Summary
-
1.
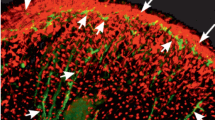
Nerve terminals associated with longitudinal muscle in the leech show FMRFamide-like immuno-reactivity.
-
2.
Structure-activity studies using FMRFamide analogs show that the C-terminal RFamide portion of the molecule is crucial for biological activity on leech longitudinal muscle.
-
3.
The putative protease inhibitor FA (Phe-Ala) increases the peak tension produced by longitudinal muscle in response to superfused FMRFamide and the majority of its analogs, suggesting the presence of peripheral proteases capable of degrading RFamide peptides.
-
4.
FMRFamide decreases the relaxation rate of neurally evoked contractions of longitudinal muscle. FA also decreases the relaxation rate of neurally evoked contractions.
-
5.
Intact and isolated muscle cells respond to superfused FMRFamide with a conductance increase, that leads to depolarization and often with a delayed conductance decrease as the membrane potential is restored to resting levels.
-
6.
The depolarizing response of isolated muscle cells to FMRFamide is dependent on external calcium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal RA, Greenberg MJ (1969) A comparative study of cardioactive agents from bivalve tissue. Comp Biochem Physiol 31:835–850
Austin R, Weiss S, Lukowiak K (1982) FMRFamide effects on spontaneous and induced contractions of the anterior gizzard in Aplysia. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 61:949–953
Bacq ZM, Coppee B (1937) Action de l'eserine sur la préparation neuromusculaire du siponcle et de la sangsue. CR Soc Biol (Paris) 124:1244–1277
Chou J, Tang J, Del Rio J, Yang H-YT, Costa E (1984) Action of peptidase inhibitors on methionine5-enkephalin-argine6-phenylalanine7 (YGGFMRF) and methionine5-enkephalin (YGGFM) metabolism and on electroacupuncture antinociception. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 230:349–352
Cottrell GA, Greenberg MJ, Price DA (1983) Differential effects of the molluscan neuropeptide FMRFamide and the related met-enkephalin derivative YGGFMRFamide on the Helix tentacle retractor muscle. Comp Biochem Physiol 75C: 373–375
Cowden C, Stretton AOW, Davis RE (1989) AF1, a sequenced bioactive neuropeptide from the nematode Ascaris suum. Neuron 2
Doble KE, Greenberg MJ (1982) The clam rectum is sensitive to FMRFamide, the enkephalins, and their common analogs. Neuropeptides 2:157–167
Dockray GJ, Reeve JR, Shively J, Gayton RJ, Barnard CS (1983) A novel active pentapeptide from chicken brain identified by antibodies to FMRFamide. Nature 305:328–330
Ebberink RHM, Price DA, van Loenhout H, Doble KE, Riehm JP, Geraerts WPM, Greenberg MJ (1987) The brain of Lymnaea contains a family of FMRFamide-like peptides. Peptides 8:515–522
Evans BD, Calabrese RL (1989) Small cardioactive peptide-like immunoreactivity and its colocalization with FMRFamide-like immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the leech, Hirudo medicinalis. Cell Tissue Res 257:187–199
Evans PD, Meyers CM (1986) The modulatory actions of FMRFamide and related peptides on locust skeletal muscle. J Exp Biol 126:403–422
Flacke W, Yeoh TS (1968) The action of some cholinergic agonists and anticholinesterase agents on the dorsal muscle of the leech. Br J Pharmacol Chemother 33:145–153
Fuhner J (1918) Untersuchungen über den Synergismus von Giften. IV. Die chemische Erregbarkeitssteigerung glatter Muskulatur. Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol 82:51–85
Grimmelikhuijzen CJP, Graff D (1986) Isolation of pGlu-Gly-Arg-Phe-NH2 (Antho-RFamide), a neuropeptide from sea anemones. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:9817–9821
Higgins WJ, Price DA, Greenberg MJ (1978) FMRFamide increases the adenylate cyclase activity and cyclic AMP level of the molluscan heart. Eur J Pharmacol 48:425–430
Holman GM, Cook BJ, Nachman RJ (1986) Isolation, primary structure and synthesis of leucomyosuppressin, an insect neuropeptide that inhibits spontaneous contractions of the cockroach hindgut. Comp Biochem Physiol 85C: 329–333
