Summary
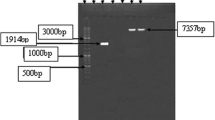
A hybrid plasmid (pAP1) containing the α-amylase gene from Bacillus subtilis was constructed, using the pMFY40 plasmid as a cloning vector. The pAP1 plasmid was introduced into Xanthomonas campestris cells either by conjugation or transformation. The pAP1 plasmid proved to be stable under an antibiotic selection medium. The relative orientation of transcription of the α-amy gene in plasmid pMFY40 was deduced from single and double digestion with restriction enzymes. The expression of the amy gene was detected in non-amylolytic strains of X. campestris and Escherichia coli using an iodine staining assay in solid medium and measuring starch degradation and production of reducing sugars in liquid medium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkins DT, Barber CE, Daniels MJ (1987) Transformation of Xanthomonas campestris pathovar campestris with plasmid DNA. J Gen Microbiol 133:2727–2731
Balbás P, Soberón X, Merino E, Zurita M, Lomeli FV, Valle F, Flores N, Bolivar F (1986) Plasmid vector pBR322 and its special-purpose derivatives — a review. Gene 50:3–40
Barrere GC, Barber CE, Daniels MJ (1986) Molecular cloning of genes involved in the production of the extracellular polysaccharide xanthan by Xanthomonas campestris pv campestris. Int J Biol Macromol 8:372–374
Birnboin HC, Doly J (1979) A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 7:1513–1523
Boyer HW, Roulland-Dussoix D (1969) A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol 41:459–472
Bradbury JF (1984) Xanthomonas Dowson 1939 In: Krieg NR, Holt JC (eds) Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology vol 1. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 199–210
Caraway WT (1959) A stable starch substrate for the determination of amylase in serum and other body fluids. Am J Clin Path 32:97–99
Castro MEB (1988) Análise do gene a α-amylase de Bacillus subtilis visando o desenvolvimento de um vetor bifunctional de expressão-secreção. Master's thesis, University of Brasília, Brasília, Brazil
Dragert M, Ehrlich SD (1979) Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene 6:23–28
Daniels MJ, Barber CE, Turner PC, Cleary WG, Sawczyc MK (1984) Isolation of mutants of Xanthomonas campestris pv campestris showing altered pathogenicity. J Gen Microbiol 130:2447–2455
Dow JM, Scofield G, Trafford K, Turner PC, Daniels MJ (1987) A gene cluster in Xanthomonas campestris pv campestris required for pathogenicity controls the excretion of polygalacturonate lyase and other enzymes. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 31:261–271
Dye DW, Lelliott RA (1974) Genus II XanthomonasDowson 1939 In: Buchanan RE, Gibbons NE (eds) Bergey's manual of determinative bacteriology. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 243–249
Figurski H, Helinski DR (1979) Replication of an origin containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:1648–1652
Fukuda M, Yano K (1985) Construction of broad host range cloning vectors for Gram-negative bacteria. Agric Biol Chem 49:2719–2724
Harding E, Cleary JM, Cabanas DK, Rosen AG, Kang K (1987) Genetical and physical analysis of a cluster of genes essential for xanthan gum biosynthesis in Xanthomonas campestris. J Bacteriol 169:2854–2861
Haynes WC, Wickerham LJ, Hesseltine CW (1955) Maintenance of cultures of industrially important microorganisms. Appl Microbiol 3:361–368
Jeanes A, Pittsley JE, Senti FRJ (1961) Polysaccharide B-1459: a new hydrocolloid polyelectrolyte produced from glucose by bacterial fermentation. J Appl Polym Sci 5:519–520
Lanza SA, Rosato YB (1986) Produção de goma xantana por diferentes mutantes e recombinantes de Xanthomonas campestris. Abstracts 13th Reunião Anual Genética de Microorganismos, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil, Jan 29–31, p 84.
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Murooka Y, Iwamoto H, Hamamoto A, Tatsushi Y (1987) Efficient transformation of phytopathogenic strains of Xanthomonas species. J Bacteriol 169:4406–9
Osbourn AE, Barber CE, Daniels MJ (1987) Identification of plant induced genes of the bacterial pathogen Xanthomonas campestris using a promoter-probe plasmid. EMBO J 6:23–28
Ramaley RF (1979) Molecular biology of extracellular enzymes. Adv Appl Microbiol 25:37–57
Shaw JJ, Kado I (1986) Development of a Vibrio bioluminescence gene set to monitor phytopathogenic bacteria during the ongoing disease process in a non-disruptive manner. Bio/Technology 4:560–564
Sjöström M, Wold S, Wieslander A, Rilfors L (1987) Signal peptide amino acid sequences in Escherichia coli contain information related to final protein localization. A multivariate data analysis. EMBO J 6:823–831
Souza MBNS (1986) Clonagem molecular e expressão do gene da alfa-amilase be Bacillus sp. Masters' thesis, University of Brasília, Brasília, Brazil
Stall RE, Loschke DC, Jones JB (1986) Linkage of copper resistance and avirulance loci on a self-transmissible plasmid in Xanthomonas campestris pv vesicatoria. Phytopathology 76:240–243
Stripecke R, Rosato YB (1988) Variabilidade no perfil eletroforético de alfa-esterases e plasmideos em patovares de Xanthomonas campestris. Fitopat Brasil 13:358–361
Sumner JB (1925) The determination of sugar in diabetic urine using dinitrosalicylic acid. J Biol Chem 62:287–290
Tang JL, Gough CL, Barber CE, Dow JM, Daniels MJ (1987) Molecular cloning of protease gene(s) from Xanthomonas campestris pv campestris: expression in Escherichia coli and role in pathogenicity. Mol Gen Genet 210:443–448
Thorne L, Tansey L, Pollock TJ (1987) Clustering of mutations blocking synthesis of xanthan gum by Xanthomonas campestris. J Bacteriol 169:3593–3600
Turner P, Barber C, Daniels MJ (1984) Behaviour of the transposons Tn5 and Tn7 in Xanthomonas campestris pv campestris. Mol Gen Genet 195:101–107
Williams PH (1980) Black rot: a continuing threat to world crucifers. Plant Dis 64:736–742
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stripecke, R., Rosato, Y.B. & Astolfi-Filho, S. Subcloning and expression of the α-amylase gene from Bacillus subtilis in Xanthomonas campestris . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 31, 512–517 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00270786
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00270786