Abstract
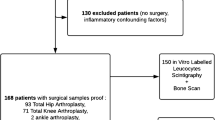
Forty-three patients with suspected infection of a hip or a knee prosthesis were studied with white blood cell scintigraphy (WBC), using technetium-99m (n = 37) or iodine-123 (n = 6) labelled monoclonal mouse antibody (MoAb). Previously, all patients had undergone skeletal scintigraphy, which was performed as a three-phase study in 33 cases. The final diagnosis was established by open surgery, histology and culture in 37 cases, by puncture and culture in 3 cases, and by clinical follow-up of at least 6 months in 3 cases. Eighteen prostheses were infected, 25 uninfected. The delayed phase of skeletal scintigraphy had a sensitivity of 92%, a specificity of 24% and an accuracy of 48% in the detection of infection. The perfusion and blood pool activity of the three-phase bone scan had a sensitivity of 67%, a specificity of 71% and an accuracy of 70%. The diagnostic value of WBC was sensitivity 89%, specificity 84% and accuracy 86%. WBC with 99m-Tc-MoAb is easy to perform and always available. Its diagnostic accuracy is similar to conventional WBC scintigraphy with either indium-111 or technetium-99m.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alazraki PN (1990) Diagnosing prosthetic joint infection. JNM 31:1955–1957
Aliabadi P, Tumeh SS, Weissman BN, McNeil BJ (1989) Cemented total hip prosthesis: radiographic and scintigraphic evaluation. Radiology 173:203–206
Al-Sheikh W, Sfakianakis GN, Mnaymneh W, Hourani M, Heal A, Duncan RC, Burnett A, Ashkar FS, Serafini AN (1985) Subacute and chronic bone infections: diagnosis using In-111, Ga-67 and Tc-99m MDP bone scintigraphy and radiography. Radiology 155:501–506
Andrews HJ, Arden GP, Hart GM, Owen JW (1981) Deep infection after total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 63:53–57
Becker W, Borst U, Fischbach W, Pasurka B, Schäfer R, Börner W (1989a) Kinetic data of in vivo labelled granulocytes in humans with a murine Tc-99m-labelled monoclonal antibody. Eur J Nucl Med 15:361–366
Becker W, Pasurka B, Börner W (1989b) Bedeutung der Leukozytenszintigraphie bei der infizierten Totalendoprothese. Fortschr Röntgenstr 150:284–289
Eftekhar NS (1979) Wound infection complicating total hip joint arthroplasty. Scope of the problem, and its diagnosis. Orthop Rev 8:49
Fink-Bennett D, Stanisavljevic S, Blake D, Weber K, Weir J, Mayne B (1988) Improved accuracy for detecting an infected hip arthroplasty (HA): sequential technetium-99m sulfur colloid (TSC)/indium-111 (In-111) WBC imaging (abstract). J Nucl Med 27:P887
Fitzgerald RH, Nolan DR, Ilstrup DM, Van Scoy RE, Washington JA, Coventry MB (1977) Deep wound sepsis following total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 59:847–855
Gelman MI, Coleman RE, Stevens PM, Davey BW (1978) Radiography, radionuclide imaging and arthrography in the evaluation of total hip and knee replacement. Radiology 138:677–682
Gómez-Luzuriaga M, Galán V, Villar JM (1988) Scintigraphy with Tc, Ga and In in painful total hip prosthesis. Int Orthop 12:163–167
Hunter GA, Welsh RP, Cameron HU, Bailey WH (1979) The results of revision of total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 61:419–421
Johnson JA, Christie NJ, Sandler MP, Parks PF Jr, Homra L, Kaye JJ (1988) Detection of occult infection following total joint arthroplasty using sequential technetium-99m HDP bone scintigraphy and indium-111 WBC imaging. J Nucl Med 29:1347–1353
Joseph K, Höffken H, Bosslet K, Schorlemmer HU (1988) In vivo labelling of granulocytes with Tc-99m anti-NCA monoclonal antibodies for imaging inflammation. Eur J Nucl Med 14:367–373
