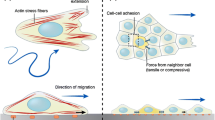
Summary
Cell motility (i.e., movement) is an essential component of normal development, inflammation, tissue repair, angiogenesis, and tumor invasion. Various molecules can affect the motility and positioning of mammalian cells, including peptide growth factors, (e.g., EGF, PDGF, TGF-beta), substrate-adhesion molecules (e.g., fibronectin, laminin), cell adhesion molecules (CAMs), and metalloproteinases. Recent studies have demonstrated a group of motility-stimulating proteins which do not appear to fit into any of the above categories. Examples include: 1)scatter factor (SF), a mesenchymal cell-derived protein which causes contiguous sheets of epithelium to separate into individual cells and stimulates the migration of epithelial as well as vascular endothelial cells; 2)autocrine motility factor (AMF), a tumor cell-derived protein which stimulates migration of the producer cells; and 3)migration-stimulating factor (MSF), a protein produced by fetal and cancer patient fibroblasts which stimulates penetration of three-dimensional collagen gels by non-producing adult fibroblasts. SF, AMF, and MSF are soluble and heat labile proteins with Mr of 77, 55, and 70 kd by SDS-PAGE, respectively, and may be members of a new class of cell-specific regulators of motility. Their physiologic functions have not been established, but available data suggest that they may be involved in fetal development and/or tissue repair.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atnip, K. D.; Carter, L. M.; Nicolson, G. L., et al. Chemotactic response of rat mammary adenocarcinoma cell clones to tumor-derived cytokines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 146: 996–1002; 1987.
Aznavoorian, S. A.; Stracke, M. L.; Liotta, L. A. Differential effect of pertussis toxin on chemotaxis vs haptotaxis to components of the extracellular matrix. J. Cell Biol. 107 (Part 3): 586a; 1988 (abstract).
Barrandon, Y.; Green, H. Cell migration is essential for sustained growth of keratinocyte colonies: the role of transforming growth factors and epidermal growth factor. Cell 50: 1131–1137; 1987.
Bebawy, S. T.; Gorka, J.; Hyers, T. M., et al. In vitro effects of platelet factor 4 on normal human neutrophil functions. J. Leukocyte Biol. 39: 423–434; 1986.
Behrens, J.; Birchmeier, W.; Goodman, S. L., et al. Dissociation of Madin-Darby kidney epithelial cells by the monoclonal antibody anti-Arc-1: Mechanistic aspects and identification of the antigen as a component related to uvomorulin. J. Cell Biol. 101: 1307–1315; 1985.
Behrens, J.; Mareel, M. M.; Van Roy, F. M., et al. Dissecting tumor cell invasion: epithelial cells acquire invasive properties after loss of uvomorulin-mediated cell-cell adhesion. J. Cell Biol. 108: 2435–2447; 1989.
Blay, J.; Brown, K. D. Epidermal growth factor promotes the chemotactic migration of cultured rat intestinal epithelial cells. J. Cell Physiol. 124: 107–112; 1985.
Bowersox, J. C.; Sorgente, N. Chemotaxis of aortic endothelial cells in response to fibronectin. Cancer Res. 42: 2547–2551; 1982.
Burk, R. R. A factor from a transformed cell line that affects cell migration. PNAS USA 70: 369–372; 1973.
Bussolino, F.; Wang, J. M.; Defilippi, P., et al. Granulocyte- and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factors induce human endothelial cells to migrate and proliferate. Nature 337: 471–473; 1989.
Cereijido, M.; Ehrenfeld, J.; Meza, I., et al. Structural and functional membrane polarity in cultured monolayers of MDCK cells. J. Membrane Biol. 52: 147–159; 1980.
Connolly, D. T.; Stoddard, B. L.; Harakes, N. K., et al. Human fibroblast-derived growth factor is a mitogen and chemoattractant for endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 144: 705–712; 1987.
Damsky, H. C.; Richa, J.; Solter, D., et al. Identification and purification of a cell surface glycoprotein mediating intercellular adhesion in embryonic and adult tissue. Cell 34: 455–466; 1983.
