Abstract
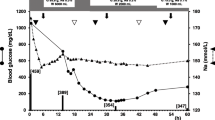
This study presents the electron microscopic evolution of lesions in electrolyte-induced demyelination (EID) in rats, a lesion which bears striking histological and clinical similarity to central pontine myelinolysis. The earliest change was observed during the hyponatremic phase and consisted of minimal intracellular edema present throughout the brain. Following the injection of hypertonic saline, additional changes were observed which were restricted to sites previously reported to be frequently involved in EID. Early dilatation of the inner tongue of oligodendrocyte cytoplasm in myelinated nerve fibers was observed at 3h post hypertonic saline injection (PHS). This was followed, at 48h PHS, by the appearance of degenerative changes consistent with dying oligodendrocytes. Well-delineated, vacuolar and spongy lesions, seen by light microscopy, were present by 48h PHS at the same sites as above. Electron microscopically, this appearance was found to be due to striking intramyelinic edema. By 96h PHS, macrophages containing myelin and other cellular debris were frequently present at these sites. Concomitantly, myelin sheaths underwent vesicular disruption and disintegration. This sequence of events suggest a lesion of the oligodendrocyte-myelin complex, secondary to initial blood-brain barrier damage and edema.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JH (1961) Central pontine myelinolysis. In: Jacob H (ed) Proceedings of the Fourth International Congress of Neuropathology, Munich, W. Germany, vol 3. Thieme, Stuttgart, pp 303–308
Adams RD, Victor M, Mancall EL (1959) Central pontine myelinolysis: a hitherto unpublished disease occurring in alcoholic and malnourished patients. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 81: 154–172
Balentine JD (1988) Presidential address. Spinal cord trauma: in search of the meaning of granular axoplasm and vesicular myelin. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 47: 77–92
Banik N (1979) The degradation of myelin basic protein by serum proteinase in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis and control rats. Neurosci Lett 11: 307–312
Blakemore WF (1972) Observations on oligodendrocyte degeneration, the resolution of status spongiosis and remyelination in Cuprizone intoxication in mice. J Neurocytol 1: 413–426
Blakemore WF (1973) Remyelination of the superior cerebellar peduncle in the mouse following demyelination induced by feeding Cuprizone. J Neurol Sci 20: 73–83
Berry K, Olszewski J (1963) Central pontine myelinolysis. Neurology 13: 531–537
Burcar PJ, Norenberg MD, Yarnell PR (1977) Hyponatremia and central pontine myelinolysis. Neurology 27: 223–226
Cammer W, Bloom BR, Norton WT, Gordon S (1978) Degradation of basic protein in myelin by neutral proteases secreted by stimulated macrophages: a possible mechanism of inflammatory demyelination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75: 1554–1558
Conger JF, McIntyre JA, Jacoby WJ (1969) Central pontine myelinolysis associated with inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion. Am J Med 74: 813–817
Finlayson MH, Snider S, Oliva LA, Gault MH (1973) Cerebral and pontime myelinolysis: two cases with fluid and electrolyte imbalance and hypotension. J Neurol Sci 18: 399–409
Hirsch HE (1981) Proteinases and demyelination. J Histochem Cytochem 29: 425–430
Illowsky BP, Laureno R (1987) Encephalopathy and myelinolysis after rapid correction of experimental hyponatremia. Brain 110: 855–867
Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Norenberg MD (1981) Rapid correction of hyponatremia causes demyelination: relation to central pontine myelinolysis. Science 211: 1068–1080
Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Norenberg MD (1982) Neuropathologic observations in electrolyte-induced myelinolysis in the rat. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 41: 67–80
Laureno R (1980) Experimental pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis (abstract). Ann Nerol 8: 117
Laureno R (1983) Central pontine myelinolysis following rapid correction of hyponatremia. Ann Neurol 13: 232–242
Ludwin SK (1978) Central nervous system demyelination and remyelination in the mouse. An ultrastructural study of Cuprizone toxicity. Lab Invest 39: 597–612
Ludwin SK, Johnson ES (1981) Evidence for a dying-back gliopathy in demyelinating disease. Ann Neurol 9: 301–305
Norenberg MD, Papendick RE (1984) Pathogenetic factors in electrolyte-induced myelinolysis (abstract). Ann Neurol 16: 1
Norenberg MD, Leslie KO, Robertson AS (1982) Association between rise in serum sodium and central pontine myelinolysis Ann Neurol 11: 128–138
Powers JM, McKeever PE (1976) Central pontine myelinolysis: an ultrastructural and elemental study. J Neurol Sci 29: 65–81
Prineas JW (1981) Pathology of the Guillain-Barre syndrome. Ann Neurol 9 [Suppl]: 6–19
Rojiani AM, Prineas JW, Cho E-S (1987) Protective effect of steroids in electrolyte induced demyelination. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 46: 495–505
Rojiani AM, Prineas W, Cho E-S (1994) Electrolyte-induced demyelination in rats. 1. Role of blood-brain barrier and edema. Acta Neuropathol 88: 287–292
Schlaepfer WW (1977) Vesicular disruption of myelin simulated by exposure of nerve to calcium ionophore. Nature 265: 734–736
Smith ME (1977) The role of proteolytic enzymes in demyelination in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Neurochem Res 2: 233–246
Tomlinson BE, Pierides AM, Bradley WG (1976) Central pontine myelinolysis: two cases with associated electrolyte disturbance. Q J Med 45: 373–386
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by the V.A. Medical Reserach Service and the National Multiple Sclerosis Society
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rojiani, A.M., Cho, ES., Sharer, L. et al. Electrolyte-induced demyelination in rats. Acta Neuropathol 88, 293–299 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00310372
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00310372