Abstract
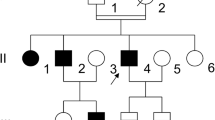
We report the case of a family with type I von Willebrand disease (vWD), characterized by a quantitative defect in von Willebrand factor (vWF), associated with a defective binding of vWF to factor VIII (FVIII) also called the “Normandy” variant of vWD. PCR products from genomic DNA of the family members were analysed in the region coding for the binding domain of vWF to FVIII. It showed that the proposita and one of her sons were heterozygous for the Arg91Gln missense mutation, abolishing an MspI restriction enzyme site located in exon 20. The transcription of the normal and mutated alleles was tested by the amplification of cDNA after reverse transcription of platelet mRNA in this region. A total lack of expression of the normal allele was observed in the proposita, who appeared as a compound heterozygous with one allele mutated at Arg91 and a “silent” expression of the other one. The segregation of the “silent” allele was studied in the family with the exonic BstEII RFLP both at the DNA and mRNA levels. The proposita has transmitted her “silent” allele to her daughter and to another son. As this son was informative for this RFLP, the absence of expression of the allele could be demonstrated at the mRNA level, providing evidence that this defect was responsible for his type I vWD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahnak BR, Lavergne JM, Verweij C, Rothschild C, Pannekoek H, Larrieu MJ, Meyer D (1988) Carrier detection in severe (Type III) von Willebrand disease using two intragenic restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Thromb Haemost 60:178–181
Baruch D, Bahnak BR, Girma JP, Meyer D (1989) von Willebrand factor and platelet function. In: Cean JP (ed) Platelet disorders. Bailllière Tindall-WB London, pp 627–672
Bonthron D, Orr EC, Mitsock LM, Ginsburg D, Handin RI, Orkin SH (1986) Nucleotide sequence of pre-pro-von Willebrand factor cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res 14:7125–7127
Cacheris PM, Nichols WC, Ginsburg D (1991) Molecular characterization of a unique von Willebrand disease variant: a novel mutation affecting von Willebrand factor/factor VIII interaction. J Biol Chem 266:13499–13502
Chomczynski P, Succhi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Eikenboom JCJ, Ploos Amstel HK van, Reitsma PH, Briët E (1992) Mutations in severe, type III von Willebrand's disease in the Dutch population: candidate missense mutations associated with reduced levels of von Willebrand factor messenger RNA. Thromb Haemost 68:448–454
Foster PA, Fulcher CA, Marti T, Titani K, Zimmerman TS (1987) A major Factor VIII binding domain resides within the aminoterminal 272 amino acid residues of von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem 262:8443–8446
Gaucher C, Mercier B, Jorieux S, Oufkir D, Mazurier C (1991) Identification of two point mutations in the von Willebrand factor gene of three families with the Normandy variant of von Willebrand disease. Br J Haematol 78:506–514
Ginsburg D, Sadler JE (1993) von Willebrand disease: a database of point mutations, insertions and deletions. Thromb Haemost 69:177–184
Jorieux S, Tuley EA, Gaucher C, Mazurier C, Sadler JE (1992) The mutation Arg (53) → Trp causes von Willebrand disease Normandy by abolishing binding to factor VIII. Studies with recombinant von Willebrand factor. Blood 79:563–567
Kroner PA, Friedman KD, Fahs SA, Scott P, Montgomery RR (1991) Abnormal binding of factor VIII is linked with the substitution of glutamine for arginine 91 in von Willebrand factor in a variant form of von Willebrand disease. J Biol Chem 266:19146–19149
Mancuso DJ, Tuley E, Westfield LA, Worrall NK, Shelton-Inloes BB, Sorace JM, Alevy YG, Sadler JE (1989) Structure of the gene for human von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem 264:19514–19527
