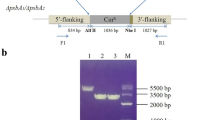
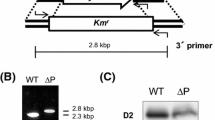
Abstract
Photoinhibition of photosystem II in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis 6803 was followed after site-specific mutagenesis of the D1 polypeptide. Mutations were created in the stromal/cytosolic loop connecting helices D and E. Two mutations E243K and CA1, a deletion of the three glutamates 242–244 and a substitution Q241H, were made in the putative cleavage area of the D1 polypeptide. A third mutation E229D was made in the PEST-like sequence. Mutants and control cells were illuminated and FV/FM was recorded. Compared to the control, the mutants were less photoinhibited. Fluorescence relaxation after a single flash was delayed in CA1. Restoration of FV/FM after photoinhibition in the mutants was totally dependent on protein synthesis while control cells were able to recover partially also when protein synthesis was inhibited. In addition, the protein synthesis-dependent recovery of CA1 was slowed down. Our results indicate a correlation between the mutated amino acids and photoinhibition of photosystem II.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aro E-M, Hundal T, Carlberg I, Andersson B: In vitro studies on light-induced inhibition of Photosystem II and D1-protein degradation at low temperatures. Biochim Biophys Acta 1019: 269–275 (1990).
Barber J, Andersson B: Too much of a good thing: light can be bad for photosynthesis. Trends Biochem Sci 17: 61–66 (1992).
Casanova JL, Pannetier C, Jaulin C, Kourilsky P: Optimal conditions for directly sequencing double-stranded PCR products with Sequenase. Nucl Acids Res 18: 4028 (1990).
Davis LG, Dibner MD, Battley JF: Basic methods in molecular biology. New York, NY: Elsevier Science Publishers (1986).
De Las Rivas J, Andersson B, Barber J: Two sites of primary degradation of the D1-protein induced by acceptor or donor side photoinhibition in photosystem II core complexes. FEBS Lett 301: 246–252 (1992).
Erickson JM, Pfister K, Rahire M, Togasaki RK, Mets L, Rochaix J-D: Molecular and biophysical analysis of herbicide-resistant mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: Structure-function relationship of the photosystem II D1 polypeptide. The Plant Cell 1: 361–371 (1989).
Giersch C, Krause GH: A simple model relating photoinhibitory fluorescence quenching in chloroplasts to a population of altered Photosystem II reaction centers. Photosynth Res 30: 115–121 (1991).
Gong H, Ohad I. The PQ/PQH2 ratio and occupancy of photosystem II-QB site by plastoquinone control the degradation of D1 protein during photoinhibition in vivo. J Biol Chem 266: 21293–21299 (1991).
Govindjee: Photosystem II heterogeneity: the acceptor side. Photosynth Res 25: 151–160 (1990).
Greenberg BM, Gaba V, Mattoo AK, Edelman M: Identification of a primary in vivo degradation product of the rapidly-turning-over 32 kd protein of photosystem II. EMBO J: 2865–2869 (1987).
Haag E, Gleiter HM, Renger G: Effects of photoinhibition on the PS II acceptor side including the endogenous high spin Fe2+ in thylakoids, PS II membrane fragments and PS II core complexes. Photosynth Res 31: 113–126 (1992).
Hundal T, Aro E-M, Carlberg I, Andersson B: Restoration of light-induced photosystem II inhibition without de novo protein synthesis. FEBS Lett 267: 203–206 (1990).
Jansson C, Debus RJ, Osiewacz HD, Gurevitz M, McIntosh L: Construction of an oblicate photoheterotrophic mutant of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis 6803. Inactivation of the psbA gene family. Plant Physiol 85: 1021–1025 (1987).
Kallio T, Aro E-M, Jansson C, Mäenpää P: Light-dependent turnover rate of the D1 polypeptide in new sitespecific Synechocystis PCC 6803 mutants. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Congress on Photosynthesis (in press).
Kirilovsky DL, Ajlani G, Picaud M, Etienne A-L: Mutations responsible for high light sensitivity in an atrazineresistant mutant of Synechocystis 6714. Plant Mol Biol 13: 355–363 (1989).
Kirilovsky DL, Ducruet J-M, Etienne A-L: Primary events occurring in photoinhibition in Synechocystis 6714 wild-type and an atrazine-resistant mutant. Biochim Biophys Acta 1020: 87–93 (1990).
Krause GH, Weis E: Chlorophyll fluorescence and photosynthesis: the basics. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 42: 313–349 (1991).
Krupa Z, Öquist G, Gustafsson P: Photoinhibition and recovery of photosynthesis in psbA gene-inactivated strains of cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans. Plant Physiol 93: 1–6 (1990).
Kunkel TA, Roberts JD, Zakour RA: Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Meth Enzymol 154: 367–382 (1987).
Kyle DJ, Ohad I, Arntzen CJ: Membrane protein damage and repair: selective loss of a quinone-protein function in chloroplast membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 4070–4074 (1984).
Mackinney G: Absorption of light by chlorophyll solutions. J Biol Chem 140: 315–322 (1941).
Mattoo AK, Marder JB, Edelman M: Dynamics of the photosystem II reaction center. Cell 56: 241–246 (1989).
