Abstract
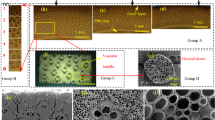
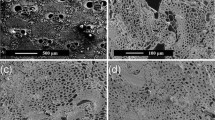
Dendrocalamus farinosus and Phyllostachys heterocycla bamboo logs were subjected to a novel treatment process for the preparation of bamboo fiber mats (BFMs), and the obtained BFM were used to fabricate bamboo fiber reinforced composite (BFRC). We studied the mechanical properties of the BFRCs manufactured from the mats with and without bamboo nodes. The presence of nodes in BFM greatly reduced tensile strength, compressive strength, modulus of elasticity, and modulus of rupture of the BFRCs, while the BFRCs fabricated from BFMs with nodes possessed higher horizontal shear strength. Therefore, the nodes in bamboo culms were an important factor in the uniform distribution of mechanical properties, and BFMs should be homogeneously arranged to reduce the impact of nodes on the mechanical strengths of BFRCs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahari SA, Ahmad M (2009) Effects of culm height levels and node presence on mechanical properties and fracture modes of Gigantochloa scortechinii strips loaded in shear parallel to grain. J Am Bamboo Soc 22(1):41–44
Chen FM, Jiang ZH, Deng JC, Wang G, Zhang D, Zhao QC, Cai LP, Shi SQ (2014) Evaluation of the uniformity of density and mechanical properties of bamboo-bundle laminated veneer lumber (BLVL). Bioresources 9(1):554–565
Hisham HN, Othman S, Rokiah H, Latif MA, Ani S, Tamizi MM (2006) Characterization of bamboo Gigantochloa scortechinii at different ages. J Trop For Sci 18(4):236–242
Shao ZP (2004) Mechanical behavior of bamboo with large deformation: the characteristics of microcosmic deformation. China Wood Ind 18(1):27–28
Yu YL, Huang XN, Yu WJ (2014) A novel process to improve yield and mechanical performance of bamboo fiber reinforced composite via mechanical treatments. Compos Part B 56:48–53
Zhang YM, Yu YL, Yu WJ (2013) Effect of thermal treatment on the physical and mechanical properties of Phyllostachys pubescen bamboo. Eur J Wood Wood Prod 71:61–67
Acknowledgments
The project was supported by “Key Laboratory of Wood Industry and Furniture Engineering of Sichuan Provincial Colleges and Universities” and the National Forestry Public Welfare Scientific Research Program (201304503). The Science and Technology Innovation Foundation for College Students was also greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project funding: This work was financially supported by the Key Laboratory of Wood Industry and Furniture Engineering of Sichuan Provincial Colleges and Universities, the National Forestry Public Welfare Scientific Research Program (201304503), and the Science and Technology Innovation Foundation for College Students.
The online version is available at http://www.springerlink.com.
Corresponding editor: Yu Lei.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, J., Xie, J., Yu, W. et al. Effects of characteristic inhomogeneity of bamboo culm nodes on mechanical properties of bamboo fiber reinforced composite. J. For. Res. 26, 1057–1060 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-015-0106-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-015-0106-0