Abstract
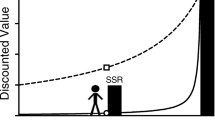
Delay of Gratification (DG) and Delay Discounting (DD) represent two indices of impulsive behavior often treated as though they represent equivalent or the same underlying processes. However, there are key differences between DG and DD procedures, and between certain research findings with each procedure, that suggest they are not equivalent. In the current article, evidence is presented to support the argument that DG and DD measure discrete, yet related, processes involved in delay-related impulsive behavior. Also presented is a theoretical “feedback model” for the relation between DG and DD. In the model, it is proposed that the processes measured by DG are less cognitive and less learning-mediated than those measured by DD. However, as proposed, ability to sustain choices for delayed rewards (DG) is still represented in the choice processes measured by DD through an individual’s learning history with DG types of situations; that is, the less a person is able to sustain choices for delayed rewards the more likely he or she will be to choose immediate rewards when given choices between larger delayed and smaller but more immediate options. The proposed model is consonant with observed consistencies and differences between DG and DD measures. From the proposed model, new research questions arise that would be lost in a continued conceptualization of DG and DD as equivalent measures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ALLEN, T., MOELLER, G., RHOADES, H., & CHEREK, D. (1998). Impulsivity and a history of drug dependence. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 50, 137–145.
ALLPORT, G. W. (1961). Pattern and growth in personality. New York: Holt, Rinehart, & WINSTON.
AYDUK, O., MENDOZA-DENTON, R., MISCHEL, W., DOWNEY, G., PEAKE, P., & RODRIGUEZ, M. (2000). Regulating the interpersonal self: Strategic self-regulation for coping with rejection sensitivity. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 79, 776–792.
BICKEL, W., ODUM, A., & MADDEN, G. (1999). Impulsivity and cigarette smoking: Delay discounting in current, never, and ex-smokers. Psychopharmacology, 146, 447–454.
CARDINAL, R. N., PENNICOTT, D. R., SUGATHAPALA, C. L., ROBBINS, T. W., & EVERITT, B. J. (2001). Impulsive choice induced in rats by lesions of the nucleus accumbens core. Science, 292, 2499–2501.
CHAPMAN, M. (1988). Constructive evolution: Origins and development of Piaget’s thought. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
COFFEY, S. F., GUDLESKI, G. D., SALADIN, M. E., & BRADY, K. T. (2003). Impulsivity and rapid discounting of delayed hypothetical rewards in cocaine-dependent individuals. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology, 11, 18–25.
CREAN, J. P., DE WIT, H., & RICHARDS, J. B. (2000). Reward discounting as a measure of impulsive behavior in a psychiatric outpatient population. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology, 8, 155–162.
EVENDEN, J. L., & RYAN, C. N. (1996). The pharmacology of impulsive behavior in rats: The effects of drugs on response choice with varying delays of reinforcement. Psychopharmacology, 128, 161–170.
GRANT, H., & DWECK, C. S. (1999). A goal analysis of personality and personality coherence. In D. Cervone & Y Shoda (Eds.), The coherence of personality: Social-cognitive basis of consistency, variability, and organization (pp. 345–371). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
GREEN, L., FRY, A., & MYERSON, J. (1994). Discounting of delayed rewards: A life-span comparison. Psychological Science, 5, 33–36.
HINSON, J. M., JAMESON, T. L., & WHITNEY, P. (2003). Impulsive decision making and working memory. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, & Cognition, 29, 298–306
JOHNSON, M. W., & BICKEL, W. (2002). Within-subject comparison of real and hypothetical money rewards in delay discounting. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 77, 129–146.
LUTZ, D. J., & STERNBERG, R. J. (1999). Cognitive development. In M. H. Bornstein & M. E. Lamb (Eds.), Developmental psychology: An advanced textbook (pp. 275–311). New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum.
MADDEN, G., BICKEL, W., & JACOBS, E. A. (1999). Discounting of delayed rewards in opioid-dependent outpatients: Exponential and hyperbolic discounting functions? Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology, 7, 284–293.
