Abstract
The adrenal gland is a key component of the stress system in the human body. Multiple direct and paracrine interactions between different cell types and their progenitors take place within the adrenal gland microenvironment. These unique interactions are supported by high vascularization and the adrenal cortex extracellular matrix. Alterations in the adrenal gland microenvironment are known to influence the progression of several pathological conditions, such as obesity and sepsis, and to be influenced by these disorders. For example, it has been suggested that activation of immune-adrenal crosstalk during sepsis induces elevated adrenal glucocorticoid levels, whereas crosstalk between adrenocortical cells and sonic hedgehog responsive stem cells was found to contribute to the increased size of the adrenal cortex during obesity. By contrast to sepsis, where activation of adrenal glucocorticoid production has protective effects, chronic exposure to high levels of glucocorticoids induces adverse effects, typically manifested in patients with Cushing syndrome, such as increased body weight, dyslipidemia, glucose intolerance, and hypertension. Therefore, a better understanding of factors involved in the regulation of the adrenal gland microenvironment is crucial. This review highlights bidirectional interactions occurring between the adrenal gland microenvironment and systemic responses during obesity and sepsis. Furthermore, it presents and discusses recent advancements and challenges in attempts to restore or regenerate adrenal gland function, including the use of oxygenated immune-isolating devices.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nicolaides NC, Kyratzi E, Lamprokostopoulou A, Chrousos GP, Charmandari E, 2015 Stress, the stress system and the role of glucocorticoids. Neuroimmunomodulation 22: 6–19.
Bornstein SR, Briegel J, 2003 A new role for glucocorticoids in septic shock: balancing the immune response. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 167: 485–486.
Chrousos GP, 1995 The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and immune-mediated inflammation. N Engl J Med 332: 1351–1362.
Ensinger H, Geisser W, Brinkmann A, et al, 2002 Metabolic effects of norepinephrine and dobutamine in healthy volunteers. Shock 18: 495–500.
Galon J, Franchimont D, Hiroi N, et al, 2002 Gene profiling reveals unknown enhancing and suppressive actions of glucocorticoids on immune cells. FASEB J 16: 61–71.
Briet M, Schiffrin EL, 2010 Aldosterone: effects on the kidney and cardiovascular system. Nat Rev Nephrol 6: 261–273.
Baudrand R, Vaidya A, 2015 Cortisol dysregulation in obesity-related metabolic disorders. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 22: 143–149.
Baudrand R, Campino C, Carvajal CA, et al, 2014 High sodium intake is associated with increased glucocorticoid production, insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 80: 677–684.
Vreeburg SA, Zitman FG, van Pelt J, et al, 2010 Salivary Cortisol levels in persons with and without different anxiety disorders. Psychosom Med 72: 340–347.
Vreeburg SA, Hoogendijk WJ, van Pelt J, et al, 2009 Major depressive disorder and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity: results from a large cohort study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66: 617–626.
Wu VC, Chang CH, Wang CY, et al, 2017 Risk of fracture in primary aldosteronism: A population-based cohort study. J Bone Miner Res 32: 743–752.
Sowers JR, Whaley-Connell A, Epstein M, 2009 Narrative review: the emerging clinical implications of the role of aldosterone in the metabolic syndrome and resistant hypertension. Ann Intern Med 150: 776–783.
Di Dalmazi DG, Vicennati V, Garelli S, et al, 2014 Cardiovascular events and mortality in patients with adrenal incidentalomas that are either non-secreting or associated with intermediate phenotype or subclinical Cushing’s syndrome: a 15-year retrospective study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2: 396–340.
Bornstein SR, Allolio B, Arlt W, et al, 2016 Diagnosis and treatment of primary adrenal insufficiency: An endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 101: 364–389.
Tyczewska M, Rucinski M, Ziolkowska A, et al, 2014 Enucleation-induced rat adrenal gland regeneration: expression profile of selected genes involved in control of adrenocortical cell proliferation. Int J Endocrinol 2014: 130359.
