCsx2, a homeobox-containing gene, is expressed in cardiac muscle during Xenopus development, while the XMEF2A gene is expressed in both cardiac and skeletal muscle. Microinjection of either XCsx2 or XMEF2A mRNA into single blastomeres of two-cell stage Xenopus embryos induced precocious expression of the myosin heavy-chain alpha (XMHCα) gene at the neural plate stage (stage 14). Co-injection of both XCsx2 and XMEF2A mRNAs induced still earlier expression at the late gastrula stage (stage 12). These changes were evident in whole embryos but not in animal pole explants from injected embryos. Overexpression of XCsx2 or XMEF2A also caused an enlarged heart and abnormalities of notochord and tail in Xenopus embryos. These findings suggest that both XCsx2 and XMEF2A transcription factors have an important role in regulating the expression of the XMHCα gene and the morphogenesis of heart tissue in Xenopus development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azpiazu N, Frasch M (1993) Tinman and bagpipe: two homeobox genes that determine cell fates in the dorsal mesoderm of Drosophila. Genes Dev 7:1325–1340
Bodmer R (1993) The gene tinman is required for the specification of the heart and visceral muscles in Drosophila. Development 118:719–729
Bodmer R (1995) Heart development in Drosophila and its relationship to vertebrates. Trends Cardiovasc Med 5:21–28
Breitbart R, Liang C, Smoot L, Laheru D, Mahdavi V Nadal-Ginard B (1993) A fourth human MEF-2 transcription factor, hMEF2D, is an early marker of the myogenic lineage. Development 118:1095–1106
Chambers AE, Kotecha S, Towers N, Mohun TJ (1992) Musclespecific expression of SRF-related genes in the early embryo of Xenopus laevis. EMBO J 11:4981–4991
Chambers AE, Logan M, Kotecha S, Towers N, Sparrow D, Mohun TJ (1994) The RSRF/MEF2 protein SL1 regulates cardiac muscle-specific transcription of a myosin light-chain gene in Xenopus embryos. Genes Dev 8:1324–1334
Drysdale TA, Tonissen KF, Patterson KD, Crawford MJ, Krieg PA (1994) Cardiac troponin I is a heart-specific marker in the Xenopus embryo: expression during abnormal heart morphogenesis. Dev Biol 165:432–441
Edmondson DG, Lyons GE, Martin JF, Olson EN (1994) Mef2 gene expression marks the cardiac and skeletal muscle lineages during mouse embryogenesis. Development 120:1251–1263
Fu Y, Hosokawa K, Shiokawa K (1989) Expression of circular and linearized bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase genes with or without viral promoters after injection into fertilized eggs, unfertilized eggs and oocytes of Xenopus laevis. Rouxs Arch Dev Biol 198:148–156
Harland RM (1991) In situ hybridization: an improved whole mount method for Xenopus embryos. In: Kay BK, Peng HB (eds) Xenopus laevis: practical uses in cell and molecular biology. Academic Press, London, pp 685–695
Kelly GM, Eib DW, Moon RT (1991) Histological preparation of Xenopus laevis oocytes and embryos. In: Kay BK, Peng HB (eds) Xenopus laevis: practical uses in cell and molecular biology. Academic Press, London, pp 389–417
Komuro I, Izumo S (1993) Csx: a murine homeobox-containing gene specifically expressed in the developing heart. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:8145–8149
Krieg PA, Melton DA (1984) Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 12:7057–7070
Leifer D, Krainc D, Yu Y-T, McDermott J, Breitbart RE, Heng J, Neve RL, Kosofsky B, Nadal-Ginard B, Lipton SA (1993) MEF2C, a MADS/MEF2-family transcription factor expressed in a laminar distribution in cerebral cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:1546–1550
Lints TJ, Parsons LM, Hartley L, Lyons I, Harvey RP (1993) Nkx-2.5.: a novel murine homeobox gene expressed in early heart progenitor cells and their myogenic descendants. Development 119:419–431
Logan M, Mohun TJ (1993) Induction of cardiac muscle differentiation in isolated animal pole explants of Xenopus laevis embryos. Development 118:865–875
Ludolph DC, Neff AW, Mescher AL, Malacinski GM, Parker MA, Smith RC (1994) Overexpression of XMyoD or Xmyf5 in Xenopus embryos induces the formation of enlarged myotomes through recruitment of cells of nonsomitic lineage. Dev Biol 166:18–33
Martin JF, Schwarz JJ, Olson EN (1993) Myocyte enhancer factor (MEF) 2C: a tissue-restricted member of the MEF-2 family of transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 5282–5286
Martin JF, Miano JM, Hustad CM, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Olson EN (1994) A Mef2 gene that generates a muscle-specific isoform via alternative RNA splicing. Mol Cell Biol 14:1647–1656
McDermott J, Cardoso M, Yu Y-T, Andres V, Leifer D, Krainc D, Lipton SA, Nadal-Ginard B (1993) hMEF2C gene encodes skeletal muscle- and brain-specific transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol 13:2564–2577
McGinnis M, Garber RL, Wirz J, Kuroiwa A, Gegring W (1984) A homologous protein-coding sequence in Drosophila homeotic genes and its conservation in other metazoans. Cell 37:403–408
Nieuwkoop P, Faber J (1956) Normal table of Xenopus laevis (Daudin). North-Holland, Amesterdam
Peng HB (1991) Solutions and protocols. In: Kay BK, Peng HB (eds) Xenopus laevis: practical uses in cell and molecular biology. Academic Press, London, pp 657–662
Pollock R, Treisman R (1991) Human SRF-related proteins: DNA-binding properties and potential regulatory targets. Genes Dev 5:2327–2341
Scott MP (1994) Intimations of a creature. Cell 79:1121–1124
Scott MP, Weiner AJ (1984) Structural relationships among genes that control development: sequence homology between the Antennapedia, Ultrabithorax and fushi tarazu loci of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:4115–4119
Tonissen KF, Drysdale TF, Lints TJ, Harvey RP, Krieg PA (1994) XNkx-2.5, a Xenopus gene related to Nkx-2.5 and tinman: evidence for a conserved role in cardiac development. Dev Biol 162:325–328
Yu Y, Breitbart R, Smoot L, Lee Y, Mahdavi V, Nadal-Ginard B (1992) Human myocyte specific enhancer factor 2 (MEF2) comprises a group of tissue restricted MADS box transcription factors. Genes Dev 6:1783–1798
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, Y., Izumo, S. Cardiac myogenesis: overexpression of XCsx2 or XMEF2A in whole Xenopus embryos induces the precocious expression of XMHCα gene. Roux's Arch Dev Biol 205, 198–202 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00357766
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00357766