Abstract
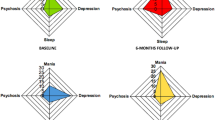
The symptom dimensions of childhood-onset schizophrenia (COS) are described by focussing on the clinical features of 44 patients at onset of illness during the first episode and at follow-up investigation 42 years after onset. All subjects were re-diagnosed according to DSM IV. The symptomatology was evaluated with the Positive and Negative Symptom Scale (PANSS) at onset and at follow-up. Two principal component factor analyses with varimax-rotation were applied to the complete items set of the PANSS. The frequencies of positive, negative, and global symptoms were compared longitudinally in an ANOVA-repeated measures design. The factor analysis revealed 5 orthogonal symptom dimensions (factors) at onset of psychosis: Cognition, social withdrawal, antisocial behaviour, excitement, and reality distortion. At follow-up a five-factor solution was found, too, but different dimensions emerged: a positive, negative, excitement, cognitive, and anxiety/depression component which fits to the 5-factor model of White et al. (1997). The first psychotic episode of EOS is accompanied with more unspecific symptoms such as social withdrawal and antisocial behavior. In the later stages of (COS) the structure of symptom dimensions changes to that known from adult-onset schizophrenia (AOS). The results indicate that COS and AOS are comparable nosological entities and that more than 3 dimensions are required to describe the relevant clinical symptom structure. Positive and global symptoms decreased significantly during the course of illness. The frequencies of negative symptoms did not change which demonstrates their disabling impact.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach TM, Conners KC, Quay HC, Verhulst FC, Howell CT (1989) Replication of empirically derived syndromes as a basis for taxonomy of child/adolescent psychopathology. J Abn Child Psychol 17: 299–336
Andreasen NC, Flaum M, Schultz S, Duzyurek S, Miller D (1997) Diagnosis, methodology and subtypes of schizophrenia. Neuropsychobiol 35: 61–63
Andreasen NC, Grove WM (1986) Evaluation of positive and negative symptoms in schizophrenia. Psychiatr Psychobiol 1: 108–121
Arndt S, Allinger R, Andreasen NC (1991) The distinction of positive and negative symptoms: the failure of a two-dimensional model. Br J Psychiatry 158: 317–321
Arndt S, Andreasen NC, Flaum M, Miller D, Nopoulos P (1995) A longitudinal study of symptom dimensions in schizophrenia: Prediction and patterns of change. Arch Gen Psychiatry 52: 352–360
Asarnow JR (1994) Childhood-onset schizophrenia. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 35: 1345–1371
Asarnow JR, Thompson MC, Goldstein MJ (1994) Childhood-onset schizophrenia: A follow-up study. Schizophr Bull 20: 599–617
Bell MD, Lysacker PH, Beam-Goulet JL, Milstein RM, Lindenmayer JP (1993) Five-component model of schizophrenia: Assessing the factorial invariance of the positive and negative syndrome scale. Psychiatry Res 52: 295–303
Berner P (1997) Conceptualization of schizophrenia: The symptom-orientated approach. Psychopathology 30: 251–256
Cuesta M, Peralta V (1995) Psychopathological dimensions in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 21: 473–482
Czobor P, Volavka J (1996) Positive and negative symptoms: Is their change related? Schizophr Bull 22: 577–590
van der Does AJW, Linszen DH, Dingemans PM (1993) A dimensional and categorical approach to the symptomatology of recent-onset schizophrenia. J Nerv Men Dis 181: 744–749
van der Does AJW, Dingemans P, Linszen DH, Nugter AM, Scholte WF (1995) Dimensions and subtypes of recent onset schizophrenia: A longitudinal analysis. J Nerv Men Dis 183: 681–687
Dollfus S, Brazo P (1997) Clinical heterogeneity of schizophrenia. Psychopathology 30: 275–287
Dollfus S, Petit M (1995) Stability of positive and negative symptoms in schizophrenic patients: A 3-year follow-up study. Eur Psychiatry 10: 228–236
Eaton WW, Thara R, Federman B, Melton B, Liang KY (1995) Structure and course of positive and negative symptoms in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 52: 127–134
Eggers C (1973) Verlaufsweisen kindlicher und präpubertaler Schizophrenien. Monographien aus dem Gesamtgebiete der Psychiatrie, Bd 9 Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York
Eggers C (1978) Course and prognosis in childhood schizophrenia. J Autism Childhood Schizophrenia 8: 21–36
Eggers C, Bunk D (1997) The long-term course of childhood-onset schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 23: 105–117
Eggers C, Bunk D, Krause D (1998) The long-term course of early-onset schizophrenia. Neurology, Psychiatry and Brain Research 6: 29–36
Green WH, Padron-Gayol M, Hardesty AS, Bassiri M (1992) Schizophrenia with childhood onset: A phenomenological study of 38 cases. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 31: 968–976
Grube BS, Bilder RM, Goldman RS (1998) Meta-analysis of symptom factors in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 31: 113–120
Häfner H, Novotny B (1995) Epidemiology of early-onset schizophrenia. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 245: 80–92
