Abstract
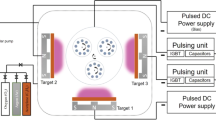
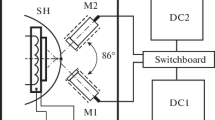
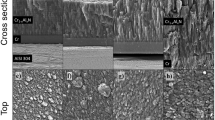
Multilayer superlattice coatings of TiN/CrN were deposited on silicon substrates using a reactive d.c. magnetron sputtering process. Superlattice period, also known as modulation wavelength (A), was controlled by controlling the dwell time of the substrate underneath Ti and Cr targets. X-ray diffraction (XRD), nanoindentation and atomic force microscopy (AFM) were used to characterize the films. The XRD data showed 1st and 2nd order satellite reflections along the principal reflection for films having 132 Å > Å > 84 Å, thus confirming the formation of superlattice. The multilayer coatings exhibited hardness(H) as high as 3200 kg/mm2, which is 2 times the rule-of-mixtures value (i.e.)H TiN = 2200 kg/mm2 andH CrN = 1000 kg/mm2). Detailed investigations on the effects of various process parameters indicated that hardness of the superlattice coatings was affected not only by modulation wavelength but also by nitrogen partial pressure and ion bombardment during deposition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chu X and Barnett S 1995J. Appl. Phys. 77 4403
Chu X, Wong M S, Sproul W D, Rohde S L and Barnett S A 1992J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A10 1604
Koehler J S 1970Phys. Rev. B2 547
Madan A, Yashar P, Shinn M and Barnett S A 1997Thin Solid Films 302 147
Oliver W C and Pharr G M 1992J. Mater. Res. 7 1564
Sproul D S 1996Science 273 889
Veprek S 1999J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A17 2401
Yang Q, He C, Zhao L R and Immarigeon J P 2002Scr. Mater. 46 293
Yashar P C and Sproul W D 1999Vacuum 55 179
Yashar P, Barnett S A, Rechner J and Sproul W D 1998J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A16 2913
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barshilia, H.C., Rajam, K.S. Deposition of TiN/CrN hard superlattices by reactive d.c. magnetron sputtering. Bull Mater Sci 26, 233–237 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02707797
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02707797