Michel H, Deisenhofer J: X-ray diffraction studies on a crystalline bacterial photosynthetic reaction center: a progress report and conclusions on the structure of photosystem II reaction center. In: Staehelin LA, Arntzen CJ (eds) Encyclopedia of Plant Physiology, vol 19, pp. 371–381. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (1986).
Miller AG, Sepie GS, Canvin DT: The effects of inorganic carbon and oxygen on fluorescence in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus UTEX 625. Can J Bot 69: 1151–1160 (1991).
Mohamed A, Eriksson J, Osiewacz HD, Jansson C: Differential expression of the psbA genes in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis 6803. Mol Gen Genet (in press).
Mohamed A, Jansson C: Influence of light on accumulation of photosynthesis-specific transcripts in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis 6803. Plant Mol Biol 13: 693–700 (1989).
Ohad I, Koike H, Shochat S, Inoue Y: Changes in the properties of reaction center II during the initial stages of photoinhibition as revealed by thermoluminescence measurements. Biochim Biophys Acta 933: 288–298 (1988).
Ohad N, Amir-Shapira D, Koike H, Inoue Y, Ohad I, Hirschberg J: Amino acid substitutions in the D1 protein of photosystem II affect QB- stabilization and accelerate turnover of D1. Z Naturforsch 45c: 402–408 (1990).
Prasil O, Adir N, Ohad I: Dynamics of photosystem II: mechanism of photoinhibition and recovery processes. In: Barber J (ed) The Photosystems: Structure, Function and Molecular Biology. Topics in Photosynthesis, vol 11, pp. 295–348. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1992).
Prentki P, Kirsch HM: In vitro insertional mutagenesis with a selectable DNA fragment. Gene 29: 303–313 (1984).
Rogers S, Wells R, Rechsteiner M: Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis. Science 234: 364–368 (1986).
Salter AH, Virgin I, Hagman Å, Andersson B: On the molecular mechanism of light-induced D1 protein degradation in photosystem II core particles. Biochemistry 31: 3990–3998 (1992).
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1989).
Samuelsson G, Lönneborg A, Rosenqvist E, Gustafsson P, Öquist G. Photoinhibition and reactivation of photosynthesis in the cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans. Plant Physiol 79: 992–995 (1985).
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR: DNA sequencing with chain-termination inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 5463–5468 (1977).
Shipton CA, Marder JB, Barber J: Determination of catabolism of the photosystem II D1 subunit by structural motifs in the polypeptide sequence. Z Naturforsch 45c: 388–394 (1990).
Shipton CA, Barber J: Photoinduced degradation of the D1 polypeptide in isolated reaction centers of photosystem II: Evidence for an autoproteolytic process triggered by the oxidizing side of the photosystem. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 6691–6695 (1991).
Shochat S, Adir N, Gal A, Inoue Y, Mets L, Ohad I: Photoinactivation of photosystem II and degradation of the D1 protein are reduced in a cytochrome b6/f-less mutant of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Z Naturforsch 45c: 395–401 (1990).
Svensson B, Vass I, Cedergren E, Styring S: Structure of donor side components in photosystem II predicted by computer modelling. EMBO J 9: 2051–2059 (1990).
Svensson B, Vass I, Styring S: Sequence analysis of the D1 and D2 reaction center proteins of photosystem II. Z Naturforsch 46c: 765–776 (1991).
Trebst A: The topology of plastoquinone and herbicide binding peptides of photosystem II in the thylakoid membrane. Z Naturforsch 41c: 240–245 (1986).
Trebst A: A contact site between the two reaction center polypeptides of photosystem II is involved in photoinhibition. Z Naturforsch 46c: 557–562 (1991).
Trebst A, Depka B: Degradation of the D-1 protein subunit of photosystem II in isolated thylakoids by UV light. Z Naturforsch 45c: 765–771 (1990).
Trebst A, Depka B, Kipper M: The topology of the reaction center polypeptides of photosystem II. In: Baltscheffsky M (ed) Current Research in Photosynthesis, pp. 217–222. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (1990).
Trebst A, Draber W: Inhibitors of photosystem II and the topology of the herbicide and QB binding polypeptide in the thylakoid membrane. Photosynth Res 10: 381–382 (1986).
Tyystjärvi E, Karunen J: A microcomputer program and fast analog to digital converter and for the analysis of fluorescence induction transients. Photosynth Res 26: 127–132 (1990).
van der Bolt F, Vermaas W: Photoinactivation of Photosystem II as studied with site-directed mutants of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC6803. Biochim Biophys Acta 1098: 247–254 (1992).
Vass I, Styring S, Hundal T, Koivuniemi A, Aro E-M, Andersson B: Reversible and irreversible intermediates during photoinhibition of photosystem II: Stable reduced QA species promote chlorophyll triplet formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 1408–1412 (1992).
Virgin I, Ghanotakis DF, Andersson B: Light-induced D1-protein degradation in isolated photosystem II core complexes. FEBS Lett 269: 45–48 (1990).
Williams JGK: Construction of specific mutations in Photosystem II photosynthetic reaction center by genetic engineering methods in Synechocystis 6803. Meth Enzymol 167: 766–778 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mäenpää, P., Kallio, T., Mulo, P. et al. Site-specific mutations in the D1 polypeptide affect the susceptibility of Synechocystis 6803 cells to photoinhibition. Plant Mol Biol 22, 1–12 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00038991
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00038991