Kramer RH, Zucker RS (1985) Calcium-dependent inward current in Aplysia bursting pacemaker neurons. J Physiol 362:107–130
Kuffler DP (1978) Neuromuscular transmission in the longitudinal muscle of the leech, Hirudo medicinalis. J Comp Physiol 124:333–338
Kuhlman JR, Li C, Calabrese RL (1985a) FMRFamide-like substances in the leech. I. Immunocytochemical localization. J Neurosci 5:2301–2309
Kuhlman JR, Li C, Calabrese RL (1985b) FMRFamide-like substances in the leech. II. Bioactivity on the heartbeat systems. J Neurosci 5:2310–2317
Lentzen H, Reinsch I, Linke J (1984) Angiotensin-converting enzyme, enkephalinase A and amino peptidases in the breakdown of enkephalin — studies in cell culture. Clin Exp Hypert A — Theory and Practice A6:1829–1832
Li C, Calabrese RL (1985) Evidence for proctolin-like substances in the central nervous system of the leech Hirudo medicinalis. J Comp Neurol 232:414–424
Li C, Calabrese RL (1987) FMRFamide-like substances in the leech. III. Biochemical characterization and physiological action. J Neurosci 7:595–603
Maranto AR, Calabrese RL (1984b) Neural control of the hearts in the leech, Hirudo medicinalis. II. Myogenic activity and its control by heart motor neurons. J Comp Physiol A 154:381–391
Marder E, Calabrese RL, Nusbaum MP, Trimmer BA (1987) Distribution and partial characterization of FMRFamide-like peptides in the stomatogastric nervous systems of the rock crab, Cancer borealis, and the spiny lobster, Panulirus interruptus. J Comp Neurol 259:150–163
McKelvey JF, Blumberg S (1986) Inactivation and metabolism of peptides. Annu Rev Neurosci 9:415–434
Muneoka Y, Matsumura M (1985) Effects of the molluscan neuropeptide FMRFamide and the related opioid peptide YGGFMRFamide on Mytilus muscle. Comp Biochem Physiol 81C:61–70
Muneoka Y, Saitoh H (1986) Pharmacology of FMRFamide in Mytilus catch muscle. Comp Biochem Physiol 85C:207–214
Norris BJ, Calabrese RL (1987) Identification of motor neurons that contain a FMRFamide-like peptide and the effects of FMRFamide on longitudinal muscle in the medicinal leech, Hirudo medicinalis. J Comp Neurol 266:95–111
Ort CA, Kristan WB, Stent GS (1984) Neuronal control of swimming in the medicinal leech. II. Identification and connections of neurons. J Comp Physiol 94:121–156
O'Donahue TL, Bishop JF, Chronwall BM, Groome J, Watson WH (1984) Characterization and distribution of FMRFamide immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system. Peptides 5:563–568
O'Shea M, Schaffer M (1985) Neuropeptide function: the invertebrate contribution. Annu Rev Neurosci 8:171–198
Painter SD (1982a) FMRFamide catch contractures of a molluscan smooth muscle: pharmacology, ionic dependence and cyclic nucleotides. J Comp Physiol 148:491–501
Painter SD (1982b) FMRFamide inhibition of a molluscan heart is accompanied by increases in cyclic AMP. Neuropeptides 3:19–27
Painter SD, Price DA, Greenberg MJ (1974) Responses of bivalve myocardia to 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) and the molluscan neuropeptide FMRFamide. Am Zool 19:959
Painter SD, Greenberg MJ (1982) A survey of the responses of bivalve hearts to the molluscan neuropeptide FMRFamide and to 5-hydroxytryptamine. Biol Bull 162:311–332
Painter SD, Morley JS, Price DA (1982) Structure-activity relations of the molluscan neuropeptide FMRFamide on some molluscan muscles. Life Sci 31:2471–2478
Price DA (1982) The FMRFamide-like peptide of Helix aspersa. Comp Biochem Physiol 72C:325–328
Price DA (1986) Evolution of a molluscan cardioexcitatory neuropeptide. Am Zool 26:1007–1015
Price DA, Greenberg MJ (1977a) The structure of a molluscan cardioexcitatory neuropeptide. Science 197:670–671
Price DA, Greenberg MJ (1977b) Purification and characterization of a cardioexcitatory neuropeptide from the central ganglia of a bivalve mollusc. Prep Biochem 7:261–281