Engeland WC, Gomez-Sanchez CE, Fitzgerald DA, Rogers LM, Holzwarth MA, 1996 Phenotypic changes and proliferation of adrenocortical cells during adrenal regeneration in rats. Endocr Res 22: 395–400.
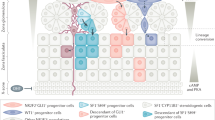
Wood MA, Acharya A, Finco I, et al, 2013 Fetal adrenal capsular cells serve as progenitor cells for steroidogenic and stromal adrenocortical cell lineages in M. musculus. Development 140:4522–4532.
Ehrhart-Bornstein M, Hinson JP, Bornstein SR, Scherbaum WA, Vinson GP, 1998 Intraadrenal interactions in the regulation of adrenocortical steroidogenesis. Endocr Rev 19: 101–143.
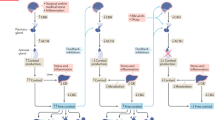
Kanczkowski W, Sue M, Zacharowski K, Reincke M, Bornstein SR, 2015 The role of adrenal gland microenvironment in the HPA axis function and dysfunction during sepsis. Mol Cell Endocrinol 408: 241–248.
Kanczkowski W, Sue M, Bornstein SR, 2016 Adrenal gland microenvironment and its involvement in the regulation of stress-induced hormone secretion during sepsis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 7: 156.
Lerario AM, Finco I, LaPensee C, Hammer GD, 2017 Molecular mechanisms of stem/progenitor cell maintenance in the adrenal cortex. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 8: 52.
Rubin de Celis MF, Garcia-Martin R, Wittig D, et al, 2015 Multipotent glia-like stem cells mediate stress adaptation. Stem Cells 33: 2037–2051.
Santana MM, Chung KF, Vukicevic V, et al, 2012 Isolation, characterization, and differentiation of progenitor cells from human adult adrenal medulla. Stem Cells Transi Med 1: 783–791.
Stavreva DA, Wiench M, John S, Conway-Campbell BL, McKenna MA, Pooley JR, 2009 Ultradian hormone stimulation induces glucocorticoid receptor-mediated pulses of gene transcription. Nat Cell Biol 11: 1093–1102.
Son GH, Chung S, Kim K, 2011 The adrenal peripheral clock: glucocorticoid and the circadian timing system. Front Neuroendocrinol 32: 451–465.
Son GH, Chung S, Choe HK, et al, 2008 Adrenal peripheral clock controls the autonomous circadian rhythm of glucocorticoid by causing rhythmic steroid production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105: 20970–20975.
Chung S, Lee EJ, Cha HK, Kim J, Kim D, Son GH, 2017 Cooperative roles of the suprachiasmatic nucleus central clock and the adrenal clock in controlling circadian glucocorticoid rhythm. Sci Rep 7: 46404.
Elenkov IJ, Wilder RL, Chrousos GP, Vizi ES, 2000 The sympathetic nerve—an integrative interface between two supersystems: the brain and the immune system. Pharmacol Rev 52: 595–638.
Winkler H, Apps DK, Fischer-Colbrie R, 1986 The molecular function of adrenal chromaffin granules: established facts and unresolved topics. Neuroscience 18: 261–290.
Wurtman RJ, 2002 Stress and the adrenocortical control of epinephrine synthesis. Metabolism 51: 11–14.
Yoshida-Hiroi M, Bradbury MJ, Eisenhofer G, et al, 2002 Chromaffin cell function and structure is impaired in corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor type 1-null mice. Mol Psychiatry 7: 967–974.
Gut P, Huber K, Lohr J, et al, 2005 Lack of an adrenal cortex in Sf1 mutant mice is compatible with the generation and differentiation of chromaffin cells. Development 132: 4611–4619.
Finotto S, Krieglstein K, Schober A, et al, 1999 Analysis of mice carrying targeted mutations of the glucocorticoid receptor gene argues against an essential role of glucocorticoid signalling for generating adrenal chromaffin cells. Development 126: 2935–2944.
