Abstract
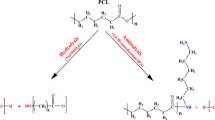
A procedure for the surface hydrolysis of an electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) fibrous scaffold was developed to enhance the adhesion and proliferation of osteoblasts. The surface hydrolysis of fibrous scaffolds was performed using NaOH treatment for the formation of carboxyl groups on the fiber surfaces. The hydrolysis process did not induce deformation of the fibers, and the fibers retained their diameter. The cell seeding density on the NaOH-treated PCL fibrous scaffolds was more pronounced than on the non-treated PCL fibers used as a control. The alkaline phosphatase activity, osteocalcin and a mineralization assay strongly supported that the surface-hydrolyzed PCL fibrous scaffolds provided more favorable environments for the proliferation and functions of osteoblasts compared to the non-treated PCL fibrous scaffolds use as a control.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Luong-Van, L. Grøndahl, K. N. Chua, K. W. Leong, V. Nurcombe, and S. M. Cool,Biomaterials,27, 2042 (2006).
D. S. Katti, K. W. Robinson, F. K. Ko, and C. T. Laurencin,J. Biomed. Mater. Res.,70B, 286 (2004).
K. Kim, Y. K. Luu, C. Chang, D. F. Fang, B. S. Hsiao, B. Chu, and M. Hadjiargyrou,J. Control. Release,98, 47 (2004).
J. Zeng, X. Xu, X. Chen, Q. Liang, X. Bian, L. Yang, and X. Jing,J. Control. Release,92, 227 (2003).
E. Kenawy, G. L. Bowlin, K. Mansfield, J. Layman, D. G. Simpson, E. H. Sanders, and G. E. Wnek,J. Control. Release,81, 57 (2002).
G. Verreck, I. Chun, J. Rosenblatt, J. Peeters, A. V. Dijck, J. Mensch, M. Noppe, and M. E. Brewster,J. Control. Release,92, 349 (2003).
Y. K. Luu, K. Kim, B. S. Hsiao, B. Chu, and M. Hadjiargyrou,J. Control. Release,89, 341 (2003).
W. Cui, X. Li, X. Zhu, G. Yu, S. Zhou, and J. Weng,Biomacromolecules,7, 1623 (2006).
C. L. Casper, N. Yamaguchi, K. L. Kiick, and J. F. Rabolt,Biomacromolecules,6, 1998 (2005).
H. Park, K. Y. Lee, S. J. Lee, K. E. Park, and W. H. Park,Macromol. Res.,15, 238 (2007).
H. Yoshimoto, Y. M. Shina, H. Terai, and J. P. Vacanti,Biomaterials,24, 2077 (2003).
J. Chen, B. Chu, and B. S. Hsiao,J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A,79A, 307 (2006).
M. C. Serrano, M. T. Portolés, M. Vallet-Regä, I. Izquierdo, L. Galletti, J. V. Comas, and R. Pagani,Macromol. Biosci.,5, 415 (2005).
K. H. Lee, H. Y. Kim, M. S. Khil, Y. M. Ra, and D. R. Lee,Polymer,44, 1287 (2003).
Y. Zhu, M. F. Leong, W. F. Ong, M. B. Chan-Park, and K. S. Chian,Biomaterials,28, 861 (2007).
W. J. Li, J. A. Cooper, Jr., R. L. Mauck, and R. S. Tuan,Acta. Biomater.,2, 377 (2006).
G. Ciapetti, L. Ambrosio, L. Savarino, D. Granchi, E. Cenni, N. Baldini, S. Pagani, S. Guizzardi, F. Causa, and A. Giunti,Biomaterials,24, 3815 (2003).
S. E. Kim, H. K. Rha, S. Surendran, C. W. Han, S. C. Lee, H. W. Choi, Y.-W. Choi, K.-H. Lee, J. W. Rhie, and S. T. Ahn,Macromol. Res.,14, 565 (2006).
Z. Cheng and S. H. Teoh,Biomaterials,25, 1991 (2004).
Y. Zhu, C. Gao, and J. Shen,Biomaterials,23, 4889 (2002).
G. E. Parka, M. A. Pattisona, K. Park, and T. J. Webster,Biomaterials,26, 3075 (2005).
J. Gao, L. Niklason, and R. Langer,J. Biomed. Mater. Res.,42, 417 (1998).
H. M. Kowalczynska and J. Kaminski,J. Cell Sci.,99, 587 (1991).
A. Curtis and J. Forrester,J. Cell Sci.,71, 17 (1984).
S. S. Kim, M. S. Park, O. Jeon, C. Y. Choi, and B. S. Kim,Biomaterials,27, 1399 (2006).
K. Y. Lee, E. Alsberg, S. Hsiong, W. Comisar, J. Linderman, R. Ziff, and D. Mooney,Nano. Lett.,4, 1501 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J.S., Kim, JM., Lee, S.J. et al. Surface hydrolysis of fibrous poly(ε-caprolactone) scaffolds for enhanced osteoblast adhesion and proliferation. Macromol. Res. 15, 424–429 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03218809
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03218809