Price DA, Cottrell GA, Doble KE, Greenberg MJ, Jorenby W, Lehman HK, Riehm JP (1985) A novel FMRFamide-related peptide in Helix: pQDPFLRFamide. Biol Bull 169:256–266
Price DA, Cobb CG, Doble KE, Kline JK, Greenberg MJ (1987) Evidence for a novel FMRFamide-related heptapeptide in the pulmonate snail Siphonaria pectinata. Peptides 8(3):533–538
Raffa RB, Bianchi CP (1986) Further evidence for a neuromodulatory role of FMRFamide involving intracellular Ca++ pools in smooth muscle of Mytilus edulis. Comp Biochem Physiol 84C: 23–28
Rocques BP, Fournie-Zaluski MC, Soroca E, Lecomte JM, Malfroy B, Llorens C, Schwartz JC (1980) The enkephalinase inhibitor thiorphan shows antinociceptive activity in mice. Nature 288:286–288
Sargent PB (1977) Synthesis of acetylcholine by excitatory motoneurons in central nervous system of the leech. J Neurophysiol 40:453–460
Schaefer M, Picciotto MR, Kriener T, Kaldany RR, Taussig R, Scheller RH (1985) Aplysia neurons express a gene encoding multiple FMRFamide neuropeptides. Cell 41:457–467
Schneider LE, Taghert PH (1988) Isolation and characterization of a Drosophila gene that encodes multiple neuropeptides related to Phe-Met-Arg-Phe-NH2 (FMRFamide). Proc Natl Acad Scin USA 85:1993–1997
Schwartz JC, Malfroy B, De La Baume S (1981) Biological inactivation of enkephalins and the role of enkephalin-dipeptidylcarboxypeptidase (‘enkephalinase’) as a neuropeptidase. Life Sci 29:1715–1724
Spencer AN, Grimmelikhuijzen CJP, Hahn M, Przysiezniak J (1987) RFamide neuropeptides in the hydromedusa Polyorchis penicillatus: localization, isolation and electrophysiology. Soc Neurosci Abstr 13:1256
Standen NB (1981) Calcium channel inactivation by intracellular calcium injection into Helix neurons. Nature 293:158–159
Trimmer BA, Kobierski LA, Kravitz E (1987) Purification and characterization of FMRFamide immunoreactive substances from the lobster nervous system: isolation and sequence analysis of two closely related peptides. J Comp Neurol 266:16–26
Veenstra JA (1984) Immunocytochemical demonstration of a homology in peptidergic neurosecretory cells in the suboesophageal ganglion of a beetle and a locust with antisera to bovine pancreatic polypeptide, FMRFamide, vasopressin and a-MSH. Neurosci Lett 48:185–190
Voigt KH, Kiehling C, Geis R, Falke N, Martin R (1983) Identification of met-enkephalin-Arg6-Phe7-amide: an opioid and cardioexcitatory peptide from the mollusc. Proc Int Narcotic Res Conf Garmisch, FRG 52L
Walker RJ, Woodruff GN, Kerkut GA (1970) The action of cholinergic antagonists on spontaneous excitatory potentials recorded from the body wall of the leech, Hirudo medicinalis. Comp Biochem Physiol 32:691–701
Wallace BG (1981a) Distribution of AChE in cholinergic and non-cholinergic neurons. Brain Res 219:190–195
Wallace BG (1981b) Neurotransmitter chemistry. In: Muller KJ, Nicholls JG, Stent GS (eds) Neurobiology of the leech. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, pp 147–172
Wallace BG, Gillon JW (1982) Characterization of acetylcholinesterase in individual neurons in the leech central nervous system. J Neurosci 2:1108–1118
Walther C, Schiebe M, Voigt KH (1984) Synaptic and non-synaptic effects of molluscan cardioexcitatory neuropeptides on locust skeletal muscle. Neurosci Lett 45:99–104
Weiss S, Goldberg JI, Cohan KS, Stell WK, Drummond GI, Lukowiak K (1984) Evidence from FMRFamide as a transmitter in the gill of Aplysia californica. J Neurosci 4:1994–2000
Yang HYT, Fratta W, Majane EA, Costa E (1985) Isolation, sequencing, synthesis and pharmacological characterization of two brain neuropeptides that modulate the action of morphine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:7757–7761
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Norris, B.J., Calabrese, R.L. Action of FMRFamide on longitudinal muscle of the leech, Hirudo medicinalis . J Comp Physiol A 167, 211–224 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00188114
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00188114