Green-Golan L, Yates C, Drinkard B, et al, 2007 Patients with classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia have decreased epinephrine reserve and defective glycemic control during prolonged moderate-intensity exercise. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92: 3019–3024.
Charmandari E, Eisenhofer G, Mehlinger SL, et al, 2002 Adrenomedullary function may predict phenotype and genotype in classic 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87: 3031–3037.
Bornstein SR, Breidert M, Ehrhart-Bornstein M, Kloos B, Scherbaum WA, 1995 Plasma catecholamines in patients with Addison’s disease. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 42: 215–218.
Haidan A, Bornstein SR, Glasow A, Uhlmann K, Lubke C, Ehrhart-Bornstein M, 1998 Basal steroidogenic activity of adrenocortical cells is increased 10-fold by coculture with chromaffin cells. Endocrinology 139: 772–780.
Guse-Behling H, Ehrhart-Bornstein M, Bornstein SR, et al, 1992 Regulation of adrenal steroidogenesis by adrenaline: expression of cytochrome P450 genes. J Endocrinol 135: 229–237.
Bornstein SR, Tian H, Haidan A, et al, 2000 Deletion of tyrosine hydroxylase gene reveals functional interdependence of adrenocortical and chromaffin cell system in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97: 14742–14747.
Kigata T, Shibata H, 2017 Anatomical variations of the arterial supply to the adrenal gland in the rat. J Vet Med Sci 79: 238–243.
Ansurudeen I, Willenberg HS, Kopprasch S, Krug AW, Ehrhart-Bornstein M, Bornstein SR, 2009 Endothelial factors mediate aldosterone release via PKA-independent pathways. Mol Cell Endocrinol 300: 66–70.
Rosolowsky LJ, Campbell WB, 1994 Endothelial cells stimulate aldosterone release from bovine adrenal zona glomerulosa cells. Am J Physiol 266: E107–E117.
Schwafertz C, Schinner S, Kuhn MC, et al, 2017 Endothelial cells regulate beta-catenin activity in adrenocortical cells via secretion of basic fibroblast growth factor. Mol Cell Endocrinol 441: 108–115.
Kanczkowski W, Chatzigeorgiou A, Grossklaus S, Sprott D, Bornstein SR, Chavakis T, 2013 Role of the endothelial-derived endogenous anti-inflammatory factor Del-1 in inflammation-mediated adrenal gland dysfunction. Endocrinology 154: 1181–1189.
Bornstein SR, Ziegler CG, Krug AW, et al, 2006 The role of toll-like receptors in the immune-adrenal crosstalk. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1088: 307–318.
Schober A, Huber K, Fey J, Unsicker K, 1998 Distinct populations of macrophages in the adult rat adrenal gland: a subpopulation with neurotrophin-4-like immunoreactivity. Cell Tissue Res 291: 365–373.
Gonzalez-Hernandez JA, Bornstein SR, Ehrhart-Bornstein M, Geschwend JE, Adler G, Scherbaum WA, 1994 Macrophages within the human adrenal gland. Cell Tissue Res 278: 201–205.
Naccache A, Louiset E, Duparc C, et al, 2016 Temporal and spatial distribution of mast cells and steroidogenic enzymes in the human fetal adrenal. Mol Cell Endocrinol 434: 69–80.
Wolkersdorfer GW, Lohmann T, Marx C, et al, 1999 Lymphocytes stimulate dehydroepiandrosterone production through direct cellular contact with adrenal zona reticularis cells: a novel mechanism of immune-endocrine interaction. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84: 4220–4227.
Bornstein SR, Rutkowski H, Vrezas I, 2004 Cytokines and steroidogenesis. Mol Cell Endocrinol 215: 135–141.
Gonzalez-Hernandez JA, Bornstein SR, Ehrhart-Bornstein M, et al, 1995 IL-1 is expressed in human adrenal gland in vivo. Possible role in a local immune-adrenal axis. Clin Exp Immunol 99: 137–141.
Path G, Bornstein SR, Spath-Schwalbe E, Scherbaum WA, 1996 Direct effects of interleukin-6 on human adrenal cells. Endoer Res 22: 867–873.
