Abstract
In terms of statistical physics, a fluid such as the atmosphere is a many-body system which has a vast amount of degree of freedom and thus obeys the second law of thermodynamics.
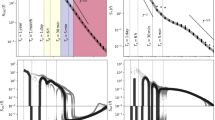
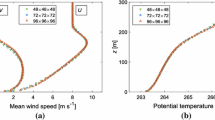
In this paper, a noticeable improvement of the prognostic outputs is made by reconstructing the terms of the horizontal diffusion of MM5 according to the principles of the second law of thermodynamics; besides, the computational noise is effectively and significantly suppressed since the physical dissipative technique for reconstructing suggested in this paper is based on the physical law rather than on the computational method such as the artificial viscosity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu Chongjian, Zhang Daoming, Li Jinglong et al., Improvement of a global spectral model by introducing the second law of thermodynamics, Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 1995, 9: 95–100.
Smagorinsky, J., Manabe, S., Holloway, J. L., Jr., Numerical results from a nine-level general circulation model of the atmosphere, Mon. Wea. Rev., 1965, 93: 727–767.
Pielke, R. A., Mesoscale Meteorological Modeling, Orlando: Academic Press, 1984, 324–331.
Cheng Linsheng, Chou Jifan, Atmospheric Numerical Simulations (in Chinese), Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 1991, 76–77.
Fu Dexun, Numerical Simulations for Fluid Dynamics (in Chinese), Beijing: Defensive Industry Press of China, 1993, 235–249.
Xing Xiaokang, Liu Ruxun, Jiang Bocheng, Computational Fluid Dynamics (in Chinese), Changsha: Defensive Science and Technology University Press, 1989, 97–99.
Xue, M., High-order monotonie numerical diffusion and smoothing, Mon. Wea. Rew., 2000, 128: 2853–2864.
Crandall, M. G., Majda, A., Monotone difference approximations for scalar conservation laws, Mathematics of Computations, 1980, 34: 1–21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Liu, Y. & Kang, H. A new technique of physical dissipation and its application to a mesoscale numerical weather prediction model. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 45, 769–780 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02879512
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02879512