DeLarco, J. E.; Pigott, D. A.; Lazarus, J. A. Ectopic peptides released by a human melanoma cell line that modulate the transformed phenotype. PNAS USA 82: 5015–5019; 1985.
Edelman, G. M. Cell adhesion molecules in the regulation of animal form and tissue pattern. Ann. Rev. Cell Biol. 2: 81–116; 1986.
Edlman, G. M. Topobiology. Scientific American, May 1989; 76–88.
Folkman, J. Tumor angiogenesis. Adv. Cancer Res. 43: 175–203; 1985.
Folkman, J. Angiogenesis: initiation and control. In: Fishman, A. P., ed. Endothelium. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 401: 212–227; 1982.
Garbisa, S.; Pozzatti, R.; Muschel, R. J., et al. Secretion of type IV collagenolytic protease and metastatic phenotype: Induction by transfection with c-Ha-ras but not c-Ha-ras plus Ad2-Ela. Cancer Res. 47: 1523–1528; 1987.
Gausse-Muller, V.; Kleinman, H. K.; Martin, G. R., et al. Role of attachment factors and attractants in fibroblast chemotaxis. J. Lab Clin. Med. 96: 1071–1080; 1980.
Gherardi, E.; Grey, J.; Stoker, M., et al. Purification of scatter factor, a fibroblast-derived basic protein which modulates epithelial interactions and movement. PNAS USA 86: 5844–5848; 1989.
Gomez-Cambronero, J.; Yamazuki, M.; Metwally, F., et al. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and human neutrophils: role of guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. PNAS USA 86: 3569–3573; 1989.
Grant, M.; Jerdan, J.; Merimee, T. J. Insulin-like growth factor-I modulates endothelial cell chemotaxis. J. Clin. Endocrin. Metab. 46: 370–371; 1987.
Grey, A.-M.; Schor, A. M.; Rushton, G., et al. Purification of the migration stimulating factor produced by fetal and breast cancer patient fibroblasts. PNAS USA 86: 2438–2442; 1989.
Grotendorst, G. R.; Seppa, H. E. J.; Kleinman, H. K., et al. Attachment of smooth muscle cells to collagen and their migration toward platelet-derived growth factor. PNAS USA 78: 3669–3672; 1981.
Grotendorst, G. R.; Soma, Y.; Takehara, K., et al. EGF and TGF-alpha are potent chemoattractants for endothelial cells and EGF-like peptides are present at sites of tissue regeneration. J. Cell Physiol.139: 617–623; 1989.
Guirguis, R.; Margulies, I.; Taraboletti, G., et al. Cytokine-induced pseudopodial protrusion is coupled to tumour cell migration. Nature 329: 261–263; 1987.
Guirguis, R.; Schiffman, E.; Liu, B., et al. Detection of autocrine motility factor in urine as a marker of bladder cancer. JNCI 80: 1203–1211; 1988.
Hayashi, H.; Yoshida, K.; Ozaki, T., et al. Chemotactic factor associated with invasion of cancer cells. Nature 226: 174–175; 1970.
Heimark, R. L.; Schwartz, S. The role of membrane-membrane interactions in the regulation of endothelial cell growth. J. Cell Biol. 100: 1934–1940; 1985.
Heimark, R. L.; Twardzik, D. R.; Schwartz, S. M. Inhibition of endothelial regeneration by type-beta transforming growth factor from platelets. Science 233:1078–1080; 1986.
Herron, G. S.; Banda, M. J.; Clark, E. J., et al. Secretion of metalloproteinases by stimulated capillary endothelial cells. II. Expression of collagenase and stromelysin activities is regulated by endogenous inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 261: 2814–2818; 1986.
Hynes, R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell 48: 549–554; 1987.
Imhof, B. A.; Vollmers, H. P.; Goodman, S. L., et al. Cell-cell interaction and polarity of epithelial cells; specific perturbation using a monoclonal antibody. Cell 35: 667–675; 1983.
Ireland, G. W.; Stern, C. D.; Stoker, M. Human MRC5 cells induce a secondary primitive streak when grafted into chick embryos. J. Anat. 152: 223–224; 1987.
