Abstract
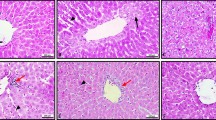
Damaging effects of reactive oxygen species on living systems are well documented. They include oxidative attack on vital cell constituents. Chronic ethanol administration is able to induce an oxidative stress in the central nervous system. In the present study, 16–18 week-old male albino rats of Wistar strain were exposed to different concentration of ethanol for 4 weeks. This exposure showed profound effect on body weight. Ascorbic acid level; and activities of alkaline phosphatase and aspartate transaminase in the brain are dependent on the concentration of ethanol exposure. Chronic ethanol ingestion elicits statistically significant increase in thiobarbituric acid reactive substances level and decrease in gluatathione level in the brain. It reduces superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase, and glutathione reductase activities in a dose dependent manner. However, histological examination could not reveal any pathophysiological changes. Therefore, we conclude that biochemical alterations and oxidative stress related parameters respond early in alcoholism than the histopathological changes in brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calabrese V, Scapagnini G, Latteri S, Colombrita C, Rayagna A, Catalano C, Pennisi G, Calvani M, Butterfield DA. Longterm ethanol administration enhances age-dependent modulation of redox state in different brain regions in the rat: protection by acetyl carnitine. Int J Tissue React 2002; 24(3): 97–104.
Diamond I, Gordon AS. Cellular and molecular neuroscience of alcoholism. Physiol Rev 1997; 77: 1–20.
Gupta YK, Gupta M, Kohli K. Neuroprotective role of melatonin in oxidative stress vulnerable brain. Ind J Physiol Pharmacol 2003; 47(4): 373–86.
Skaper SD, Floreani M, Ceccon M, Facci L, Giusti P. Excitotoxicity, oxidative stress, and the neuroprotective potential of melatonin. Ann NY Acad Sci 1999; 890: 107–18.
Gilman SC, Bonner MJ, Pellmar TC. Effect of oxidative stress on excitatory amino acid release by cerebral cortical synaptosomes. Free Radic Biol Med 1993; 15(6): 671–5.
Gilgun-Sherki Y, Rosenbaum Z, Melamed E, Offen D. Antioxidant therapy in acute central nervous system injury: current state. Pharmacol Rev 2002; 54(2): 271–84.
Gonthier B, Signorini-Allibe N, Soubeyran A, Eysseric H, Lamarche F, Barret L. Ethanol can modify the effects of certain free radical-generating systems on astrocytes. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2004; 28(4): 526–34.
Das SK, Vasude van DM. Effect of lecithin in the treatment of ethanol mediated free radical induced hepatotoxicity. Ind J Clin Biochem 2006; 21(1): 62–69.
Lowry OH, Rosenbourgh NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 1951; 193: 265–75.
Linhardt K, Walter K. Phosphatase. In: Bergmeyer HU, editor. Methods of Enzymatic Analysis; NY: Academic Press, 1963; 799.
Bergmeyer HU, Bernt E. Glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase; Glutamate pyruvate transaminase. In: Bergmeyer HU, editor. Methods of Enzymatic Analysis. NY: Academic Press Inc, 1963: 837–53.
Roe JH, Kuether CA. The determination of ascorbic acid in whole blood and urine through the 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine derivative of dehydro ascorbic acid. J. Biol Chem 1943; 147: 399–401.
Ellman GL. The sulphydryl groups. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1959; 32: 70–77.
Sinnhuber RO, Yu TC. Characterization of the red pigment formed in the thiobarbituric acid determination of oxidative rancidity. Food Res 1958; 23: 626–30.
Goldberg MD, Spooner JR. Glutathione reductase. In: Bergmayer HU, Bergmayer J, Grabi M, editors, Methods of Enzymatic Analysis, Vol. III, 3nd ed. Florida: Academic Press Inc., 1983: 258–65.
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB. Glutathione S-transferase, the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 1974; 249: 7130–9.
