Abstract
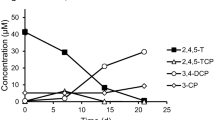
Anaerobic granules developed for the treatment of pentachlorophenol (PCP) completely minearilized14C-labeled PCP to14CH4 and14CO2. Release of chloride ions from PCP was performed by live cells in the granules under anaerobic conditions. No chloride ions were released under aerobic conditions or by autoclaved cells. Addition of sulfate enhanced the initial chloride release rate and accelerated the process of mineralization of14C-labeled PCP. Addition of molybdate (10 mM) inhibited the chloride release rate and severely inhibited PCP mineralization. This suggests involvement of sulfate-reducing bacteria in PCP dechlorination and mineralization. Addition of 2-bromoethane sulfonate slightly decreased the chloride release rate and completely stopped production of14CH4 and14CO2 from [14C]PCP. 2,4,6-trichlorophenol was observed as an intermediate during PCP dechlorination. On the basis of experimental results, dechlorination of 2,4,6-trichlorophanol by the granules was conducted through 2,4-dichlorophenol, 4-chlorophenol or 2-chlorophenol to phenol at pH 7.0–7.2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armenante PM, Kafkewitz D, Jou C-J, Lewandowski G (1993) Effect of pH on the anaerobic dechlorination of chlorophenols in a defined medium. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 39:772–777
Bhatnagar L, Wu W-M, Jain MK, Zeikus JG (1991) Design and function of biomethanation granules for hazardouz waste treatment. In: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Environmental Biotechnology Royal Flemish Society of Engineers, EEC/EERO, Belgium. pp. 1–10
Bryant FO, Hale DD, Rogers JE (1991) Regiospecific dechlorination of pentachlorophenol by dichlorophenol-adapted microorganisms in freshwater anaerobic sediment slurries. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:2293–2301
Gentner BRS, Price WA, Pritchard PH (1989) Anaerobic degradation of chloroaromatic compounds in aquatic sediments under a variety of enrichment conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:1466–1471
Gibson SA, Suflita JM (1986) Extrapolation of biodegradation results of groundwater aquifers: reductive dechlorination of aromatic compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol 52:681–688
Gunsalus RP, Romesser JA, Wolf RS (1978) Preparation of coenzyme M analogues and their activity in the methyl coenzyme M reductase system ofMethanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Biochemistry 17:2374–2377
Häggblom MM, Young LY (1990) Chlorophenol degradation coupled to sulfate reduction. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:3255–3260
Hendriksen HV, Larsen S, Ahring BK (1992) Influence of supplemented carbon source on anaerobic dechlorination of PCP in granular sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:365–370
Kenealy W, Zeikus JG (1981) Influence of corrinoid antagonists on methanogen metabolism. J Bacteriol 146:133–140
Kohring GW, Zhang X, Wiegel J (1989) Anaerobic dechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol in freshwater sediments in the presence of sulfate. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:2735–2737
Madsen T, Aamand J (1992) Anaerobic transformation and toxicity of trichlorophenols in a stable enrichment culture. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:557–561
Mikesell M, Boyd SA (1985) Reductive dechlorination of the pesticides, 2,4-D, 2,4,5-T, and pentachlorophenol in anaerobic sludges. J Environ Qual 14:337–340
Mikesell M, Boyd SA (1986) Complete reductive dechlorination and mineralization of pentachlorophenol by anaerobic microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 52:861–865
Mohn WW, Kennedy KJ (1992) Reductive dehalogenation of chlorophenols byDesulfomanile tiedjei DCB-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:1367–1370
Nicholson DK, Woods SL, Istok JD, Peek DC (1992) Reductive dechlorination of chlorophenols by a pentachlorophenol-acclimated methanogenic consortium. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2280–2286
Smith RL, Klung MJ (1981) Electron donors utilized by sulfate-reducing bacteria in entrophic lake sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 42:116–121
Smith PK, Krohn RI, Hermanson GT, Mallia AK, Gartner FH, Provenzano MD, Fujimoto EK, Goeke NM, Olson BJ, Klenk DC (1985) Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem 150:76–85
Taylor BF, Oremland RS (1979) Depletion of adenosine triphosphate inDesulfovibro by oxyanions of group VI elements. Curr Microbiol 3:101–103
Wolin EA, Wolin MRI, Wolfe RS (1963) Formation of methane by bacterial extracts. J Biol Chem 238:2882–2886
Woods SL, Ferguson JF, Benjamin MM (1989) Characterization of chlorophenol and chloromethoxybenzene degradation during anaerobic treatment. Environ Sci Technol 23:62–68
Wu W-M, Hickey RF, Bhatnager L, Jain MK, Zeikus JG (1989) Fatty acid degradation as a tool to monitor anaerobic sludge activity and toxicity. In: Proc 44th Purdue University Industrial Waste Conference, Lewis Publishers, Chelsea, Michigan, pp 225–233
Wu W-M, Hickey RF, Zeikus JG (1991) Characterization of metabolic performance of methanogenic granules treating brewery wastewater: role of sulfate-reducing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:3438–3449
Wu W-M, Bhatnagar L, Zeikus JG (1993) Performance of anaerobic granules for degradation of pentachlorophenol. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:389–397
Zhang X, Wiegel J (1990) Sequential anaerobic degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol in freshwater sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:1119–1127
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to the memory of Dr. L. Bhatnagar, who died before the manuscript was completed
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kennes, C., Wu, W.M., Bhatnagar, L. et al. Anaerobic dechlorination and mineralization of pentachlorophenol and 2,4,6-trichlorophenol by methanogenic pentachlorophenol-degrading granules. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 44, 801–806 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00178622
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00178622