Jones, J. C. R.; Yokoo, K. M.; Goldman, R. D. A cell surface desmosomal-associated component: Identification of a tissue-specific cell adhesion molecule. PNAS USA 83: 7282–7286; 1986.
Kaever, V.; Damerau, B.; Wessel, K., et al. Biologic properties of dihydro-leukotriene B4, an alternative leukotriene B4 metabolite. FEBS Lett. 231: 385–388; 1988.
Liotta, L. A.; Mandler, R.; Murano, G., et al. Tumor cell autocrine motility factor. PNAS USA 83: 3302–3306; 1986.
Liotta, L. A.; Stetler-Stevenson, W. Editorial: Metalloproteinases and malignant conversion: Does correlation imply causality? JNCI 81: 556–557; 1989.
Liotta, L. A.; Thorgeirsson, U. P.; Garbisa, S. Role of collagenases in tumor cell invasion. Cancer Metast. Rev. 1: 277–288; 1982.
Maciag, T.; Mehlman, T.; Friesel, R. Heparin binds endothelial cell growth factor, the principal cell mitogen in bovine brain. Science 225: 932–935; 1984.
Madri, J. A.; Pratt, B. M.; Tucker, A. M. Phenotypic modulation of endothelial cells by transforming growth factorbeta depends upon the composition and organization of the extracellular matrix. J. Cell Biol. 106: 1375–1384; 1988.
Mano-Hirano, Y.; Sato, N.; Sawasaki, Y., et al. Inhibition of tumor-induced migration of bovine capillary endothelial cells by mouse and rabbit tumor necrosis factor. JNCI 78: 115–120; 1987.
Mege, J. L.; Gomez-Cambronero, J.; Molski, T. F., et al. Effect of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor on superoxide production in cytoplasts and intact human neutrophils: role of protein kinase and G-proteins. J. Leukoc. Biol. 46: 161–168; 1989.
Mensing, H.; Albini, A.; Krieg, T., et al. Enhanced chemotaxis of tumor-derived and virus-transformed cells to fibronectin and fibroblast-conditioned medium. Int. J. Cancer 33: 43–48; 1984.
Mensing, H.; Pontz, B. F.; Muller, P. K., et al. A study on fibroblast chemotaxis using fibronectin and conditioned medium as chemoattractants. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 29: 268–273; 1983.
Merwin, J. R.; Anderson, J.; Madri, J. A. Transforming growth factor-beta induces angiogenesis of microvascular endothelial cells in three-dimensional culture. J. Cell Biol. 107: 48a; 1988.
Mignatti, P.; Tsuboi, R.; Robbins, E., et al. In vitro angiogenesis on the human amniotic membrane: requirement for basic fibroblast growth factor-induced proteinases. J. Cell Biol. 108: 671–682; 1989.
Morrison, R. S.; Sharma, A.; De Vellis, J., et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor supports the survival of cerebral cortical neurons in primary culture. PNAS USA 83: 7537–7541; 1986.
Montesano, R.; Orci, L. Transforming growth factor beta stimulates collagen-matrix contraction by fibroblasts: Implications for wound healing. PNAS USA 85: 4894–4897; 1988.
Moscatelli, D. Metabolism of receptor-bound and matrix-bound basic fibroblast growth factor by bovine capillary endothelial cells. J. Cell Biol. 107: 753–759; 1988.
Moscatelli, D.; Presta, M.; Rifkin, D. B., et al. Purification of a factor from human placenta that stimulates capillary endothelial cell protease production, DNA synthesis, and migration. PNAS USA 83:2091–2095; 1986.
Mundy, G. R.; De Martino, S.; Rowe, D. W. Collagen and collagen-derived fragments are chemotactic for tumor cells. J. Clin. Invest. 68: 1102–1105; 1981.
Ozaki, T.; Yoshida, K.; Ushijima, K., et al. Studies on the mechanisms of invasion in cancer. II. In vivo effects of a chemotactic factor on cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 7: 93–100; 1971.