Paglia DE, Valentine WN. Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterisation of erythrocyte glutathione peroxides. J Lab Clin Med 1967; 70: 158–9.
Marklund S, Marklund G. Involvement of superoxide radical in the auto oxidation, pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem 1974; 47: 469–74.
Das SK, Vasudevan DM. Effect of ethanol on liver antioxidant defense systems: a dose dependent study. Ind J Clin Biochem 2005; 20(1): 79–83.
Harper C, Matsumoto I. Ethanol and brain damage. Curr Opin pharmacol 2005; 5: 73–8.
Kril JJ, Halliday GM, Svoboda MD, Cartwright H. The cerebral cortex is damaged in chronic alcoholics. Neuroscience. 1997; 79: 983–98.
Cohen S. Phosphatases. In: Lajtha A, editor, Handbook of Neurochemistry, NY: Plenum Press, 1970; 87–131.
Sedman G L, Austin L, Langford CJ. Protein turnover in brain during the development of alcohol dependence. Neurosci. Lett 1982; 28: 93–9.
Jarlstedt J. Effect of alcohol and diet on3H leucine incorporation into brain and liver protein. I. Acute intoxication and vitamin deficiency in rats. J Stud Alcohol 1976; 37: 1178–87.
Dasgupta S, Ghosh S. Nicotine induced alterations in brain acid and alkaline phosphatase activities. Ind J Physiol Allied Sci 1993; 47: 200–6.
Anderson PJ, Song SK. Acid phosphatase in the nervous system. J Neuropathol Neurol 1962; 21: 263–83.
Matcovis B, Varga SI, Szaluo L, Witsas H. The effect of diabetes on the activities of the peroxide metabolic enzymes. Hor Metb Res 1982; 14: 77–9.
Svensson L, Wu C, Johannessen K, Engel JA. Effect of ethanol on ascorbate release in the nucleus accumbens and striatum of freely moving rats. Alcohol 1992; 9(6): 535–40.
Carney JM, Strake-Reed PE, Oliver CN, Landum RW, Chang MS, Wu JF, Floyd RA. Reversal of age-related increase in brain protein oxidation, decrease in enzyme activity and loss in temporal and spatial memory by chronic administration of the spin trapping compound N-tert-buty-alfa-pheynitrone. PNAS 1991; 88: 3633–6.
Nistico G, Cirilol HR, Fiskin K, Iannone M, Martino A, Rotilio G. NGF restores decrease in catalase activity and increases superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase activity in the brain of aged rats. Free Radic Biol Med 1992; 12: 177–81.
Scapagnini G, Ravagna A, Bella R, Colombrita C, Pennisi G, Calvani M, Alkon D, Calabrese V. Long-term ethanol administration enhances age-dependent modulation of redox state in brain and peripheral organs of rat: protection by acetyl carnitine. Int J Tissue React 2002; 24(3): 89–96.
Hemachand T, Gopalakrishnan B, Salunke DM, Totey SM, Shaha C. Sperm plasma-membrane-associated, glutathione S-transferases as gamete recognition molecules. J Cell Sci 2002; 115: 2053–65.
Davenport CJ, Ali SF, Miller FJ, Lipe GW, Morgan KT, Bonnefoi MS. Effect of methyl bromide on regional brain glutathione, glutathione-S-transferases, monoamines, and amino acids in F344 rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1992; 112(1): 120–7.
Yu BP. Cellular defense against damage from reactive oxygen species. Physiol Rev 1994; 74: 139–62.
Aydin S, Ozaras R, Uzun H, Belce A, Uslu E, Tahan V, Altug T, Dumen E, Senturk H. N-acetylcysteine reduced the effect of ethanol on antioxidant system in rat plasma and brain tissue. Tohoku J Exp Med 2002; 198(2): 71–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, S.K., Hiran, K.R., Mukherjee, S. et al. Oxidative stress is the primary event: Effects of ethanol consumption in brain. Indian J Clin Biochem 22, 99–104 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02912890
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02912890