Summary
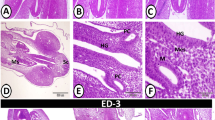
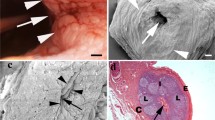
An ultrastructural study was made of the postnatal development of the tonsillar crypt epithelium in the musk shrew, Suncus murinus. On day 3 after birth, a particular kind of large lymphoid cell was first seen to move through the basement membrane into the epithelium. The next migration was that of lymphocytes, which passed through holes in the basement membrane. On days 5 to 7, the lymphocytes formed clusters, and pale epithelial cells of low electron density appeared. The cell clusters and pale epithelial cells fused on day 10. By day 14, these epithelial cells extended cytoplasmic projections to the surface of the epithelium, which had many heterophagic vacuoles and some microvilli-like structures. These findings suggest that the lymphoepithelial relationship is important for the organization of the immunological microenvironment in tonsillar crypt epithelium of the neonatal musk shrew.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brandtzaeg P (1988) Immunobarriers of the mucosa of the upper respiratory and digestive pathways. Acta Otolaryngol(Stockh) 105:172–180
Chen W, Alley MR, Manktelow BW, Hopcroft D, Bennett R (1991) The potential role of the ovine pharyngeal tonsil in respiratory tract immunity: a scanning and transmission electron microscopy study of its epithelium. J Comp Pathol 104:47–56
Gaudecker B von, Müller-Hermelink HK (1982) The development of the human tonsilla palatina. Cell Tissue Res 224:579–600
Hashimoto Y, Komuro T (1988) Close relationships between the cells of the immune system and the epithelial cells in the rat small intestine. Cell Tissue Res 254:41–47
Higashikawwa T, Ohtani O, Masuda Y (1990) Ultrastructures of the epithelial basement membrane and the subepithelial capillaries in rabbit palatine tonsils. Arch Histol Cytol 53:31–39
Howie AJ (1980) Scanning and transmission electron microscopy on the epithelium of human palatine tonsils. J Pathol 130:91–98
Karnovsky MJ (1965) A formaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative of high osmolality for use in electron microscopy (abstract). J Cell Biol 27:137A
Kimura M, Tohya K (1989) Scanning, transmission and immunoe-lectron microscopical studies of the tonsil-like lymphoid organ of normal and horseradish-peroxidase-injected laboratory sun-cuses. Acta Anat 136:177–184
Komuro T (1985) Fenestrations of the basal lamina of intestinal villi of the rat. Scanning and transmission electron microscopy. Cell Tissue Res 239:183–188
Mitani T, Tomoda K, Maeda N, Yamashita T, Kumazawa T (1990) The tonsillar immune system: its response to exogenous antigens. Acta Otolaryngol [Suppl] (Stockh) 475:1–14
Nishikawa K, Takagi T (1988) Comparative immunobiology of the palatine tonsil. Acta Otolaryngol [Suppl] (Stockh) 454:43–47
Oláh I, Everett NB (1975) Surface epithelium of the rabbit palatine tonsil: scanning and transmission electron microscopic study. J Reticuloendothelial Soc 18:53–62
Oláh I, Takács L, Törö I (1988) Formation of lymphoepithelial tissue in the sheep's palatine tonsil. Acta Otolaryngol [Suppl] (Stockh) 454:7–17
Owen RL, Jones AL (1974) Epithelial cell spezialization within human Peyer's patches: an ultrastructural study of intestinal lymphoid follicles. Gastroenterology 66:189–203
Perry ME, Jones MM, Mustafa Y (1988) Structure of the crypt epithelium in human palatine tonsils. Acta Otolaryngol [Suppl] (Stockh) 454:53–59
Sato Y, Wake K (1990) Lymphocyte traffic between the crypt epithelium and the subepithelial lymphoid tissue in human palatine tonsils. Biomed Res 11:365–372
Sato Y, Wake K, Watanabe I (1990) Differentiation of crypt epithelium in human palatine tonsils: the microenvironment of crypt epithelium as a lymphoepithelial organ. Arch Histol Cytol 53:41–54
Simpson LO (1980) Basement membranes and biological thixotro-phy: a new hypothesis. Pathology 12:377–389
Surján L Jr (1987) Tonsils and lympho-epithelial structures in the pharynx as immuno-barriers. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 103:369–372
Warfel KA, Hull MT (1984) Migration of lymphocytes through the cutaneous basal lamina in normal skin: an ultrastructural study. Anat Rec 208:349–355
Weltzin R, Lucia-Jandris P, Michetti P, Kraehenbuhl JP, Neutra MR (1989) Binding and transepithelial transport of immuno-globulins by intestinal M cells: demonstration using monoclonal IgA antibodies against enteric viral proteins. J Cell Biol 108:1673–1685
Wolf JL, Bye WA (1984) The membranous epithelial (M) cell and the mucosal immune system. Annu Rev Med 35:95–112
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tohya, K., Kimura, M. Ultrastructural study of postnatal development of the tonsillar crypt epithelium of the musk shrew, Suncus murinus . Anat Embryol 186, 335–340 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00185982
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00185982