Abstract
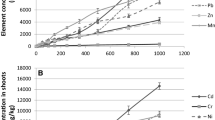
The heavy metal tolerance in corn (Zea mays L.) var. ‘Neelum’ was assessed at germination and seedling growth after having subjected it to different concentrations of CuSO4 and ZnSO4. Germination was not affected by any of the metal tested, whereas initial growth was strongly inhibited by increasing concentrations of ZnSO4. Seedlings developed toxicity symptoms in the presence of both metals but more chlorotic and necrotic regions were observed at varying levels of ZnSO4 than CuSO4. The metal accumulation was concentration dependent. Z. mays seedlings accumulated more copper in roots but greater contents of zinc in their shoots. On the basis of results presented here, it can be concluded that the cultivar of the species tested has shown a marked sensitivity to the presence of small amounts of metals present in the growth medium. The data support the assumption that metal sensitivity is probably due to strong tendency of the species to accumulate them. This justifies that the corn variety ‘Neelum’ is not suitable for the cultivation under situations where water and soil suffer from occasional and/ or transitory metal pollution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barcelo J., Vazquez M. D. and Poschenrieder C., (1998). Structural and ultra-structural disorders in cadmium treated bush bean plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). New Phytol. 108, 37–49.
Becerril J. M., Munoz-Rueda A., Aparicio-Tejo P. and Gonzalez-Murua C., (1988). The effects of cadmium and lead on photosynthetic electron transport in clover and lucerne. New Phytol. 26, 357–363.
Chatterjee J. and Chatterjee C., (2000). Phytotoxicity of cobalt, chromium and copper in cauliflower. Environ. Pollut. 109, 69–74.
Claire L. C., Adriano D. C., Sajwan K. S., Abel S. L., Thomas D. P. and Driver J. T., Effects of selected trace metals on germinating seeds of six plant species. Water, Air and Soil Poll. 59, 231–240.
Ernst W.H.O., Phytotoxicity of heavy metals. in: C. Rodrigues-Barrueco (ed.), Fertilizers and environment. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrechett, The Netherlands. Pages 423–430, 1996.
Fiussello N., (1973). Lead pollution: Effects on chlorophyll. Infor. Bot. 5, 107–108.
Leyval C., Singh V B. R. and Joner E. J., (1995). Occurrence and infectivity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in some Norwegian soils influenced by heavy metals and soil properties. Water, Air Soil Pollut. 84, 201–216.
Lindon F. C. and Henriques F. S., (1992). Copper toxicity in rice: Diagnostic criteria and effect on tissue Mn and Fe. Soil Sci., 154, 130–135.
Mullar D. H., Van Oort F. and Balbane M., (2000). Strategies of heavy metal uptake by three plant species growing near a metal smelter. Environ. Poll. 109, 231–238.
Nishizono H., Kubta K. and Suzuki S., (1989). Accumulation of heavy metals in cell walls of Polygonum cuspidatum roots from metalliferous habitats. Plant. Cell. Physiol., 30, 595–598.
Scherbatskoy T., Klein R. M. and Badger G. J., (1987). Germination responses of forest tree seeds to acidity and metal ions. Environ. Exp. Bot. 27, 157–164.
Sela M, Garty J., and Tel-Or E., (1989). The accumulation and the effect of heavy metals on the water fern Azolla filiculoides. New Phytol. 112, 7–12.
Stefani A., Arduini I. and Onnis A., (1991). Juncus acutus: Germination and initial growth in presence of heavy metals. Ann. Bot. Fenn. 28, 37–43.
Vojtechova M. and Leblova S., (1991). Uptake of lead and cadmium by maize seedlings and the effects of heavy metals on the activity of phosphoenol pyruvate carboxilase isolated from maize. Biol. Plant. 33:386–394.
Walley Y. A., Khan M. R. and Bradshaw A.D., (1974). The potential for evolution of heavy metals tolerance in plants.I. Copper and zinc tolerance in Agrostis tenuis. Heredity, 32: 309–319.
Welbaum G. E., Bradford K. J., Kyu-Ock Y., Booth D. T. and Oluoch M. O., (1998). Biophysical, physiological and biochemical processes regulating seed germination. Soil Sci. Res. 8: 161–172.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmood, S., Hussain, A., Saeed, Z. et al. Germination and seedling growth of corn (Zea mays l.) under varying levels of copper and zinc. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2, 269–274 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03325886
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03325886