Abstract
Objective
The early diagnosis and treatment of cognitive impairment in cirrhotic patients is needed to improve the patients’ daily living. In this study, alterations of regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) were evaluated in cirrhotic patients using statistical parametric mapping (SPM). The relationships between rCBF and neuropsychological test, severity of disease and biochemical data were also assessed.
Methods
99mTc-ethyl cysteinate dimer single photon emission computed tomography was performed in 20 patients with non-alcoholic liver cirrhosis without overt hepatic encephalopathy (HE) and in 20 age-matched healthy subjects. Neuropsychological tests were performed in 16 patients; of these 7 had minimal HE. Regional CBF images were also analyzed in these groups using SPM.
Results
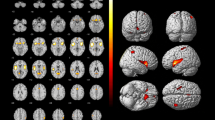
On SPM analysis, cirrhotic patients showed regions of significant hypoperfusion in the superior and middle frontal gyri, and inferior parietal lobules compared with the control group. These areas included parts of the premotor and parietal associated areas of the cortex. Among the cirrhotic patients, those with minimal HE had regions of significant hypoperfusion in the cingulate gyri bilaterally as compared with those without minimal HE.
Conclusions
Abnormal function in the above regions may account for the relatively selective neuropsychological deficits in the cognitive status of patients with cirrhosis. These findings may be important in the identification and management of cirrhotic patients with minimal HE.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dam M, Burra P, Tedeschi U, Cagnin A, Chierichetti F, Ermani M, et al. Regional cerebral blood flow changes in patients with cirrhosis assessed with99mTc-HM-PAO single- photon emission computed tomography: effect of liver transplantation.J Hepatol 1998; 29:78–84.
Catafau AM, Kulisevsky J, Berna L, Pujol J, Martin JC, Otermin P, et al. Relationship between cerebral perfusion in frontal-limbic-basal ganglia circuits and neuropsychologic impairment in patients with subclinical hepatic encephalopathy.J Nucl Med 2000; 41:405–410.
Lockwood AH, Weissenborn K, Bokemeyer M, Tietge U, Burchert W. Correlations between cerebral glucose metabolism and neuropsychological test performance in nonalcoholic cirrhotics.Metab Brain Dis 2002; 17:29–40.
Lockwood AH, Yap EW, Rhoades HM, Wong WH. Altered cerebral blood flow and glucose metabolism in patients with liver disease and minimal encephalopathy.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1991; 11:331–336.
O’Carroll RE, Hayes PC, Ebmeier KP, Dougall N, Murray C, Best JJ, et al. Regional cerebral blood flow and cognitive function in patients with chronic liver disease.Lancet 1991; 337:1250–1253.
Trzepacz PT, Tarter RE, Shah A, Tringali R, Faett DG, Van ThielDH. SPECT scan and cognitive findings in subclinical hepatic encephalopathy.J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 1994; 6:170–175.
Iwasa M, Matsumura K, Kaito M, Ikoma J, Kobayashi Y, Nakagawa N, et al. Decrease of regional cerebral blood flow in liver cirrhosis.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2000; 12:1001–1006.
Brett M, Johnsrude IS, Owen AM. The problem of functional localization in the human brain.Nat Rev Neurosci 2002; 3:243–249.
Friston KJ, Holmes AP, Worsley KJ, Poline JP, Frith CD, Frackowiak RSJ. Statistical parametric maps in functional imaging: a general linear approach.Hum Brain Mapping 1995; 2:189–210.
Fristen KJ, Ashburner J, Frith CD, Poline JB, Heather JD, Frackowiak RSJ. Spatial realignment and normalization of images.Hum Brain Mapping 1995; 2:165–189.
Imon Y, Matsuda H, Ogawa M, Kogure D, Sunohara N. SPECT image analysis using statistical parametric mapping in patients with Parkinson’s disease.J Nucl Med 1999; 40:1583–1589.