Bancos I, Hazeldine J, Chortis V, et al, 2017 Primary adrenal insufficiency is associated with impaired natural killer cell function: a potential link to increased mortality. Eur J Endocrinol 176: 471–480.
Arens C, Bajwa SA, Koch C, et al, 2016 Sepsis-induced long-term immune paralysis—results of a descriptive, explorative study. Crit Care 20: 93.
Elenkov IJ, Chrousos GP, 1999 Stress hormones, Th1/Th2 patterns, pro/anti-inflammatory cytokines and susceptibility to disease. Trends Endocrinol Metab 10: 359–368.
Margaryan S, Hyusyan A, Martirosyan A, Sargsian S, Manukyan G, 2017 Differential modulation of innate immune response by epinephrine and estradiol. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig 30: [Epub ahead of print].
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, et al, 2016 The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3). JAMA 315: 801–810.
Chan CM, Mitchell AL, Shorr AF, 2012 Etomidate is associated with mortality and adrenal insufficiency in sepsis: a meta-analysis. Crit Care Med 40: 2945–2953.
McKechnie K, Dean HG, Furman BL, Parratt JR, 1985 Plasma catecholamines during endotoxin infusion in conscious unrestrained rats: effects of adrenal demedullation and/or guanethidine treatment. Circ Shock 17: 85–94.
Boonen E, Bornstein SR, Van den Berghe G, 2015 New insights into the controversy of adrenal function during critical illness. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 3: 805–815.
Boonen E, Vervenne H, Meersseman P, et al, 2013 Reduced Cortisol metabolism during critical illness. N Engl J Med 368: 1477–1488.
Mazzocchi G, Musajo FG, Malendowicz LK, Andreis PG, Nussdorfer GG, 1993 Interleukin-1beta stimulates corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) and adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) release by rat adrenal gland in vitro. Mol Cell Neurosci 4: 267–270.
Lang CH, Bagby GJ, Ferguson JL, Spitzer JJ, 1984 Cardiac output and redistribution of organ blood flow in hypermetabolic sepsis. Am J Physiol 246: R331–R337.
Jung B, Nougaret S, Chanques G, et al, 2011 The absence of adrenal gland enlargement during septic shock predicts mortality: a computed tomography study of 239 patients. Anesthesiology 115: 334–343.
Kanczkowski W, Chatzigeorgiou A, Samus M, et al, 2013 Characterization of the LPS-induced inflammation of the adrenal gland in mice. Mol Cell Endocrinol 371: 228–235.
Jennewein C, Tran N, Kanczkowski W, et al, 2016 Mortality of septic mice strongly correlates with adrenal gland inflammation. Crit Care Med 44: e190–e199.
Bethin KE, Vogt SK, Muglia LJ, 2000 Interleukin-6 is an essential, corticotropin-releasing hormone-independent stimulator of the adrenal axis during immune system activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97: 9317–9322.
Andreis PG, Neri G, Belloni AS, Mazzocchi G, Kasprzak A, Nussdorfer GG, 1991 Interleukin-1 beta enhances corticosterone secretion by acting directly on the rat adrenal gland. Endocrinology 129: 53–57.
Fattori E, Cappelletti M, Costa P, et al, 1994 Defective inflammatory response in interleukin 6-deficient mice. J Exp Med 180: 1243–1250.
Hadid R, Spinedi E, Chautard T, Giacomini M, Gaillard RC, 1999 Role of several mediators of inflammation on the mouse hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis response during acute endotoxemia. Neuroimmunomodulation 6: 336–343.
Lukewich MK, Lomax AE, 2013 Toll-like receptor 4 activation reduces adrenal chromaffin cell excitability through a nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent pathway. Endocrinology 154: 351–362.
Zacharowski K, Zacharowski PA, Koch A, et al, 2006 Toll-like receptor 4 plays a crucial role in the immune-adrenal response to systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103: 6392–6397.
