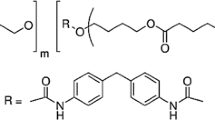
Abstract
The present study describes the isolation of bacteria from soil with the ability to degrade plastic polyurethane (PU). Bacterial strains attached on the polyurethane film, after soil burial for 6 months, were isolated and identified asBacillus sp. AF8,Pseudomonas sp AF9,Micrococcus sp. 10,Arthrobacter sp. AF11, andCorynebacterium sp. AF12. In plate assay, zones of hydrolysis were visualised around the bacterial colonies on mineral salt agar plates containing polyurethane as a sole carbon source. The results of the Sturm test for degradability showed more CO2 production in the test than in control. The production of esterase was detected in the presence of polyurethane as a substrate. The Scanning Electron Microscopy and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy showed certain changes on the surface of PU film and formation of some new intermediate products after polymer breakdown.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akutsu Y., Nakajima-Kambe T., Nomura N., Nakahara T. (1998). Purification and properties of a polyester polyurethane-degrading enzyme fromComamonas acidovorans TB-35. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 64: 62–67.
Allen A., Hilliard N., Howard G.T. (1999). Purification and characterization of a soluble polyurethane degrading enzyme fromComamonas acidovorans. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 43: 37–41.
Augusta J., Muller R.J., Widdecke H. (1993). A rapid evaluation plate-test for the biodegradability of plastics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 39: 673–678.
Barratt S.R., Ennos A.R., Greenhalgh M., Robson G.D., Handley P.S. (2003). Fungi are the predominant micro-organisms responsible for the degradation of soil-buried polyester polyurethane over a range of soil water holding capacities. J. Appl. Microbiol., 94: 1–8.
Bentham R.H., Morton L.G.H., Allen N.G. (1987). Rapid assessment of the microbial deterioration of polyurethanes. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 23: 377–386.
Bouwer E.J. (1992). Bioremediation of organic contaminants in the subsurface. In: Mitchell R., Ed., Environmental Microbiology Wiley-Liss, New York, NY, pp. 287–318.
Cosgrove L., McGeechan P.L., Robson G.D., Handley P.S. (2007). Fungal communities associated with degradation of polyester polyurethane in soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 73: 5817–5824.
Crabbe J.R., Campbell J.R., Thompson L., Walz S.L., Schultz W.W. (1994). Biodegradation of a colloidal ester-based polyurethane by soil fungi. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 33: 103–113.
Eggert T., Pencreac’h G., Douchet I., Verger R., Jaeger K.E. (2000). A novel extracellular esterase fromBacillus subtilis and its conversion to a monoacylglycerol hydrolase. Eur. J. Biochem., 267: 6459–6469.
Filip Z. (1978). Decomposition of Polyurethane in garbage landfill leakage water and by soil microorganisms. Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 5: 225–231.
Gautam R., Bassi A., Yanful E. (2007).Candida rugosa lipasecatalyzed polyurethane degradation in aqueous medium. Biotechnol. Lett., 29: 1081–1086.
Griffin G.J.L. (1980). Synthetic polymers and the living environment. Pur. Appl. Chem., 52: 399–407.
Holt J.G. (1993). Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, 9th edn., The Lippincott Williams and Wilkins Company, Baltimore.
Howard G.T. (2002). Biodegradation of polyurethane: a review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 40: 245–252.
Howard G.T., Blake R.C. (1998). Growth ofPseudomonas fluorescens on a polyester-polyurethane and the purification and characterization of a polyurethanase-protease enzyme. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 42: 213–220.
Howard G.T., Hilliard N.P. (1999). Use of coomassie blue-polyurethane interaction in detection of polyurethanease proteins and polyurethanolytic bacteria. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 43: 23–30.
Howard G.T., Ruiz C., Hilliard N.P. (1999). Growth ofPseudomonas chlororaphis on a polyester-polyurethane and the purification and characterization of a polyurethanase-esterase enzyme. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 43: 7–12.
Kay M.J., Mccabe R.W., Morton L.H.G. (1993). Chemical and physical changes occurring in polyester polyurethane during biodegradation. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 31: 209–225.
Kay M.J., Morton L.H.G., Prince E.L. (1991). Bacterial degradation of polyester polyurethane. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 27: 205–222.
Kim M.N., Lee B.Y., Lee I.M., Lee H.S., Yoon J.S. (2001). Toxicity and biodegradation of products from polyester hydrolysis. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox. Hazard Subst. Environ. Eng., 3: 447–463.