Jupiter JB, Karchmer AW, Lowell JD, Harris WH (1981) Total hip arthroplasty in the treatment of adult hips with current or quiescent sepsis. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 63:194–200
LaManna MM, Garbarino JL, Berman AT, Brady LW (1983) An assessment of technetium and gallium scanning in the patient with painful total joint arthroplasty. Orthopedics 6: 580–582
Lind P, Langsteger W, Kö1tringer P, Dimai HP, Passl R, Eber O (1990) Immunoscintigraphy of inflammatory processes with a Tc-99m-labelled monoclonal antigranulocyte antibody (MAB BW 259/183). J Nucl Med 31:417–423
Locher JTH, Seybold K, Andres RY, Schubiger PA, Mach JP, Buchegger F (1986) Imaging of inflammatory and infectious lesions after injection of radioiodinated monoclonal antigranulocyte antibodies. Nucl Med Commun 7:659–670
Lovelock JE, Griffith HJ, Silverstein AM, Anson PS (1984) Complications of total knee replacement. AJR 141:985–992
Maderazo EG, Judson S, Pasternak H (1986) Late infections of total joint prostheses. Clin Orthop 229:131–142
Magnuson JE, Brown ML, Hauser MF, Berquist TH, Fitzgerald RH, Klee GG (1988) In-111-labeled leukocyte scintigraphy in suspected orthopedic prosthesis infection: comparison with other imaging modalities. Radiology 168:235–239
Merkel KD, Brown ML, Fitzgerald RH, Dewanjee MK, Hauser MF (1983) Prospective In-111 WBC scan vs Tc 99m-MDP-Ga67 scan for lowgrade osteomyelitis. J Nucl Med 24:P72
Merkel KD, Brown ML, Dewanjee MK, Fitzgerald RH Jr (1985) Comparison of indium-labeled-leukocyte imaging with sequential technetium-gallium scanning in the diagnosis of lowgrade musculoskeletal sepsis. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 67:465–476
Merkel KD, Brown ML, Fitzgerald RH Jr (1986) Sequential technetium-99m HMDP-gallium-67 citrate imaging for the evaluation of infection in the painful prosthesis. J Nucl Med 27:1413–1417
Mulamba L, Ferrant A, Leners N, Nayer P de, Rombouts JJ, Vincent A (1983) Indium-111 leucocyte scanning in the evaluation of painful hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Scand 54:695–697
Oswald SG, Van Nostrand D, Savory CG, Callaghan JJ (1989) Three-phase bone scan and indium white blood cell scintigraphy following porous coated hip arthroplasty: a prospective study of the prosthetic tip. J Nucl Med 30:1321–1331
Oswald SG, Van Nostrand D, Savory CG, Anderson JH, Callaghan JJ (1990) The acetabulum: a prospective study of three-phase bone and indium white blood cell scintigraphy following porous-coated hip arthroplasty. J Nucl Med 31:274–280
Ouzounian TJ, Thompson L, Grogan TJ, Webber MM, Amstutz HC (1987) Evaluation of musculoskeletal sepsis with indium-111 white blood cell imaging. Clin Orthop 221:304–311
Palestro CJ, Kim CK, Swyer AJ, Capozzi JD, Solomon RW, Goldsmith SJ (1990) Total-hip arthroplasty: periprosthetic indium-111-labeled leukocyte activity and complementary technetium-99m-sulfur colloid imaging in suspected infection. J Nucl Med 31:1950–1955
Palestro CJ, Swyer AJ, Kim CK, Goldsmith SJ (1991) Infected knee prosthesis: diagnosis with In-111 leukocyte, Tc-99m sulfur colloid, and Tc-99m MDP imaging. Radiology 179:645–648
Pring DJ, Henderson RG, Keshavarzian A, Rivett AG, Krausz T, Coombs RRH, Lavender JP (1986a) Indium-granulocyte scanning in the painful prosthetic joint. AJR 146:167–172
Pring DJ, Henderson RG, Rivett AG, Krausz T, Coombs RRH, Lavender JP (1986b) Autologous granulocyte scanning of painful prosthetic joints. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 68:647–652