Kanczkowski W, Alexaki VI, Tran N, et al, 2013 Hypothalamo-pituitary and immune-dependent adrenal regulation during systemic inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110: 14801–14806.
Kanczkowski W, Zacharowski K, Wirth MP, Ehrhart-Bornstein M, Bornstein SR, 2009 Differential expression and action of toll-like receptors in human adrenocortical cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 300: 57–65.
Kawai T, Adachi O, Ogawa T, Takeda K, Akira S, 1999 Unresponsiveness of MyD88-deficient mice to endotoxin. Immunity 11: 115–122.
Lukewich MK, Rogers RC, Lomax AE, 2014 Divergent neuroendocrine responses to localized and systemic inflammation. Semin Immunol 26: 402–408.
Gosselin D, Rivest S, 2008 MyD88 signaling in brain endothelial cells is essential for the neuronal activity and glucocorticoid release during systemic inflammation. Mol Psychiatry 13: 480–497.
Breslow MJ, 1992 Regulation of adrenal medullary and cortical blood flow. Am J Physiol 262: H1317–H1330.
Engeland WC, Gann DS, 1989 Splanchnic nerve stimulation modulates steroid secretion in hypophysectomized dogs. Neuroendocrinology 50: 124–131.
Ansurudeen I, Kopf PG, Gauthier KM, Bornstein SR, Cowley AW Jr, Campbell WB, 2014 Aldosterone secretagogues increase adrenal blood flow in male rats. Endocrinology 155: 127–132.
Hinson JP, Vinson GP, Pudney J, Whitehouse BJ, 1989 Adrenal mast cells modulate vascular and secretory responses in the intact adrenal gland of the rat. J Endocrinol 121: 253–260.
Mikhaylova IV, Kuulasmaa T, Jaaskelainen J, Voutilainen R, 2007 Tumor necrosis factor-alpha regulates steroidogenesis, apoptosis, and cell viability in the human adrenocortical cell line NCI-H295R. Endocrinology 148: 386–392.
von Bruhl ML, Stark K, Steinhart A, et al, 2012 Monocytes, neutrophils, and platelets cooperate to initiate and propagate venous thrombosis in mice in vivo. J Exp Med 209: 819–835.
Tominaga T, Fukata J, Naito Y, et al, 1990 Effects of corticostatin-I on rat adrenal cells in vitro. J Endocrinol 125: 287–292.
Boonen E, Langouche L, Janssens T, et al, 2014 Impact of duration of critical illness on the adrenal glands of human intensive care patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 99: 4214–4222.
Flierl MA, Rittirsch D, Chen AJ, et al, 2008 The complement anaphylatoxin C5a induces apoptosis in adrenomedullary cells during experimental sepsis. PLoS One 3: e2560.
GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators, Afshin A, Forouzanfar MH, Reitsma MB, et al, 2017 Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries over 25 years. N Engl J Med 377: 13–27.
Wormser D, Kaptoge S, Di AE, et al, 2011 Separate and combined associations of body-mass index and abdominal adiposity with cardiovascular disease: collaborative analysis of 58 prospective studies. Lancet 377: 1085–1095.
Global BMI MC, Di Angelantonio AE, Bhupathiraju S, Wormser D, et al, 2016 Body-mass index and all-cause mortality: individual-participant-data meta-analysis of 239 prospective studies in four continents. Lancet 388: 776–786.
Pasquali R, Vicennati V, Cacciari M, Pagotto U, 2006 The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity in obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1083: 111–128.
McGinnis R, Walker J, Margules D, Aird F, Redei E, 1992 Dysregulation of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis in male and female, genetically obese (ob/ob) mice. J Neuroendocrinol 4: 765–771.
Muller-Fielitz H, Raasch W, 2013 Angiotensin II impairs glucose utilization in obese Zucker rats by increasing HPA activity via an adrenal-dependent mechanism. Horm Metab Res 45: 173–180.
Naeser P, 1974 Function of the adrenal cortex in obesehyperglycemic mice (gene symbol ob). Diabetologia 10: 449–453.