Mancuso DJ, Tuley EA, Westfield MA, Lester-Mancuso TL, Lebeau MM, Sorace JM, Sadler JE (1991) Human von Willebrand factor gene and pseudogene: structural analysis and differentiation by polymerase chain reaction. Biochemistry USA 30:253–269
Mazurier C (1992) von Willebrand disease masquerading as haemophilia A. Thromb Haemost 67:391–396
Mazurier C, Diéval J, Jorieux S, Delobel J, Goudemand M (1990a) A new von Willebrand factor (vWF) defect in a patient multimeric patterns of both plasma and platelet vWF. Characterization of abnormal vWF/FVIII interaction. Blood 75:20–26
Mazurier C, Gaucher C, Jorieux S, Parquet-Gernez A, Goudemand M (1990b) Evidence for a von Willebrand factor defect in factor VIII binding in three members of a family previously misdiagnosed mild haemophilia A and haemophilia A carriers: consequences for therapy and genetic counselling. Br J Haematol 76:372–379
Nichols WC, Lyons SE, Harrison JS, Cody RL, Ginsburg D (1991) Severe von Willebrand disease due to a defect at the level of von Willebrand factor mRNA expression: detection by exonic PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:3857–3861
Nishino M, Girma JP, Rothschild C, Fressinaud E, Meyer D (1989) A new variant of von Willebrand disease with defective binding to factor VIII. Blood 74:1591–1599
Peerlinck K, Eikenboom JC, Ploos Amstel HK van, Sangtawesin W, Arnout J, Reitsma PH, Vermylen J, Briët E (1992) A patient with von Willebrand's disease characterized by a compound heterozygosity for a substitution of Arg 854 by Gln in the putative factor-VIII binding domain of von Willebrand factor (vWF) on one allele and very low levels of mRNA from the second vWF allele. Br J Haematol 80:358–363
Piétu G, Ribba AS, Meulien P, Meyer D (1989) Localization within the 106 N-terminal amino acids of von Willebrand factor (vWF) of the epitope corresponding to a monoclonal antibody which inhibits vWF binding to factor VIII. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 163:618–626
Ribba AS, Lavergne JM, Bahnak BR, Derlon A, Piétu G, Meyer D (1991) Duplication of a methionine within the glycoprotein Ib binding domain of von Willebrand factor detected by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis in a patient with type IIB von Willebrand disease. Blood 78:1738–1743
Rodeghiero F, Castaman G, Dini E (1987) Epidemiological investigation of the prevalence of von Willebrand's disease. Blood 69:454–459
Ruggeri ZM, Zimmerman TS (1987) von Willebrand factor and von Willebrand disease. Blood 70:895–904
Sadler JE, Ginsburg D (1993) A database of polymorphisms in the von Willebrand factor gene and pseudogene. Thromb Haemost 69:185–191
Saiki RK, Gelfand DH, Stoffel S, Scharf SJ, Higuchi R, Horn GT, Mullis KB, Erlich HA (1988) Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 239:487–491
Takahashi Y, Kalafatis M, Girma JP, Sewerin K, Andersson LO, Meyer D (1987) Localization of a factor VIII binding domain on a 34 kilodalton fragment of the N-terminal portion of von Willebrand factor. Blood 70:1679–1682
Tuley EA, Gaucher C, Jorieux S, Worrall NK, Sadler JE, Mazurier C (1991) Expression of von Willebrand factor Normandy: an autosomal mutation that mimics hemophilia A. Proc Natl Sci USA 88:6377–6381
Zhong N, Martiniuk F, Tzall S, Hirschhorn R (1991) Identification of a missense mutation in one allele of a patient with Pompe disease, and use of endonuclease digestion of PCR-amplified RNA to demonstrate lack of mRNA expression from the second allele. Am J Hum Genet 49:635–645
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siguret, V., Lavergne, JM., Chérel, G. et al. A novel case of compound heterozygosity with “Normandy”/type I von Willebrand disease (vWD). Direct demonstration of the segregation of one allele with a defective expression at the mRNA level causing type I vWD. Hum Genet 93, 95–102 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00210590
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00210590