Häfner H, Riecher-Rössler A, Hambrecht M (1992) IRAOS: an instrument for the assessment of the onset and early course of schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 6: 209–223
Jacobsen LK, Rapoport JL (1998) Research update: Childhood-onset schizophrenia: Implications of clinical and neurobiological research. J Child Psychol Psychiat 1: 101–113
Kawasaki Y, Maeda Y, Sakai N, Higashima M, Urata K, Yamaguchi N, Kurachi M (1994) Evaluation and interpretation of symptom structure in patients with schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand 89: 399–404
Kay SR, Opler LA, Fiszbein A (1986) Positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) Department of Psychiatry, Albert Einstein College of Medicine-Montefiori Medical Center and Schizophrenia Research Unit New York
Kay SR, Sevy S (1990) Pyramidical model of schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 16: 537–545
Klosterkötter J (1998) Zur definitorischen Neufassung der schizophrenen Störungen in ICD10 und DSM-IV. Fortschr Neurol Psychiat 66: 133–143
Kulhara P, Chandiramani K (1990) Positive and negative subtypes of schizophrenia: A follow-up study from India. Schizophr Res 3: 107–116
Kulhara P, Kota SK, Joseph S (1986) Positive and negative subtypes of schizophrenia: A study from India. Acta Psychiatr Scand 74: 353–359
Lepine JP, Piron JJ, Chapatot E (1989) Factor analysis of the PANSS in schizophrenia patients. In: Stefanis CN, Soldatos CR, Rabavilas AD (eds) Psychiatry Today: Accomplishments and Promises. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam
Liddle PF (1987) The symptoms of chronic schizophrenia: A re-examination of the positive-negative dichotomy. Br J Psychiatry 151: 145–151
Lindenmayer JP, Bernstein-Hyman R, Grochowski S (1994) Five-factor model of schizophrenia: Initial validation. J Nerv Ment Dis 182: 631–638
Lindenmayer JP, Grochowski S, Bernstein-Hyman R (1995) Five-factor model of schizophrenia: replication across samples. Schizophr Res 14: 229–234
Mason P, Harrison G, Glazebrook C, Medley I, Dalkin T, Croudace T (1995) Characteristics of outcome in schizophrenia at 13 years. Br J Psychiatry 167: 596–603
Maziade M, Gingras N, Rodrigue C, Bouchard S, Cardinal A, Gauthier B, Tremblay G, Côté S, Fournier Ch, Boutin P, Hamel M, Roy M-A, Martinez M, Mérette Ch (1996a) Long-term stability of diagnoses and symptom dimensions in a systematic sample of patients with onset of schizophrenia in childhood and early adolescence I: Nosology, sex and age of onset. Br J Psychiatry 169: 361–370
Maziade M, Bouchard S, Gingras N, Charron L, Cardinal A, Roy M-A, Gauthier B, Tremblay G, Côté S, Fournier Ch, Boutin P, Hamel M, Martinez M, Mérette Ch (1996b) Long-term stability of diagnoses and symptom dimensions in a systematic sample of patients with onset of schizophrenia in childhood and early adolescence II: Positive/negative distinction and childhood predictors of adult outcome. Br J Psychiatry 169: 371–378
Overall JE, Gorham DR (1962) The brief psychiatric rating scale. Psychol Rep 10: 799–812
Peralta V, Cuesta MJ (1994) Psychometric properties of the positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 53: 31–40
Peralta V, Cuesta MJ, DeLeon J (1995) Positive and negative symptoms/syndromes in schizophrenia: reliability and validity of different diagnostic systems. Psychol Med 25: 43–50
Russell AT (1994) The clinical presentation of childhood-onset schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 20: 631–646
Smith D, Mar C, Turoff B (1998) The structure of schizophrenic symptoms: a meta-analytic confirmatory factor analysis. Schizophr Res 31: 57–70
Thibaut F, Petit M (1997) The deficit syndrom of schizophrenia: towards heterogeneity. Psychopathology 30: 257–262
Werry JS (1992) Child and adolescent (early onset) schizophrenia: A review in light of DSM-III-R. J Autism Dev Disord 22: 601–624
Werry JS, McClellan JM, Chard L (1991) Childhood and adolescent schizophrenia, bipolar, and schizoaffective disorders: A clinical and outcome study. J Am Acad Child Adoelsc Psychiatry 30: 457–465
Werry JS, McClellan JM (1992) Predicting outcome in child and adolescent (early onset) schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 31: 147–150
White L, Harvey Ph, Opler L, Lindenmayer JP and the PANSS Study Group (1997) Empirical assessment of the factorial structure of climical symptoms in schizophrenia. Psychopathology 30: 263–274
Wing JK, Cooper JE, Sartorius N (1974) The Description and Classification of Psychiatric Symptoms: An Instruction Manual for the PSE and CATEGO System. Cambridge University Press, London
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The phi-coefficient matrices of PANSS symptomes at onset and at follow-up are available from the first author on request
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bunk, D., Eggers, C. & Klapal, M. Symptom dimensions in the course of childhood-onset schizophrenia. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry 8 (Suppl 1), S29–S35 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00010688
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00010688