Abstract
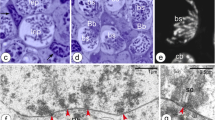
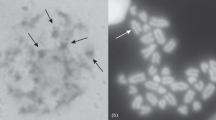
In previtellogenic oocytes of the neuropteran, Hemerobius spp., two distinct, DNA-positive intranuclear structures have been observed. Chromosomes of meiotic prophase assemble in the center of the oocyte nucleus forming a highly polymorphic karyosphere, which persists in this position until the very late stages of vitellogenesis. The extrachromosomal DNA body, containing amplified ribosomal genes, undergoes fragmentation and dispersion in the nucleoplasm. At the onset of previtellogenic growth, transcription of extra rDNA starts, which is accompanied by the appearance of dense, granular material (multiple nucleoli). Arising nucleoli gradually fill the nucleoplasm. At the electron microscopic (EM) level two electron dense structural forms of the granular material have been described. Together with general histological and ultrastructural analysis the amplification of rDNA genes in Hemerobius spp. oocytes has been demonstrated by means of the spreading technique, which has shown that extra rDNA is organized in rings containing various numbers of active ribosomal genes. The transcription activity of amplified genes is manifested in the form of typical “Christmas tree” structures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AndreuccettiP (1992) An ultrastructural study of differentiation of pyriform cells and their contribution to oocyte growth in representative squamata. J Morphol 212:1–11
BüningJ, SohstS (1989) The ovary of Hystrichopsylla: Structure and previtellogenic growth. In: TonnerM, SoldanT, BennettovaB (eds) Regulation of insect reproduction IV. Proceedings of a Symposium, Zinkovy, September 1987, Publishing House, Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences, Praha, pp 113–124
CaveMD (1982) Morphological manifestations of ribosomal DNA amplification during insect oogenesis. In: KingRC, AkaiH (eds) Insect ultrastructure. Foliogen Plenum, New York, pp 86–117
CoimbraA, AzevedoC (1984) Structure and evolution of the nucleolus during oogenesis. In: VanBlerkomJ, MottaPH (eds) Ultrastructure of reproduction. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, Boston The Hague Dordrecht Lancaster, pp 127–139
DavidsonEH (1986) Gene activity in early development, 3rd ed. Academic Press, New York
DeLoofA, GeysenJ, CardoenJ, VerachtertB (1990) Comparative developmental physiology and molecular cytology of the polytrophic ovarian follicles of the blowfly Sareophaga bullata and the fruitfly Drosophila melanogaster. Comp Biochem Physiol [A] 96:309–321
delPinoEM, SteibeisserH, HofmanA, DreyerC, CamposM, TrendelenburgMF (1986) Oogenesis in the egg-brooding frog Gastrotheca riobambae produces large oocytes with fewer nucleoli and low RNA content in comparison to Xenopus laevis. Differentiation 32:24–33
DittmannF, HornerR, EngelsW (1984) Endopolyploidization of tropharium nuclei during larval development and the first gonocycle in Dysdercus intermedius (Heteroptera). Int J Inv Reprod Dev 7:279–290
FrankeW, ScheerU, TrendelenburgMF, ZentgrafH, SpringH (1978) Morphology of transcriptionally active chromatin. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 42:755–772
GruzovaMN, ZaichikovaZP, SokolovIZ (1972) Functional organization of the nucleus in the oogenesis of Chrysopa perla L. (Insecta, Neuroptera). Chromosoma 37:353–386
KingRC, BüningJ (1984) The origin and functioning of insect oocytes and nurse cells. In: KerkutGS, GilbertLJ (eds) Comprehensive insect physiology, biochemistry and pharmacology, vol 1. Embryogenesis and reproduction. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 37–83
KlocM (1980) Extrachromosomal DNA and its activity in RNA synthesis in oogonia and oocytes in the pupal ovary of Creophilus maxillosus (Staphylinidae, Coleoptera-Polyphaga). Eur J Cell Biol 21:328–334
MacgregorHC (1982) Ways of amplifying ribosomal genes. In: JordanEG, KullisGA (eds) The nucleolus. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 129–151
MacgregorHC, delPinoEM (1982) Ribosomal gene amplification in multinucleolate oocytes of the egg-brooding hylid frog Flectonotus pymaeus. Chromosoma 85:475–488
MatuszewskiB, HoserP (1975) Gene amplification and its effect on the structure and function of the oocyte nucleus in the whirligig beetle Gyrinus natator (Gyrinidae, Coleoptera-Adephaga). Experientia 31:431–432
MatuszewskiB, KlocM (1976) Gene amplification in oocytes of the rove beetle Creophilus maxillosus (Staphylinidae, Coleoptera-Polyphaga). Experientia 32:34–36
MillerOL, BeattyBR (1969) Visualization of nucleolar genes. Science 164:955–957
MottaCM, AndreuccettiP, FilosaS (1991) Ribosomal gene amplification in oocytes of the lizard Podarcis sicula. Mol Reprod Dev 29:95–102
SchäferM, KunzW (1987) Ribosomal gene amplification does not occur in the oocytes of Locusta migratoria. Dev Biol 120:418–424
ScheerU (1987) Contributions of electron microscopy spreading preparations (“Miller spreads”) to the analysis of chromosome structure. In: HenningW (ed) Results and problems in cell differentiation, vol 14. Structure and function of eukaryotic chromosomes. Springer Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 147–171
ScheerU, ZentgrafH (1978) Nucleosomal and supranucleosomal organization of transcriptionally inactive rDNA circles in Dystiscus oocytes. Chromosoma 69:243–254
TelferW (1975) Development and physiology of the oocyte-nurse cell-syncytium. Adv Insect Physiol 11:223–319
TrendelenburgMF (1974) Morphology of ribosomal RNA cistrons in oocytes of the water beetle, Dytiscus marginalis L. Chromosoma 48:119–135
TrendelenburgMF, McKinnellRC (1979) Transcriptionally active and inactive regions of nucleolar chromatin in amplified nucleoli of fully grown oocytes of hibernating frogs, Rana pipiens (Amphibia, Anura). Differentiation 15:73–95
TrendelenburgMF, Puvion-DutilleulF (1987) Visualizing active genes. In: SommervilleJ, ScheerU (eds) Electron microscopy in molecular biology. IRL Press, Oxford, UK, pp 101–146
TrendelenburgMF, ScheerU, FrankeWW (1973) Structural organization of ribosomal DNA in oocytes of the house cricket. Nature New Biol 245:167–170
TrendelenburgMF, ScheerU, ZentgrafH, FrankeWW (1976) Heterogeneity of spacer lengths in circles of amplified ribosomal DNA of two insect species, Dytiscus marginalis and Acheta domesticus. J Mol Biol 108:453–470
TrendelenburgMF, FrankeWW, ScheerU (1977) Frequencies of circular units of nucleolar DNA in oocytes of two insects, Acheta domesticus and Dytiscus marginalis, and changes of nucleolar morphology during oogenesis. Differentiation 7:133–158
UrbaniE (1969) Cytochemical and ultrastructural studies of oogenesis in the Dytiscidae. Monitore Zool Ital 3:55–87
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kubrakiewicz, J., Biliński, S.M. Extrachromosomal amplification of rDNA in oocytes of Hemerobius spp. (Insecta, Neuroptera). Chromosoma 103, 606–612 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00357687
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00357687