Abstract
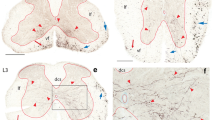
The courses and terminal patterns of the fasciculus retroflexus (FR) in the interpeduncular nucleus (IP) were studied in the mouse, using the rapid Golgi method. Mainly on the basis of the distribution areas and terminal patterns, the FR fibers are divided into two types. The type 1 FR fibers are coarse in contour and take zigzag courses to distribute throughout the entire rostral half and core region of the caudal IP. In contrast, the type 2 fibers are fine, travel caudally along the lateral boundary of the IP and terminate in the lateral regions of the caudal half, forming a dense fiber plexus. The distribution areas of the type 1 and type 2 fibers are clearly differentiated from each other, from the cytoarchitectural as well as the fibroarchitectural viewpoint. Thus, the type 1 and type 2 FR fibers form different fiber systems in the IP. These results are discussed in the light of the known hodological, histochemical and ultrastructural studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai R, Winsky L, Arai M, Jacobowitz DM (1991) Immunohistochemical localization of calretinin in the rat hindbrain. J Comp Neurol 310:21–44
Artymyshyn R, Murray H (1985) Substance P in the interpeduncular nucleus of the rat: normal distribution and the effects of deafferentiation. J Comp Neurol 231:78–90
Calderon L (1927–28) Sur la structure du ganglion interpedonculaire. Trab Lab Rech Biol Univ Madrid 25:297–306
Contestabile A, Flumerfelt BA (1981) Afferent connections of the interpeduncular nucleus and the topographic organization of the habenulo-interpeduncular pathway: an HRP study in the rat. J Comp Neurol 196:253–270
Contestabile A, Villani L, Fasilo A, Franzoni MF, Gribaudo L, Oktedalen O, Fonnum F (1987) Topography of cholinergic and substance P pathways in the habenulo-interpeduncular system of the rat. An immunocytochemical and microchemical approach. Neuroscience 21:253–270
Cuello AC, Emson PC, Paxinos G, Jessell T (1978) Substance P-containing and cholinergic projections from the habenula. Brain Res 149:413–429
Eckenrode TC, Barr GA, Battisti WP, Murray M (1987) Acetylcholine in the interpeduncular nucleus of the rat: normal distribution and effects of deafferentation. Brain Res 418:273–286
Flumerfelt BA, Contestabile A (1982) Acetylcholinesterase histochemistry of the habenulo-interpeduncular pathway in the rat and the effects of electrolytic and kainic acid lesions. Anat Embryol163:435–446
Groenewegen HJ, Ahlenius S, Haber SN, Kowall NW, Nauta WJH (1986) Cytoarchitecture, fiber connections, and some histochemical aspects of the interpeduncular nucleus in the rat. J Comp Neurol 249:65–102
Hamill GS, Jacobowitz DM (1984) A study of afferent projections to the rat interpeduncular nucleus. Brain Res Bull 13:527–539
Hamill GS, Lenn NJ (1983) Synaptic plasticity within the interpeduncular nucleus after unilateral lesions of the habenula in neonatal rats. Neuroscience 3:2128–2145
Hamill GS, Lenn NJ (1984) The subnuclear organization of the rat interpeduncular nucleus: a light and electron microscopic study. J Comp Neurol 222:396–408
Hamill GS, Olschowska JA, Lenn NJ, Jacobowitz DM (1984) The subnuclear distribution of substance P, cholecystokinin, vasoactive intestinal peptide, somatostatin, leu-enkephalin, dopamine-B-hydrozylase and serotonin in the rat interpeduncular nucleus. J Comp Neurol 226:580–596
Hayakawa T, Zyo K (1982) Organization of the habenulo-interpeduncular connections in cats: a horseradish peroxidase study. Brain Res 240:3–11
Hemmendinger LM, Moore RY (1984) Interpeduncular nucleus organization in the rat: Cytoarchitecture and histochemical analysis. Brain Res Bull 13:163–179
Herkenham M, Nauta WJH (1979) Efferent connections of the habenular nuclei in the rat. J Comp Neurol 187:19–48
Herrick CH (1934) The interpeduncular nucleus of the brain of Necturus. J Comp Neurol 60:111–135
Herrick CH (1948) The brain of the tiger salamander. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Jacobowitz DM, Winsky L (1991) Immunocytochemical localization of calretinin in the forebrain of the rat. J Comp Neurol 304:198–218
Kawaja MD, Flumerfelt BA, Hrycyshyn AW (1988) Topographical and ultrastructural investigation of the habenulo-interpeduncular pathway in the rat: a wheat germ agglutinin-horseradish peroxidase anterograde study. J Comp Neurol 275:117–127
Kawaja MD, Flumerfelt BA, Hrycyshyn AW (1990) Simultaneous demonstration of choline acetyltransferase and glutamic acid decarboxylase immunoreactivity in the rat interpeduncular nucleus. J Chem Neuroanat 3:165–177
Kawaja MD, Flumerfelt BA, Hrycyshyn AW (1991) Substance P immunoreactivity in the rat interpeduncular nucleus: synaptic interactions between substance P-positive profiles and choline acetyltransferaseor glutamate decarboxylase-immunoreactive structures. Neuroscience 42:739–755
Lenn NJ (1976) Synapses in the interpeduncular nucleus: electron microscopy of normal and habenular lesioned rats. J Comp Neurol 166:73–100
Lenn NJ, Hamill GS (1984) Subdivisions of the interpeduncular nucleus: a proposed nomenclature. Brain Res Bull 13:203–204
Marchand ER, Riley JN, Moore RY (1980) Interpeduncular nucleus afferents in the rat. Brain Res 193:339–352
Morley BJ (1986) The interpeduncular nucleus. Int Rev Neurobiol 28:157–182
Murray M, Zimmer J, Raisman G (1979) Quantitative electron microscopic evidence for reinnervation in adult rat interpeduncular nucleus after lesions of the fasciculus retroflexus. J Comp Neurol 187:447–468
Ramón y Cajal R (1911) Histologie du Système Nerveux de l'Homme et des Vertébrés. Tome II, Masson, Paris, pp 270–275
Rotter A, Jacobowitz DM (1984) Localization of substance P, acetylcholinesterase and muscarinic receptors and alpha-bungarotoxin-binding sites in the rat interpeduncular nucleus. Brain Res Bull 12:83–94
Shibata H, Suzuki T, Matsushita M (1986) Afferent projections to the interpeduncular nucleus in the rat, as studied by retrograde and anterograde transport of wheat germ agglutinin conjugated to horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol 248:272–284
Shinoda K, Michigami T, Awano K, Shiotani Y (1988) Analysis of the rat interpeduncular subnuclei by immunocytochemical double-staining for enkephalin and substance P, with some reference to the coexistence of both peptides. J Comp Neurol 271:243–256
Woolf NJ, Butcher LL (1985) Cholinergic systems in the rat brain: II. Projections to the interpeduncular nucleus. Brain Res Bull 14:63–83
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iwahori, N., Nakamura, K. & Kameda, S. Terminal patterns of the fasciculus retroflexus in the interpeduncular nucleus of the mouse: a Golgi study. Anat Embryol 187, 523–528 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00214430
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00214430