MADDEN, G., PETRY, N., BADGER, G., & BICKEL, W. (1997). Impulsive and self-control choices in opioid-dependent patients and non-drug-using control participants: Drug and monetary rewards. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology, 5, 256–262.
MAZUR, J. E. (1987). An adjusting procedure for studying delayed reinforcement. In M. L. Commons, J. E. Mazur, J. A. Nevin, & H. Rachiin (Eds.), Quantitative analysis of behavior: Vol 5. The effects of delay and intervening events on reinforcement value (pp. 55–73). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum
METCALFE, J., & MISCHEL, W. (1999). A hot/cool-system analysis of delay of gratification: Dynamics of willpower. Psychological Review, 106, 3–19.
MISCHEL, H. N., & MISCHEL, W. (1983). The development of children’s knowledge of self-control strategies. Child Development, 54, 603–619.
MISCHEL, W. (1966). Theory and research on antecedents of self-imposed delay of reward. In B. A. Maher (Ed.), Progress in experimental personality research. (Vol. 3). New York: Academic Press.
MISCHEL, W. (1990). Personality dispositions revisited and revisited: A view after three decades. In L. A. Previn (Ed.), Handbook of personality: Theory and research (pp. 111–134). New York, NY: Guilford.
MISCHEL, W., & BAKER, N. (1975). Cognitive appraisals and transformations in delay behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 31, 254–261.
MISCHEL, W, CANTOR, N., & FELDMAN, S. (1996). Principals of self-regulation: The nature of willpower and self-control. In E. T. Higgins & A. Kruglanski (Eds.), Social psychology: Handbook of basic principles (pp. 329–360). New York: Guilford Publications.
MISCHEL, W., & EBBESEN, E. (1970). Attention in delay of gratification. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 16, 329–337.
MISCHEL, W., EBBESEN, E., & ZEISS, A. R. (1972). Cognitive and attentional mechanisms in delay of gratification. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 21, 204–218.
MISCHEL, W., & METZNER, R. (1962). Preference for delayed reward as a function of age, intelligence, and length of delay interval. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 64, 425–431.
MISCHEL, W., & MOORE, B. (1973). Effects of attention to symbolically presented rewards on self control. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 28, 172–179.
MISCHEL, W., SHODA, Y., & PEAKE, P. (1988). The nature of adolescent competencies predicted by preschool delay of gratification. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54, 687–696.
MISCHEL, W., SHODA, Y., & RODRIGUEZ, M. (1989, May 26). Delay of gratification in children. Science, 244, 933–938.
MITCHELL, S. (1999). Measures of impulsivity in cigarette smokers and non-smokers. Psychopharmacology, 146, 455–464.
MOBINI, S., CHIANG, T., HO, M., BRADSHAW, C. M., & SZABADI, E. (2000). Effect of central 5-hydoxytryptamine depletion on inter-temporal choice: A qualitative analysis. Psychopharmacology, 149, 313–318.
ODUM, A. L., & RAINAUD, C. P. (2003). Discounting of delayed hypothetical money, alcohol, and food. Behavioural Processes, 64, 305–313.
ORTNER, C. N. M., MACDONALD, T. K., & OLMSTEAD, M. O. (2003). Alcoholism intoxication reduces impulsivity in the delay-discounting paradigm. Alcohol & Alcoholism, 38, 151–156.
OSTASZEWSKI, P., & KARZEL, K. (2002). Discounting of delayed and probabilistic losses of different amounts. European Psychologist, 7, 295-301.
PEAKE, P., HEBL, M., & MISCHEL, W. (2002). Strategic attention deployment for delay of gratification in working and waiting situations. Developmental Psychology, 38, 313–326.
PEARS, R., & BRYANT, P. (1990). Transitive inferences by young children about spatial position. British Journal of Psychology, 81, 497–510.
PETRY, N., & CASARELLA, T. (1999). Excessive discounting of delayed rewards in substance abusers with gambling problems. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 56, 25–32.
PIAGET, J., & INHELDER, B. (1969). The psychology of the child. London: Routledge & Kegan Paul.
RACHLIN, H. (2000). The science of self-control. Cambridge, Harvard University Press.
