Summary
1. Resting potentials have been recorded in glial cells of the central nervous system of the leech in a wide range of potassium concentrations.
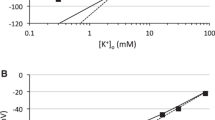
2. Increasing external K reduces the membrane potential which is determined by the relative concentrations of K on the two sides of the glial membrane. At relatively high K concentrations the glial membrane potential behaves like a potassium electrode, in accordance with the relationship predicted by the Nernst equation. In contrast, changes in Na and Cl have little effect on the resting potential.
3. It is concluded that K is the principal intracellular cation in glial cells, having a concentration of about 110 mequiv/l.
4. The relationship of neuroglia and extracellular space in the nervous system is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian, R. H.: The effect of internal and external potassium concentration on the membrane potential of frog muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 133, 631–658 (1956).
Coggeshall, R. E., and D. W. Fawcett: The fine structure of the central nervous system of the leech, Hirudo medicinalis. J. Neurophysiol. (in press).
Gray, E. G., and R. Guillery: An electronmicroscopical study of the ventral nerve cord of the leech. Z. Zellforsch. 60, 826–849 (1963).
Hild, W., J. J. Chang, and I. J. Tasaki: Electrical responses of astrocytic glia from the mammalian nervous system cultivated in vitro. Experientia (Basel) 14, 220–221 (1958).
Hodgkin, A. L., and B. Katz: The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of the giant axon of the squid. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 109, 37–77 (1949).
Katzman, R.: Electrolyte distribution in mammalian central nervous system. Are glia high sodium cells? Neurology (Minneap.) 11, 27–36 (1961).
Koch, A., B. Ranck Jr., and B. L. Newman: Ionic content of the neuroglia. Exp. Neurol. 6, 186–200 (1962).
Kuffler, S. W., and D. D. Potter: Glia in the leech central nervous system. Physiological properties and neuron-glia relationship. J. Neurophysiol. 27, 290–320 (1964).
Nicholls, J. G., and S. W. Kuffler: Extracellular space as a pathway for exchange between blood and neurons in the central nervous system of the leech. The ionic composition of glial cells and neurons. J. Neurophysiol. (in press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 1 Figure in the Text
The occasion of Otto Krayer's 65th birthday gives us an opportunity to express a long felt sense of gratitude. Not only was he the moving spirit in establishing the Neurophysiology Laboratory at Harvard Medical School, but from the beginning he has helped and encouraged our effort and, above all, has extended his unwavering personal friendship to each member of our group.
Supported by a grant from the National Institute of Neurological Diseases and Blindness (NB 02253-04), National Institutes of Health, United States Public Health Service.
Fellow of the National Multiple Sclerosis Society.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuffler, S.W., Nicholls, J.G. Glial cells in the central nervous system of the leech; their membrane potential and potassium content. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. u. Pharmak. 248, 216–222 (1964). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00348592
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00348592