Peyrieras, N.; Hayfil, F.; Louvard, D., et al. Uvomorulin: a nonintegral membrane protein of early mouse embryo. PNAS USA 80: 6274–6277; 1983.
Postlethwaite, A. E.; Keski-Oja, J.; Moses, H. L. et al. Stimulation of chemotactic migration of human fibroblasts by transforming growth factor beta. J. Exp. Med. 165: 251–256; 1987.
Postlethwaite, A. E.; Keski-Oja, J.; Ballian, G., et al. Induction of fibroblast chemotaxis by fibronectin. J. Exp. Med. 153: 494–499; 1981.
Postlethwaite, A. E.; Seyer, J. M.; Kang, A. H. Chemotactic attraction of human fibroblasts to type I, II, and III collagens and collagen-derived peptides. PNAS USA 75: 871–875; 1978.
Postlethwaite, A. E.; Snyderman, R.; Kang, A. H. The chemotactic attraction of human fibroblasts to a lymphocyte-derived factor. J. Exp. Med. 144: 1188–1203; 1976.
Roberts, A. B.; Sporn, M. B.; Assoian, R. K., et al. Transforming growth factor type beta: rapid induction of fibrosis and angiogenesisin vivo and stimulation of collagen formationin vitro. PNAS USA 83: 4167–4171; 1986.
Rosen, E. M.; Goldberg, I. D.; Kacinski, B. M., et al. Smooth muscle releases an epithelial cell scatter factor which binds to heparin. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. 25: 163–173; 1989.
Rosen, E. M.; Meromsky, L.; Setter, E., et al. Quantitation of cytokine-stimulated migration of endothelium and epithelium by a new assay using microcarrier beads. Exp. Cell Res. In press.
Rosen, E. M.; Meromsky, L.; Setter, E., et al. Smooth muscle-derived factor stimulates mobility of human tumor cells. Invasion and Metastasis. In press.
Rovasio, R. A.; Delouvee, A.; Yamada, K. M., et al. Neural crest cell migration: requirements for exogenous fibronectin and high cell density. J. Cell Biol. 96:462–473; 1983.
Ruoslahti, E.; Pierschbacher, M. D. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science 238:491–497; 1987.
Saksela, S.; Moscatelli, D.; Sommer, A., et al. Endothelial cell-derived heparan sulfate binds basic fibroblast growth factor and protects it from proteolytic degradation. J. Cell Biol. 107: 743–751; 1988.
Sato, Y.; Rifkin, D. B. Autocrine activities of basic fibroblast growth factor: regulation of endothelial cell movement, plasminogen activator synthesis, and DNA synthesis. J. Cell Biol. 107:1199–1205; 1988.
Schiffman, E. Leukocyte chemotaxis. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 44: 553–568; 1982.
Schor, S. L.; Schor, A. M. Fetal-to-adult transitions in fibroblast phenotype: their possible relevance to the pathogenesis of cancer. J. Cell Sci. Suppl. 8:165–180; 1987.
Schor, S. L.; Schor, A. M.; Grey, A. M. et al. Foetal and cancer patient fibroblasts produce an autocrine migration-stimulating factor not made by normal adult cells. J. Cell Sci. 90:391–399; 1988.
Senior, R. M.; Griffin, G. L.; Huang, J. S., et al. Chemotactic activity of platelet alpha granule proteins for fibroblasts. J. Cell Biol. 96:382–385; 1983.
Senior, R. M.; Griffin, G. L.; Mecham, R. P. Chemotactic responses of fibroblasts to tropoelastin and elastin-derived peptides. J. Clin. Invest. 70:614–618; 1982.
Seppa, H.; Grotendorst, G.; Seppa, S., et al. Platelet-derived growth factor is chemotactic for fibroblasts. J. Cell Biol. 92:584–588; 1982.
Seppa, H. E. J.; Yamada, K. M.; Seppa, S. T., et al. The cell binding fragment of fibronectin is chemotactic for fibroblasts. Cell Biol. Int. Rep. 5:813–819; 1981.
Sholley, M. M.; Ferguson, G. P.; Seibel, H. R., et al. Mechanisms of neovascularization. Vascular sprouting can occur without proliferation of endothelial cells. Lab. Invest. 54:624–634; 1984.