Hofmann A, Peitzsch M, Brunssen C, et al, 2017 Elevated steroid hormone production in the db/db mouse model of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Horm Metab Res 49: 43–49.
Kruse M, Bornstein SR, Uhlmann K, Paeth G, Scherbaum WA, 1998 Leptin down-regulates the steroid producing system in the adrenal. Endocr Res 24: 587–590.
Bornstein SR, Uhlmann K, Haidan A, Ehrhart-Bornstein M, Scherbaum WA, 1997 Evidence for a novel peripheral action of leptin as a metabolic signal to the adrenal gland: leptin inhibits Cortisol release directly. Diabetes 46: 1235–1238.
Torpy DJ, Bornstein SR, Taylor W, Tauchnitz R, Gordon RD, 1999 Leptin levels are suppressed in primary aldosteronism. Horm Metab Res 31: 533–536.
Ehrhart-Bornstein M, Lamounier-Zepter V, Schraven A, et al, 2003 Human adipocytes secrete mineralocorticoid-releasing factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100: 14211–14216.
Swierczynska MM, Lamounier-Zepter V, Bornstein SR, Eaton S, 2013 Lipoproteins and hedgehog signalling — possible implications for the adrenal gland function. Eur J Clin Invest 43: 1178–1183.
Kraemer FB, 2007 Adrenal cholesterol utilization. Mol Cell Endocrinol 265–266: 42–45.
Sarel I, Widmaier EP, 1995 Stimulation of steroidogenesis in cultured rat adrenocortical cells by unsaturated fatty acids. Am J Physiol 268: R1484–R1490.
Cai L, Ji A, de Beer FC, Tannock LR, van der Westhuyzen DR, 2008 SR-BI protects against endotoxemia in mice through its roles in glucocorticoid production and hepatic clearance. J Clin Invest 118: 364–375.
Saha S, Bornstein SR, Graessler J, Kopprasch S, 2012 Very-low-density lipoprotein mediates transcriptional regulation of aldosterone synthase in human adrenocortical cells through multiple signaling pathways. Cell Tissue Res 348: 71–80.
Tsai YY, Rainey WE, Bollag WB, 2017 Very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL)-induced signals mediating aldosterone production. J Endocrinol 232: R115–R129.
Tsai YY, Rainey WE, Johnson MH, Bollag WB, 2016 VLDL-activated cell signaling pathways that stimulate adrenal cell aldosterone production. Mol Cell Endocrinol 433: 138–146.
Trifan A, Chiriac S, Stanciu C, 2013 Update on adrenal insufficiency in patients with liver cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol 19: 445–456.
Vergeer M, Korporaal SJ, Franssen R, et al, 2011 Genetic variant of the scavenger receptor BI in humans. N Engl J Med 364: 136–145.
Illingworth DR, Lees AM, Lees RS, 1983 Adrenal cortical function in homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Metabolism 32: 1045–1052.
Mina TH, Lahti M, Drake AJ, et al, 2017 Maternal lipids in pregnancy are associated with increased offspring Cortisol reactivity in childhood. Psychoneuroendocrinology 83: 79–83.
Swierczynska MM, Mateska I, Peitzsch M, et al, 2015 Changes in morphology and function of adrenal cortex in mice fed a high-fat diet. Int J Obes (Lond) 39: 321–330.
King P, Paul A, Laufer E, 2009 Shh signaling regulates adrenocortical development and identifies progenitors of steroidogenic lineages. Proc Natl Acad Sei U S A 106: 21185–21190.
Pasquali R, Vicennati V, Cacciari M, Pagotto U, 2006 The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity in obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1083: 111–128.
Wood MA, Acharya A, Finco I, et al, 2013 Fetal adrenal capsular cells serve as progenitor cells for steroidogenic and stromal adrenocortical cell lineages in M. musculus. Development 140: 4522–4532.
Lambert E, Straznicky N, Sari CI, et al, 2013 Dyslipidemia is associated with sympathetic nervous activation and impaired endothelial function in young females. Am J Hypertens 26: 250–256.
