Abstract
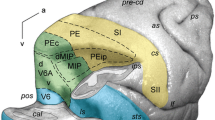
Modality specificity of neuronal responses to visual, somesthetic and auditory stimuli was investigated in the anterior ectosylvian cortex (AEC) of cats, using single-unit recording techniques. Seven classes of neurons were found, and according to their responsiveness to sensory stimuli regrouped into three categories: unimodal, bimodal and trimodal. Unimodal cells that responded to only one of the three stimulus modalities formed 59% of the units; 30.2% were bimodal, in that they showed a clear increase of neuronal discharges to two of the three stimulus types; 10.8% were defined as trimodal because they responded to all three stimulus modalities. Although the different categories of cells were intermingled within the AEC, indicating a certain degree of overlap between sensory modalities, some clustering of cell types was nonetheless evident. Thus, the somatosensory responsive cells were mainly located in the anterior two-thirds of the dorsal bank of the anterior ectosylvian sulcus. Visually responsive cells were concentrated on the ventral bank of the sulcus, whereas neurons with an auditory response occupied the banks and fundus of the posterior three-quarters of the sulcus. The histological distribution and physiological properties of AEC neurons suggest that this cortical region is a higher-order associative area whose function may be to integrate information from different sensory modalities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bishop PO, Kozak W, Vakkur JG (1962) Some quantitative aspects of the cat's eye: axis and plane of reference of visual field coordinates and optics. J Physiol (Lond) 163:466–502
Clarey JC, Irvine DRF (1986) Auditory response properties of neurons in the anterior ectosylvian sulcus of the cat. Brain Res 386:12–19
Clarey JC, Irvine DRF (1990a) The anterior ectosylvian sulcal auditory field in the cat. I. An electrophysiological study of its relationship to surrounding auditory cortical fields. J Comp Neurol 301:289–303
Clarey JC, Irvine DRF (1990b) The anterior ectosylvian sulcal auditory field in the cat. II. A horseradish peroxidase study of its thalamic and cortical connections. J Comp Neurol 301:304–324
Clemo HR, Stein BE (1982) Somatosensory cortex: a “new” somatotopic representation. Brain Res 235:162–168
Clemo HR, Stein BE (1983) Organization of fourth somatosensory area of cortex in cat. J Neurophysiol 50:910–925
Duncan GH, Dreyer DA, Mckenna TM, Whitsel BL (1982) Dose and time-dependent effects of ketamine on SI neurons with cutaneous receptive fields. J Neurophysiol 47:677–699
Fernald R, Chase R (1971) An improved method for plotting retinal landmarks and focusing eyes. Vision Res 11:95–96
Hicks TP, Benedek G, Thurlow GA (1988a) Organization and properties of neurons in a visual area within the insular cortex of the cat. J Neurophysiol 60:397–421
Hicks TP, Benedek G, Thurlow GA (1988b) Modality specificity of neuronal responses within the cat's insula. J Neurophysiol 60:422–437
Higo S, Kawamura S (1984) Topographical linkage of tecto-thalamo-anterior ectosylvian sulcal cortex in the cat: an 125I-labeled WGA autoradiographic study. Brain Res Bull 12:647–655
Imig TJ, Reale RA (1980) Patterns of cortico-cortical connections related to tonotopic maps on cat auditory cortex. J Comp Neurol 192:293–332
Irvine DRF, Phillips DP (1982) Polysensory ‘association’ areas of the cerbral cortex. Organization of acoustic input in the cat. In: Woolsey CN (ed) Cortical sensory organization. Multiple auditory areas, vol 3. Humana Press, Clifton, New Jersey, pp 111–156
Jiang H, Lepore F, Ptito M, Guillemot J-P (1991) Sensory modality interactions in the anterior ectosylvian cortex of cats. 3rd IBRO Abstr:397
Kluver H, Barrera E (1953) A method for the combined staining of cells and fibres in the nervous system, J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 12:400–403
Meredith MA, Clemo HR (1989) Auditory cortical projection from the anterior ectosylvian sulcus (field AES) to the superior colliculus in the cat: An anatomical and electrophysiological study. J Comp Neurol 289:687–707
Miceli D, Reperant J, Ptito M (1985) Intracortical connections of the anterior ectosylvian and lateral suprasylvian visual areas in the cat. Brain Res 347:291–298
Minciacchi D, Tassinari G, Antonini A (1987) Visual and somatosensory integration in the anterior ectosylvian cortex of the cat. Brain Res 410:21–31
Mucke L, Norita M, Benedek G, Creutzfeldt OD (1981) Physiologic and anatomic investigation of a visual cortical area situated in the ventral bank of anterior ectosylvian sulcus in the cat. Brain Res 221:57–69
Norita M, Mucke L, Benedek G, Albowitz B, Katoh Y, Creutzfeldt OD (1986) Connections of the anterior ectosylvian visual area (AEV). Exp Brain Res 62:225–240
Olson CR, Graybiel AM (1983) An outlying visual area in the cerebral cortex of the cat. Progr Brain Res 58:239–245
Olson CR, Graybiel AM (1987) Ectosylvian visual area of the cat: location, retinotopic organization, and connections. J Comp Neurol 261:277–294
Ptito M, Tassinari G, Antonini A (1987) Electrophysiological evidence for interhemispheric connections in the anterior ectosylvian sulcus in the cat. Exp Brain Res 66:90–98
Reinoso-Suárez F, Roda JM (1985) Topographical organization of the cortical afferent connections to the cortex of the anterior ectosylvian sulcus in the cat. Exp Brain Res 59:313–324
Roda JM, Reinoso-Suárez F (1983) Topographical organization of the thalamic projections to the cortex of the anterior ectosylvian sulcus in the cat. Exp Brain Res 49:131–139
Stein BE, Magalhaes-Castro B, Kruger L (1976) Relationship between visual and tactile representations in the cat superior colliculus. J Neurophysiol 39:401–419
Stein BE, Spencer RF, Edwards SB (1983) Corticotectal and cortico-thalamic efferent projections of SIV somatosensory cortex in cat. J Neurophysiol 50:896–909
Tamai Y, Miyashita E (1989) Subcortical connections of an ‘oculomotor’ region on the ventral bank of the anterior ectosylvian sulcus in the cat. Neurosci Res 7:249–256
Tamai Y, Miyashita E, Nakai M (1989) Eye movements following cortical stimulation in the ventral bank of the anterior ectosylvian sulcus of the cat. Neurosci Res 7:159–163
Tortelly A, Reinoso-Suárez F, Llamas A (1980) Projections from non-visual cortical areas to the superior colliculus demonstrated by retrograde axonal transport of HRP in the cat. Brain Res 188:543–549
Wallace MT, Meredith MA, Stein BE (1992) Integration of multiple sensory modalities in cat cortex. Exp Brain Res 91:484–488
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, H., Lepore, F., Ptito, M. et al. Sensory modality distribution in the anterior ectosylvian cortex (AEC) of cats. Exp Brain Res 97, 404–414 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00241534
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00241534