Sholley, M. M.; Gimbrone, M. A., Jr.; Cotran, R. S. Cellular migration and replication in endothelial regeneration: a study using irradiated endothelial cultures. Lab. Invest. 36: 18–25; 1977.
Sporn, M. B.; Roberts, A. B.; Wakefield, L. M., et al. Transforming growth factor-beta: biologic function and chemical structure. Science 233:532–534; 1986.
Stenn, K. Epibolin: a protein of human plasma that supports epithelial cell movement. PNAS USA 78:6907–6911; 1981.
Stenn, K. S.; Madri, J. A.; Tinghitella, T., et al. Multiple mechanisms of dissociated epidermal cell spreading. J. Cell Biol. 96:63–67; 1983.
Stoker, M. Effect of scatter factor on mobility of epithelial cells and fibroblasts. J. Cell Physiol. 139: 565–569; 1989.
Stoker, M.; Gherardi, E.; Perryman, M., et al. Scatter factor is a fibroblast-derived modulator of epithelial cell mobility. Nature 327:239–242; 1987.
Stoker, M.; Gherardi, E. Factors affecting epithelial interactions. Ciba Foundation Symposium 125. Chichester, Wiley, 1987:217–235.
Stoker, M.; Perryman, M. An epithelial scatter factor released by embryo fibroblasts. J. Cell Sci. 77:209–223; 1985.
Stracke, M. L.; Guirguis, R.; Liotta, L. A., et al. Pertussis toxin inhibits stimulated motility independently of the adenylate cyclase pathway in human melanoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 146:339–345; 1987.
Stracke, M. L.; Kohn, E. C.; Aznavoorian, S. A., et al. Insulin-like growth factors stimulate chemotaxis in human melanoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 153:1076–1083; 1988.
Teitel, J. M. Specific inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation by isolated endothelial plasma membranes. J. Cell Physiol. 128:329–336; 1986.
ten Dijke, P.; Iwata, K. K. Growth factors and wound healing. Biotechnology 7:793–798; 1989.
Terranova, V. P.; DiFlorio, R.; Lyall, R. M., et al. Human endothelial cells are chemotactic to endothelial cell growth factor and heparin. J. Cell Biol. 101:2330–2334; 1985.
Terranova, V. P.; Rohrbach, D. H.; Martin, G. R. Role of laminin in the attachment of PAM 212 (epithelial) cells to basement membrane collagen. Cell 22:719–726; 1980.
Thomas, K. A. Fibroblast growth factors. FASEB J1:434–440; 1987.
Vlodavsky, I.; Folkman, J.; Sullivan, R., et al. Endothelial cell-derived basic fibroblast growth factor: synthesis and deposition into subendothelial extracellular matrix. PNAS USA 84:2292–2296; 1987.
Wahl, S. M.; Hunt, D. A.; Wakefield, L. M., et al. Transforming growth factor type beta induces monocyte chemotaxis and growth factor production. PNAS USA 84:5788–5792; 1987.
Walicke, P.; Cowan, W. M.; Ueno, N., et al. Fibroblast growth factor promotes survival of dissociated hippocampal neurons and enhances neurite extension. PNAS USA 83:3012–3016; 1986.
Wong, M. K.; Gottlieb, A. I. The reorganization of microfilaments, centrosomes, and microtubules during in vitro small wound reendothelialization. J. Cell Biol. 107:1777–1783; 1988.
Yamada, K. M. Cell surface interactions with extracellular materials. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 12: 761–799; 1983.
Yoshida, K.; Ozaki, T.; Ushijima, K., et al. Studies on the mechanisms of invasion in cancer. I. Isolation and purification of a factor chemotactic for cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 6:123–132; 1970.
Zigmond, S. H.; Hirsch, J. G. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis. New methods for evaluation and demonstration of a cell-derived chemotactic factor. J. Exp. Med. 137:387–410; 1973.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosen, E.M., Goldberg, I.D. Protein factors which regulate cell motility. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 25, 1079–1087 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02621258
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02621258