Abstract
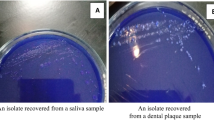
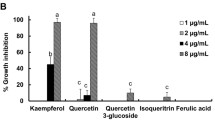
Different bacteria were separated from saliva and teeth of cariogenic patients and identified by a variety of morphological and biochemical tests. Extracts of green tea strongly inhibitedEscherichia coli, Streptococcus salivarius andStreptococcus mutans. The antibacterial effect of green and black tea extracts were compared with those of amoxicillin, cephradine and eugenol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
De Whalley, C. V., Rakin, S. M., Hoult, J. R. S., Jessup, W., Leake, D. S., Flavonoids inhibit the oxidative modification of low density lipoprotein by macrophages.Bio. Chem. Pharmacol., 39, 1743–50 (1990).
Enohara, T., Yamane, K., Fujiwara, H., Naeshiro, H., Naeshiro, H., Watanabe, H., Dentifrice containing powdered tea for controlling gingivitis.Jpn. Kokai Takyo Koho JP, 07, 33, 632 (1995).
Fujiki, H., Yoshizawa, S., Horiuchi, T., Suganuma, M., Yatsunami, J., Nishiwaki, S., Anticariogenic effect of (−) epigallocatechin gallate.Prev. Med., 2, 361–9 (1992).
Hamdaoui, M., Hedhili, A., Doghri, T., Tritar, B., Effect of tea on iron absorption from the typical Tunisian meal conscous fed to healthy rats.Ann. Nutr. Metab., 38, 226–31 (1994).
Hashimoto, F., Kashiwada, Y., Nonaka, G., Nishioka, I., Nohara, T., Cosentno, L. M., Lee, K., Anti AIDS agents. 24. Evaluation of tea polyphenols as Anti-HIV agents.Bioorg. Med. Chem, Lett. 6, 695–700 (1996).
Hayashi, S., Natural product based deodrant.Jpn. Kokai Takyo Koho Jp 07, 194, 683 (1995).
Hillson S.,Teeth, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp. 283–300, 1990.
Holt, J. G. and Murray, R. G. E., Identification of bacteria.Bergey's Manual of determinative bacteriology. William and Wilkins, Baltimore, Hong Kong, London, Sydney, Vol 1, 2, pp. 419–423, 1055–1063, 1984.
Hunt, D. E., Jsandham, H. and Gilmore, R. W., Evaluation of plating media for the determination of viable microorganisms in dental plaque.Appl. Microbiology. 17, 625–626 (1969).
Kreydiyyeh, S. I., Baydown, E. A., Churukian, Z. M., Tea extracts inhibit intestinal absorption of glucose and sodium in rats.Comp. Biochem. Physiol, C; Pharmacol; Toxicol, Endocrinol 108 C, 359–65 (1994).
Kristoferson, K. and Bratthall, D., Transient reduction ofStreptococcus mutans interdently by cholorhexidine.Scand. J. Dent. Res., 90, 417–492 (1982).
Ohmori, Y., Ito, M., Kishi, M., Mizutani, H., Katada, T., Konishi, H., Antiallergic constituents from Oolong tea stem.Biol. Pharm. Bull, 18, 683–6 (1995).
Otake, S., Makimura, M., Kuroki, T., Nishihara, Y., Hirasawa, M., Anticaries effect of polyphenolic compounds from japanese green tea.Caries Res., 25, 438–43 (1991).
Pelczar, J. J. R. and Reid, R. D.,Microbiology (Fourth Edition) McGraw-Hill Book Company, London, Toronto, New York. pp. 107–120, 1983.
Roth, G. I. and Calmes, R.,Oral Biology, C. V. Mosby Company, Toronto, London, pp. 341–350, 1981.
Sagesaka, Y. M., Uemura, T., Suzuki, Y., Sugiura, T., Yoshida, M., Yamaguchi, K., Kyuki, K., Antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory actions of tea-leaf saponin.Yakugaku Zasshi. 116, 238–43 (1996).
Sugyama, K., Manufacture of flavoring materials from tea leaves.Jpn. Kokai Tokyo Koho Jp, 06, 133, 729 (1994).
Varro, E. T., Lynn, R. B., James, E. R.,Pharmacognosy (ninth edition), Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, pp. 247, 248, 481–482, 485, 487, 1988.
Yamane, K., Fujiwara, H., Naeshiro, H., Skin cosmetics containing tea catechin.Jpn. Kokai Tokyo Koho Jp, 07, 196, 466 (1995).
Yeo, S.-G., Ahn, C.-W., Lee, Y.-W., Lee, T.-G., Park, Y.-H., Kim, S.-B., Antioxidative effect of tea extracts from green tea, Oolong tea and black tea.Han'guk Yongyang Siklyong Hakhoechi., 24, 299–304 (1995).
You, -S. Q., Study on feasibility of Chinese green tea polyphenols for preventing dental caries.Chung-Hua-Kou-Chiang-Hsueh-Tsa-Chih, 28, 197–9, 254 (1993).
Yu, -H., Oho, -T. Tagomori, -S. Morioka, -T. Anticariogenic effect of green tea.Fukuoka-Igaku-Zasshi., 83, 174–80 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rasheed, A., Haider, M. Antibacterial activity ofCamellia sinensis extracts against dental caries. Arch. Pharm. Res. 21, 348–352 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02975300
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02975300