REYNOLDS, B., DE WIT, H., & RICHARDS, J. B. (2002). Delay of gratification and delay discounting in rats. Behavioural Processes, 59, 157–168.
REYNOLDS, B., & KARRAKER, K. (2003). A Big Five model of disposition and situation interaction: why a “helpful” person may not always behave helpfully. New Ideas in Psychology, 21, 1–13.
REYNOLDS, B., KARRAKER, K., HORN, K., & RICHARDS, J. B. (2003). Delay and probability discounting as related to different stages of adolescent smoking and non-smoking. Behavioural Processes, 64, 333–344.
REYNOLDS, B., RICHARDS, J. B., HORN, K., & KARRAKER, K. (2004). Delay discounting and probability discounting as related to cigarette smoking status in adults. Behavioural Processes, 65, 35–42.
REYNOLDS, B., & SCHIFFBAUER, R. (2004). Measuring state changes in human delay discounting: An experiential discounting task. Behavioural Processes, 67, 343–356.
REYNOLDS, B., SCHIFFBAUER, R., RICHARDS, J. B., & KARRAKER, K. (2003, May). Development of a task measure of hyperbolic discounting in children: The experiential discounting task-child (Edt-C). Poster presented at the 29th annual Association for Behavior Analysis Convention, San Francisco, Ca.
REYNOLDS, B., SCHIFFBAUER, R., SWENSON, L., & KARRAKER, K. (2001, March). Delay discounting: Testing an adjusting-amount procedure with children. Poster presented at the 47th annual Southeastern Psychological Association Convention, Atlanta, Ga.
RICHARDS, J. B., CHOCK, M. A., & DE WIT, H. (1998). Depletion of serotonin causes impairments in sustained inhibition in rats. Society for Neuroscience Abstracts, 24(1): 11–83.
RICHARDS, J. B., ZHANG, L., MITCHELL, S., & DEWIT, H. (1999). Delay and probibility discounting in a model of impulsive behavior: Effect of alcohol. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 71, 121–143.
RODRIGUEZ, M. L., MISCHEL, W., & SHODA, Y. (1989). Cognitive person variable in delay of gratification of older children at risk. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 57, 358–367
ROGOFF, B. (1990). Apprenticeship in thinking. New York: Oxford University Press.
SCARR, S. (1997). The development of individual differences in intelligence and personality. In H. Reese & M. Franzen (Eds.), Biological and neuropsychological mechanisms: Life-span developmental psychology (pp. 1–22). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
SCHWEITZER, J., & SULZER-AZAROFF, B. (1995). Self-control in boys with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: Effects of added stimulation and time. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 36, 671–686.
SETHI, A., MISCHEL, W., ABER, L., SHODA, Y., & RODRIGUEZ, M. (2000). The role of strategic attention development in development of self-regulation: Predicting preschoolers’ delay of gratification from mother-toddler interactions. Developmental Psychology, 36, 767–777.
SHODA, Y., MISCHEL, W., & PEAKE, P. (1990). Predicting adolescent cognitive and self-regulatory competencies from preschool delay of gratification: Indentifying diagnostic conditions. Developmental Psychology, 26, 978–986.
SKINNER, B. F. (1938). The behavior of organisms. New York: D. Appleton-Century.
SMITH, L. (1982). Class inclusion and conclusions about Piaget’s theory. British Journal of Psychology, 73, 267–276.
VOGAL-SPROTT, M., EASDON, G., FILLMORE, M., FINN, R., & JUSTUS, A. (2001). Alcohol and behavioral control: Cognitive and neural mechanisms. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 25, 117–121.
VUCHINICH, R., & SIMPSON, C. (1998). Hyperbolic temporal discounting in social drinkers and problem drinkers. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacoloty, 6, 292–305.
WADE, T. R., DE WIT, H., & RICHARDS, J. B. (2000). Effects of dopaminergic drugs on delayed reward as a measure of impulsive behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology, 150, 90–101.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reynolds, B., Schiffbauer, R. Delay of Gratification and Delay Discounting: A Unifying Feedback Model of Delay-Related Impulsive Behavior. Psychol Rec 55, 439–460 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03395520
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03395520