Kogure D, Matsuda H, Ohnishi T, Asada T, Uno M, Kunihiro T, et al. Longitudinal evaluation of early Alzheimer’s disease using brain perfusion SPECT.J Nucl Med 2000; 41:1155–1162.
Stamatakis EA, Glabus MF, Wyper DJ, Barnes A, Wilson JT. Validation of statistical parametric mapping (SPM) in assessing cerebral lesions: a simulation study.Neuroimage 1999; 10:397–407.
Stamatakis EA, Wilson JT, Hadley DM. SPECT imaging in head injury interpreted with statistical parametric mapping.J Nucl Med 2002; 43:476–483.
Posner MI, Petersen SE. The attention system of the human brain.Annu Rev Neurosci 1990; 13:25–42.
Posner MI. Attention in cognitive neuroscience: An overview.The cognitive neurosciences. Gazzaniga MS. Cambridge Massachusetts; MIT Press, 1995: 615–624.
Goldman-Rakic PS. Topography of cognition: parallel distributed networks in primate association cortex.Annu Rev Neurosci 1988; 11:137–156.
Asenbaum S, Brücke T, Pirker W, Pietrzyk U, Podreka I. Imaging of cerebral blood flow with technetium-99m- HMPAO and technetium-99m-ECD: a comparison.J Nucl Med 1998; 39:613–618.
Hyun Y, Lee JS, Rha JH, Lee IK, Ha CK, Lee DS. Different uptake of99mTc-ECD and99mTc-HMPAO in the same brains: analysis by statistical parametric mapping.Eur J Nucl Med 2001; 28:191–197.
Oku N, Matsumoto M, Hashikawa K, Moriwaki H, Ishida M, Seike Y, et al. Intra-individual differences between technetium-99m-HMPAO and technetium-99m-ECD in the normal medial temporal lobe.J Nucl Med 1997; 38:1109- 1111.
Tsuchida T, Nishizawa S, Yonekura Y, Sadato N, Iwasaki Y, Fujita T, et al. SPECT images of technetium-99m-ethyl cysteinate dimer in cerebrovascular diseases: comparison with other cerebral perfusion tracers and PET.J Nucl Med 1994; 35:27–31.
Lockwood AH, Murphy BW, Donnelly KZ, Mahl TC, Perini S. Positron-emission tomographic localization of abnormalities of brain metabolism in patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy.Hepatology 1993; 18:1061–1068.
Mathew RJ, Wilson WH. Substance abuse and cerebral blood flow.Am J Psychiatry 1991; 148:292–305.
Melgaard B, Henriksen L, Ahlgren P, Danielsen UT, Sorensen H, Paulson OB. Regional cerebral blood flow in chronic alcoholics measured by single photon emission computerized tomography. ActaNeurol Scand 1990; 82:87–93.
Nicolás JM, Catafau AM, Estruch R, Lomena FJ, Salamero M, Herranz R, et al. Regional cerebral blood flow-SPECT in chronic alcoholism: relation to neuropsychological testing.J Nucl Med 1993; 34:1452–1459.
Tarter RE, Edwards KI, Van ThielDH. Neuropsychological dysfunction due to liver disease.Medical neuropsychology: the impact of disease on behavior. Tarter RE, Van Thiel DH, Edwards KI. New York; Plenum, 1988: 75–97.
Dunk AA, Moore JW. Cognitive dysfunction in latentfportasystemic encephalopathy.Developments in clinical and experimental neuropsychology. Crawford JR, Parker DM. London; Plenum, 1989: 39–46.
Watanabe A, Sakai T, Sato S, Imai F, Ohto M, Arakawa Y, et al. Clinical efficacy of lactulose in cirrhotic patients with and without subclinical hepatic encephalopathy.Hepatology 1997; 26: 1410–1414.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakagawa, Y., Matsumura, K., Iwasa, M. et al. Single photon emission computed tomography and statistical parametric mapping analysis in cirrhotic patients with and without minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Ann Nucl Med 18, 123–129 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02985102
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02985102