Straznicky NE, Grima MT, Sari CI, et al, 2012 Neuroadrenergic dysfunction along the diabetes continuum: a comparative study in obese metabolic syndrome subjects. Diabetes 61: 2506–2516.
Esler M, Straznicky N, Eikelis N, Masuo K, Lambert G, Lambert E, 2006 Mechanisms of sympathetic activation in obesity-related hypertension. Hypertension 48: 787–796.
Bryde AH, Raben A, Astrup A, Christensen NJ, 1994 Plasma adrenaline concentration is lower in post-obese than in never-obese women in the basal state, in response to sham-feeding and after food intake. Clin Sci (Lond) 87: 69–74.
Reimann M, Qin N, Gruber M, et al, 2017 Adrenal medullary dysfunction as a feature of obesity. Int J Obes (Lond) 41: 714–721.
Thomson SP, Stump CS, Kurukulasuriya LR, Sowers JR 2007 Adrenal steroids and the metabolic syndrome. Curr Hypertens Rep 9: 512–519.
Qi D, Rodrigues B, 2007 Glucocorticoids produce whole body insulin resistance with changes in cardiac metabolism. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 292: E654–E667.
Roberge C, Carpentier AC, Langlois MF, et al, 2007 Adrenocortical dysregulation as a major player in insulin resistance and onset of obesity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293: E1465–E1478.
Karatsoreos IN, Bhagat SM, Bowles NP, Weil ZM, Pfaff DW, McEwen BS, 2010 Endocrine and physiological changes in response to chronic corticosterone: a potential model of the metabolic syndrome in mouse. Endocrinology 151: 2117–2127.
Kinlein SA, Shahanoor Z, Romeo RD, Karatsoreos IN, 2017 Chronic corticosterone treatment during adolescence has significant effects on metabolism and skeletal development in male C57BL6/N mice. Endocrinology 158: 2239–2254.
Brandao Neto RA, de Carvalho JF, 2014 Diagnosis and classification of Addison’s disease (autoimmune adrenalitis). Autoimmun Rev 13: 408–411.
El-Maouche D, Arlt W, Merke DP, 2017 Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Lancet [Epub ahead of print].
Speiser PW, Azziz R, Baskin LS, et al, 2010 Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95: 4133–4160.
Mitchell AL, Pearce SH, 2012 Autoimmune addison disease: pathophysiology and genetic complexity. Nat Rev Endocrinol 8: 306–316.
Bornstein SR, 2009 Predisposing factors for adrenal insufficiency. N Engl J Med 360: 2328–2339.
Ruiz-Babot G, Hadjidemetriou I, King PJ, Guasti L, 2015 New directions for the treatment of adrenal insufficiency. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 6: 70.
Grodstein E, Hardy MA, Goldstein MJ, 2010 A case of human intramuscular adrenal gland transplantation as a cure for chronic adrenal insufficiency. Am J Transplant 10: 431–433.
Tajima T, Okada T, Ma XM, Ramsey W, Bornstein S, Aguilera G, 1999 Restoration of adrenal steroidogenesis by adenovirus-mediated transfer of human cytochrome P450 21-hydroxylase into the adrenal gland of 21-hydroxylase-deficient mice. Gene Ther 6: 1898–1903.
Naiki Y, Miyado M, Horikawa R, Katsumata N, Onodera M, Pang S, 2016 Extra-adrenal induction of Cyp21a1 ameliorates systemic steroid metabolism in a mouse model of congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Endocr J 63: 897–904.
Cardoso CC, Bornstein SR, Hornsby PJ, 2010 Optimizing orthotopic cell transplantation in the mouse adrenal gland. Cell Transplant 19: 565–572.
Thomas M, Hawks CL, Hornsby PJ, 2003 Adrenocortical cell transplantation in scid mice: the role of the host animals’ adrenal glands. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 85: 285–290.