Morton L.H.G., Surman S.B. (1994). Biofilms in biodeterioration — a review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 32: 203–221.
Muller R.J., Augusta J., Pantke M. (1992). An interlaboratory investigation into biodegradation of plastics. Part I: A modified Sturm-test. Mat. Organ., 27: 179–189.
Nakajima-Kambe T., Onuma F., Kimpara N., Nakahara T. (1995). Isolation and characterization of a bacterium which utilizes polyester polyurethane as a sole carbon and energy source. FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 129: 39–42.
Nakajima-Kambe T., Onuma F., Akutsu Y., Nakahara T. (1997). Determination of the polyester polyurethane breakdown products and distribution of the polyurethane degrading enzyme ofComamonas acidovorans strain TB-35. J. Ferment. Bioeng., 83: 456–460.
Nakajima-Kambe T., Shigeno-Akutsu Y., Nomura N., Onuma F., Nakahara T. (1999). Microbial degradation of polyurethane, polyester polyurethanes and polyether polyurethanes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 51: 134–140.
Nishida H., Tokiwa Y. (1993). Distribution of poly(β-hydroxybutyrate) and poly(ε-caprolactone) aerobic degrading microorganisms in different environments. J. Environ. Polym. Degrad., 1: 227–233.
Oceguera-Cervantes A., Carrillo-García A., López N., Bolaños-Nuñez S., Cruz-Gómez M.J., Wacher C., Loza-Tavera H. (2007). Characterization of the polyurethanolytic activity of twoAlicycliphilus sp. strains able to degrade polyurethane and N-methylpyrrolidone. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 73: 6214–6223.
Pathirana R.A., Seal K.J. (1984). Studies on polyurethane deteriorating fungi. Part 2. An examination of their enzyme activities. Int. Biodeterior., 20: 229–235.
Pathirana R.A., Seal K.J. (1985). Studies on polyurethane deteriorating fungi. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 21: 41–49.
Pettit D., Abbott S.G. (1975). Biodeterioration of footwear. In: Gilbert J.R., Lovelock D.W., Eds., Microbial Aspects of the Deterioration of Material. Academic Press, London, New York, San Francisco, pp. 237–253.
Robert C., Norton W.N., Howard G.T. (1998). Adherence and growth of aBacillus species on insoluble polyester polyurethane. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 42: 63–73.
Rowe L., Howard G.T. (2002). Growth ofBacillus subtilis on polyurethane and the purification and characterization of a polyurethanase-lipase enzyme. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 50: 33–40.
Ruiz C., Main T., Hilliard N.P., Howard G.T. (1999). Purification and characterization of two polyurethanase enzymes fromPseudomonas chlororaphis. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 43: 43–47.
Sabev H.A., Barratt S.R., Greenhalgh M., Handley P.S., Robson G.D. (2006a). Biodegradation of manmade polymeric materials. In: Gadd G.M., Ed., Fungi in Geochemical Cycles, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom, pp. 212–235.
Sabev H.A., Handley P.S., Robson G.D. (2006b). Fungal colonization of soil-buried plasticized polyvinyl chloride (pPVC) and the impact of incorporated biocides. Microbiology, 152: 1731–1739.
Santerre J.P., Labow R.S., Duguay D.G., Erfle D., Adams G.A. (1994). Biodegradation evaluation of polyether and polyester-urethanes with oxidative and hydrolytic enzymes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 28: 1187–1199.
Sauders J.H., Frisch K.C. (1964). Polyurethanes. In: Chemistry and Technology, Part II, Technology, Interscience Publishers, New York, pp. 103–106.
Sturm R.N.J. (1973). Biodegradability of nonionic surfactants: screening test for predicting rate and ultimate biodegradation. J. Oil Chem. Soc., 50: 159–167.
Vega R., Main T., Howard G.T. (1999). Cloning and expression inEscherichia coli of a polyurethane-degrading enzyme fromPseudomonas fluorescens. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 43: 49–55.
Whitchurch G.J., Terence A.C. (2006). Some Recent Advances in Thermoplastically Processable Biodegradable Polyvinyl Alcohol, Starch and Polylactide Based Polymer Blends. International Degradable Plastics Symposium by Stanelco plc. Chicago IL, USA, June 16.
Woods G. (1990). The ICI Polyurethanes Book, 2nd edn., John Wiley and Sons, Chichester, United Kingdom.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, A.A., Hasan, F., Akhter, J.I. et al. Degradation of polyurethane by novel bacterial consortium isolated from soil. Ann. Microbiol. 58, 381–386 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03175532
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03175532