Reuland P, Winker KH, Heuchert T, Ruck P, Müller-Schauenburg W, Weller S, Feine U (1991) Detection of infection in postoperative orthopedic patients with technetium-99m-labeled monoclonal antibodies against granulocytes. J Nucl Med 32:2209–2214
Rosenthall L, Lisbona R, Hernandez M, Hadjipavlou A (1979) 99mTc-PP and 67Ga imaging following insertion of orthopedic devices. Radiology 133:717–721
Rosenthall L, Kloiber R, Damtew B, Al Majid H (1982) Sequential use of radiophosphate and radiogallium imaging in the differential diagnosis of bone, joint and soft tissue infection: quantitative analyses. Diagn Imag 51:249–258
Rosenthall L, Ghazal ME, Brooks CE (1991) Quantitative analysis of radiophosphate uptake in asymptomatic porous-coated hip endoprostheses. J Nucl Med 32:1391–1393
Schauwecker DS, Park HM, Mock BH, Burt RW, Kernick CB, Ruoff AC III, Sinn HJ, Wellman N (1984) Evaluation of complicating osteomyelitis with Tc-99m MDP, In-111 granulocytes, and Ga-67 citrate. J Nucl Med 25:849–853
Schicha H, Perner K, Voth E, Reith HG, Willert G, Emrich D (1986) Zementfreie Implantation von Zweymüller-Endler-Tota-lendoprothesen der Hüfte. Klinische, röntgenologische und szintigraphische Verlaufskontrolle über zwei Jahre. Nucl Med 25:55–60
Schneider R, Soudry M (1985) Radiographic and scintigraphic evaluation of total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 205:108–120
Sciuk J, Brandau W, Vollet B, Stücker R, Erlemann R, Bartenstein P, Peters PE, Schober O (1991) Comparison of technetium-99m polyclonal human immunoglobulin and technetium-99m monoclonal antibodies for imaging chronic osteomyelitis. Eur J Nucl Med 18:401–407
Segarra I, Roca M, Babellas C, Velar L, Ricart Y, Mora I, Puchal R, Martin-Comin J (1991) Granulocyte-specific monoclonal antibody technetium-99m-BW 250/183 and In-111-oxine labelled leukocyte scintigraphy in inflammatory bowel disease. Eur J Nucl Med 18:715–719
Utz JA, Galvin EG, Lull RJ (1982) Natural history of technetium-99m MDP bone scan in asymptomatic total hip prostheses. J Nucl Med 23:28–29
Utz JA, Lull RJ, Galvin EG (1986) Asymptomatic total hip prosthesis: natural history determined using Tc-99m MDP bone scan. Radiology 161:509–512
Weiss PE, Mall JC, Hoffer PB, Murray WR, Rodrigo JJ, Genant HK (1979) 99mTc-methylene diphosphonate bone imaging in the evaluation of total hip prostheses. Radiology 133:727–729
Weissman BN (1983) The radiology of total joint replacement. Orthop Clin North Am 14:171–191
Wellman HN, Schauwecker DS, Capello WN (1988) Evaluation of metallic osseous implants with nuclear medicine. Semin Nucl Med 18:126–136
Williamson BRJ, McLaughlin RE, Wang GJ, Miller CW, Teates D, Bray ST (1979) Radionuclide bone imaging as a means of differentiating loosening and infection in patients with a painful total hip prosthesis. Radiology 133:723–725
Wukich DK, Abreu SH, Callaghan JJ, Van Nostrand D, Savory CG, Eggli DF, Garcia JE, Berrey BH (1987) Diagnosis of infection by preoperative scintigraphy with indium-labeled white blood cells. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 69:1353–1360
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: J. Sciuk
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sciuk, J., Puskás, C., Greitemann, B. et al. White blood cell scintigraphy with monoclonal antibodies in the study of the infected endoprosthesis. Eur J Nucl Med 19, 497–502 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00185855
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00185855