Thomas M, Wang X, Hornsby PJ, 2002 Human adrenocortical cell xenotransplantation: model of cotransplantation of human adrenocortical cells and 3T3 cells in scid mice to form vascularized functional tissue and prevent adrenal insufficiency. Xenotransplantation 9: 58–67.
Thomas M, Yang L, Hornsby PJ, 2000 Formation of functional tissue from transplanted adrenocortical cells expressing telomerase reverse transcriptase. Nat Biotechnol 18: 39–42.
Thomas M, Northrup SR, Hornsby PJ, 1997 Adrenocortical tissue formed by transplantation of normal clones of bovine adrenocortical cells in scid mice replaces the essential functions of the animals’ adrenal glands. Nat Med 3: 978–983.
Dunn JC, Chu Y, Qin HH, Zupekan T, 2009 Transplantation of adrenal cortical progenitor cells enriched by Nile red. J Surg Res 156: 317–324.
Zupekan T, Dunn JC 2011 Adrenocortical cell transplantation reverses a murine model of adrenal failure. J Pediatr Surg 46: 1208–1213.
Wei X, Peng G, Zheng S, Wu X, 2012 Differentiation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into steroidogenic cells in comparison to bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Prolif 45: 101–110.
Yazawa T, Kawabe S, Inaoka Y, et al, 2011 Differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and embryonic stem cells into steroidogenic cells using steroidogenic factor-1 and liver receptor homolog-1. Mol Cell Endocrinol 336: 127–132.
Yazawa T, Inanoka Y, Mizutani T, Kuribayashi M, Umezawa A, Miyamoto K, 2009 Liver receptor homolog-1 regulates the transcription of steroidogenic enzymes and induces the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into steroidogenic cells. Endocrinology 150: 3885–3893.
Thomas M, Hornsby PJ, 1999 Transplantation of primary bovine adrenocortical cells into scid mice. Mol Cell Endocrinol 153: 125–136.
Balyura M, Gelfgat E, Ehrhart-Bornstein M, et al, 2015 Transplantation of bovine adrenocortical cells encapsulated in alginate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112: 2527–2532.
Teebken OE, Scheumann GF, 2000 Differentiated corticosteroid production and regeneration after selective transplantation of cultured and noncultured adrenocortical cells in the adrenalectomized rat. Transplantation 70: 836–843.
Walczak EM, Hammer GD, 2015 Regulation of the adrenocortical stem cell niche: implications for disease. Nat Rev Endocrinol 11: 14–28.
Chung KF, Sicard F, Vukicevic V, et al, 2009 Isolation of neural crest derived chromaffin progenitors from adult adrenal medulla. Stem Cells 27: 2602–2613.
Rubin de Celis MF, Bornstein SR, Androutsellis-Theotokis A, et al, 2016 The effects of stress on brain and adrenal stem cells. Mol Psychiatry 21: 590–593.
Allen RA, Seltz LM, Jiang H, et al, 2010 Adrenal extracellular matrix scaffolds support adrenocortical cell proliferation and function in vitro. Tissue Eng Part A 16: 3363–3374.
Chamoux E, Narcy A, Lehoux JG, Gallo-Payet N, 2002 Fibronectin, laminin, and collagen IV as modulators of cell behavior during adrenal gland development in the human fetus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87: 1819–1828.
Chamoux E, Narcy A, Lehoux JG, Gallo-Payet N, 2002 Fibronectin, laminin, and collagen IV interact with ACTH and angiotensin II to dictate specific cell behavior and secretion in human fetal adrenal cells in culture. Endocr Res 28: 637–640.
Ludwig B, Rotem A, Schmid J, et al, 2012 Improvement of islet function in a bioartificial pancreas by enhanced oxygen supply and growth hormone releasing hormone agonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109: 5022–5027.
Schubert U, Schmid J, Lehmann S, et al, 2013 Transplantation of pancreatic islets to adrenal gland is promoted by agonists of growth-hormone-releasing hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110: 2288–2293.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanczkowski, W., Sue, M. & Bornstein, S.R. The adrenal gland microenvironment in health, disease and during regeneration. Hormones 16, 251–265 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03401519
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03401519