Abstract
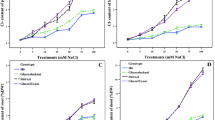
Adsorption, absorption and translocation of sodium were compared in three species showing an ascending degree in tolerance to salinity: red cabbage (tolerant) shows higher Root Cationic Exchange Capacity than tomato (sensitive) or radish (intermediate). At low NaCl concentrations, tomato accumulates the greatest quantities of sodium; but Na+ translocation remains proportional to the quantity absorbed in the three plants. At high salt concentrations, diffusive phenomena explain similar accumulation in every plant, but red cabbage quickly localises 50% of Na+ amount in cotyledons, while this element stays stored in tomato roots. The consequence of these three nutrition phases was discussed in relation to the behaviour observed at the germination time of these same plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Références
Briens, M., Larher, F.: Osmoregulation in halophytic higher plants: a comparative study of soluble carbohydrates, polyols, betaine and free proline. - Plant Cell Environ.5: 287–292, 1982.
Elzam, O. E., Epstein, E.: Salt relations of two grass species differing in salt tolerance. 2) Kinetics of the absorption of K, Na and Cl by their excised roots. - Agrochimica13: 196–206, 1969.
Erdei, L., Kuiper, P. J. C: The effects of salinity on growth, cation content, Na+ uptake and translocation in salt sensitive and salt tolerantPlantago species. - Physiol. Plant.47: 95–99, 1979.
Ferard, G., Binet, P.: ortance du transport des ions vers les feuilles dans la résistance au sel dePlantago maritima L. et dePlantago lanceolata L. - Soc. Bot. fr. Actu. Bot.3–4: 105–110, 1978.
Guerrier, G.: Influence de différentes salinités (sels de sodium et sels de chlorure) sur la germination deRaphanus sativus. - Plant Soil61: 457–469, 1981.
Guerrier, G.: Capacités germinatives des semences en fonction des doses graduelles en NaCl. Importance des transferts sur milieux sodés ou témoins. - Rev. gén. Bot.90: 3–21, 1983a.
Guerrier, G.: Germination de plantes maraîchères et oléagineuses en présence de NaCl. - Seed Sci. Techn.11: 281–292, 1983b.
Hajji, M.: La responsabilité de la racine dans la sensibilité du Laurier rose au chlorure de sodium. -Physiol. vég.18: 505–515, 1980.
Jeschke, W. D., Nassery, H.: K+-Na+ selectivity in roots ofTriticum, Helianthus andAllium. -Physiol. Plant.52: 217–224, 1981.
Lineweaver, H., Burk, D.: The determination of enzyme dissociation constants. - J. amer. Chem. Soc.56: 658–666, 1934.
Mercado, A.: Structure and function of plant cells in saline habitats. New trends in the study of salt tolerance. - John Wiley Ed., New York 1973.
Nissen, P.: Multiphasic uptake in plants. 2) Mineral cations, chloride and boric acid. - Physiol. Plant.29: 298–354, 1973.
Rains, D. W., Epstein, E.: Sodium absorption by barley roots: role of the dual mechanism of alkali cation transport. - Plant Physiol.42: 314–318, 1967.
Rush, D. W., Epstein, E.: Comparative studies on the sodium potassium and chloride relations of a wild halophytic and a domestic salt sensitive tomato species. - Plant Physiol.68: 1308–1313, 1981.
Tanczos, O. G., Erdei, L., Snijder, J.: Uptake and translocation of sodium in salt sensitive and salt tolerantPlantago species. - Plant Soil63: 27–32, 1981.
Tikhaya, N. I., Mishutina, N. E.: Comparison of some membrane bound ATPases of glycophyts and halophyts. -Plant Soil63: 25–26, 1981.
Wacquant, J. P., Passama, L.: portions d’ions K+ dans la plante et résistance au sel de divers halophytes: relation avec les propriétés d’adsorption des racines. - Soc. Bot. Fr. Actu. Bot.3–4: 111–121, 1978.
Yeo, A. R., Flowers, T. J.: Accumulation and localisation of sodium ions within the shoots of rice (Oriza sativa L.) varieties differing in salinity resistance. - Physiol. Plant.56: 343–348, 1982.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guerrier, G. Relations entre la tolérance ou la sensibilité à la salinité lors de la germination des semences et les composantes de la nutrition en sodium. Biol Plant 26, 22–28 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02880421
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02880421