Summary
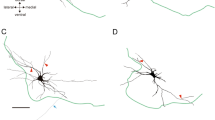
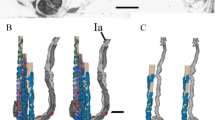
The pre- and postsynaptic structure of 243 axon terminals of bag 1, bag 2, and chain fibers were studied in cynomolgus monkey skeletal muscle spindles. The motor endings of the biceps and gastrocnemius spindles (long limb muscle) were compared to the motor endings of lumbricals and opponens pollicis (intrinsic hand muscle) spindles. In both muscle groups the only significant difference observed in the presynaptic features was in the presynaptic membrane length. The postsynaptic features of bag 1, bag 2 and chain endings were similar in the long limb muscle spindles. In the intrinsic hand muscle, however, the bag 1 and chain endings showed complex postsynaptic structure which resembled the extra fusal endings while the postsynaptic structure of bag 2 endings was much simpler. From these studies we conclude that the postsynaptic structure of various intrafusal fiber types is dissimilar in different muscles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbuthnott ER, Ballard KJ, Boyd IA, Gladden MH, Sutherland FI (1982) The ultrastructure of cat fusimotor endings and their relationship to foci of sarcomere convergence in intrafusal fibers. J Physiol (Lond) 331: 285–309
Arbuthnott ER, Sutherland FI, Boyd IA, Gladden MH (1985) Axon terminal indentation and postsynaptic folding as criteria for classifying fusimotor nerve endings. In: Boyd IA, Gladden MH (eds) The muscle spindle. Stockton Press, New York, pp 57–62
Banks RW, Harker D, Stacey MJ (1977) A study of mammalian intrafusal muscle fibers using a combined histochemical and ultrastructural technique. J Anat 123: 783–796
Banks RW (1981) A histological study of the motor innervation of the cat's muscle spindle. J Anat 133: 571–591
Banks RW, Barker D, Stacey MJ (1982) Form and distribution of sensory terminals in cat hind limb muscle spindles. Philos Trans R Soc Lond (Biol) 299: 329–364
Banks RW, Barker D, Stacey MJ (1985) Form and classification of motor endings in mammalian muscle spindles. Proc R Soc Lond B 225: 195–212
Barker D, Banks RW (1985) The muscle spindle. In: Banker BQ, Engel AG (eds) Textbook of myology. McGraw-Hill, New York (in press)
Boyd IA (1976) The mechanical properties of dynamic nuclear bag fibers, static nuclear bag fibers, and nuclear chain fibers in isolated cat spindles. Prog Brain Res 44: 33–49
Boyd IA (1981) The muscle spindle controversy. Sci Prog 67: 205–221
Boyd IA (1962) The structure and innervation of the nuclear-bag fiber system and the nuclear-chain fiber system in mammalian muscle spindles. Philos Trans B 245: 81–136
Engel AG, Santa T (1971) Histometric analysis of the ultrastructure of the neuromuscular junction in myasthenia gravis and in the myasthenic syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci 183: 46–63
Fukami Y, Hunt CC (1970) The structure of snake muscle spindles. J Neurophysiol 33: 9–27
James NT, Meek GA (1972) An electron microscopical study of avian muscle spindles. J Ultrast Res 43: 193–204
Karlsson U, Andersoon-Cedergren E (1966) Motor myoneural junctions on from intrafusal muscle fibers. J Ultrast Res 14: 191–211
Kucera J (1985) Characteristics of motor innervation of muscle spindles in the monkey. Am J Anat 173: 113–125
Kucera J (1985) Histological study of motor innervation of nuclear bag 1 intrafusal fiber in the cat. J Comp Neurol 232: 331–346
Kucera J, Walro JM (1985) Structure and classification of cat intrafusal motor endings. In: Boyd IA, Gladden MH (eds) The muscle spindle. Stockton Press, New York pp 63–68
Kucera J, Dorovini-zis K (1979) Type of human intrafusal muscle fibers. Muscle Nerve 2: 437–451
Ovalle WK (1972) Motor nerve liminals on rat intrafusal muscle fibers a correlated light and electron microscopic study. J Anat 11: 239–252
Ovalle WK Jr, Smith RS (1972) Histochemical identification of three types of intrafusal muscle fibers in the cat and monkey based on the myosin ATPase reaction. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 50: 195–202
Sutherland FI, Arbuthnott ER, Boyd IA, Gladden MH (1985) Two ultrastructural types of fusimotor ending on typical chain fibers in cat muscle spindles. In: Boyd IA, Gladden MH (eds) The muscle spindle. Stockton Press, New York, pp 51–56
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Subramani, V., Sahgal, V., Sahgal, S. et al. Morphology and morphometry of motor endings in primate intrafusal fibers. Exp Brain Res 64, 149–157 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00238211
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00238211