Summary
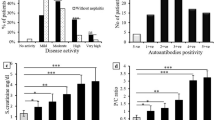
Circulating CD5+ B lymphocytes were studied in 39 Chinese patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Blood cells were stained with anti-CD5 and anti-CD19 monoclonal antibodies and were analyzed by flow cytometry. The results showed that there was no elevation of CD5+ B cells in RA patients when compared with 41 healthy control subjects. The circulating levels of CD5+ B cell correlated neither with serum titers of rheumatoid factor (RF) nor with disease activities in these patients. The CD5+ B cell levels remained relatively constant after a serial follow-up for 12 months. The similar pattern of epitope density of CD5 antigens also existed in the same patients. Although most studies in Caucasians revealed increased levels of CD5+ B cells in RA patients, measurements of this marker were not useful for the evaluation of disease activities in Chinese patients. Levels of CD5+ B cells may reflect more individual genetic background and may play a minor role in the flare-up of activities in Chinese patients with RA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antin, J.H., Emerson, S.G., Martin, P., Gadol, N., Ault. K.A. Leu-1+ (CD5+) B cells. A major lymphoid subpopulation in human fetal spleen: phenotyic and functional studies. J Immunol 1986, 136, 505–510.
Casail, P., Burastero, S., Nakamura, M., Inghirami, G., Notkins, A.L. Human lymphocytes making rheumatoid factor and antibody to ssDNA belong to Leu-1+ B cell subset. Science 1987, 236, 77–81.
Yeh, T.S., Wang, C.R., Jeng, G.W., et al. The study of anticardiolipin antibodies and interleukin-6 in cerebrospinal fluid and blood of Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and CNS involvement. Autoimmunity 1994, 18, 169–175.
Mercolino, T.J., Arnold, L.W., Haughton, G. Phosphatidyl choline is recognized by a series of Ly-1 murine B cell lymphomas specific for erythrocyte membrane. J Exp Med 1986, 163, 155–165.
Jarvis, J.N., Kaplan, J., Fine, N. Increased CD5+ B cell in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1992, 35, 204–207.
Munoz, A., Gallart T., Vinas, O., Gomis R. Increased CD5+ B lymphocytes in type 1 diabetes. Clin Exp Immunol 1989, 78, 196–200.
Dauphinee, M., Tovar, Z., Talal, N. B cells expressing CD5+ B cells are increased in Sjögren's syndrome. Arthritis Rheum 1988, 31, 642–647.
Iwatani, Y., Amino, T., Kaneda, K. et al. Marked increase of CD5+ B cells in hyperthyroid Graves disease. Clin Exp Immunol 1989, 78, 196–200.
Mix, E., Olsson, T., Correale, J. et al. B cells expressing CD5 are increased in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol 1990, 79, 21–27.
Sowden, J.A., Roberts-Thomson, P.J., Zola, H. Evaluation of CD5+ B cells in blood and synovial fluid of patients with rheumatic diseases. Rheumatol Int 1987, 7, 255–259.
Smalley, H.B., Todd, J., Bames, R.M.R., Thompson, R.N., Abraham, G.N., Johnson, P.M. Estimation of serum VkIIIb light chains in rheumatoid arthritis and correlation with CD5+ B cells. Br J Rheumatol 1990, 29, 325–330.
Kipps, T.J., Vaughn, J.H. Genetic influence on the levels of circulating CD5 B lymphocytes. J Immunol 1987, 139, 1060–1064.
Youinou, P., Mackenzie, L., Katsikis, P. et al. The relationship between CD5 expressing B lymphocytes and serologic abnormality in rheumatoid arthritis patients and their relatives. Arthritis Rheum 1990, 33, 339–348.
Liu, M.F., Hsieh, R.P., Lin, K.T., Chen, C.Y. Association of HLA antigens and rheumatoid arthritis. Chinese J Rheumatol 1986, 3, 3–10.
Hardy, R.R., Hayakawa, K. Development and physiology of Ly-1 B and its human homology, Leu-1 B. Immunol Rev 1989, 93, 53–80.
Murakami, M., Tsubata, T., Okamoto, M. et al. Antigen-induced apoptotic death of Ly-1 B cells responsible for autoimmune disease in transgenic mice. Nature 1992, 357, 77–80.
Hayakawa, K., Hardy, R.R. Normal, autoimmune and malignant CD5+ B cells:the Ly-1 B lineage? Ann Rev Immunol 1988, 6, 197–218.
Hayakawa, K., Hardy, R.R., Parks, D.R., Herzenberg, L.A. The Ly-1 B cell subpopulation in normal immunodefective and autoimmune mice. J Exp Med 1983, 157, 202–230.
Plater-Zyberk, C., Maini, R.N., Lam, K., Kennedy, T.D., Janossy, G. A rheumatoid arthritis B cell subset expresses a phenotype similar to that in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Arthritis Rheum 1985, 28, 971–976.
Hardy, R.R., Hayakawa, K., Shimizu, M., Yamasaki, K., Kishimoto, T. Rheumatoid factor secretion from human Leu-1+ B cells. Science 1987, 236, 81–83.
Xu, H.J., Roberts-Thomson, P.J., Ahern, M.J., Zola, H. Comparative evaluation of CD5 B cell in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and essential mixed cryoglobulinemia using FACS analyzer and FACScan flow cytometer. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1992, 651, 594–598.
Caligaris Cappio, F., Riva, M., Tesio, L., Schena, M., Gaidano, G.L., Bergui, L. Human normal CD5+ B lymphocytes can be induced to differentiate to CD5- B lymphocytes with germinal center cell features. Blood 1989, 73, 1259–1263.
Werner-Favre, C., Vischer, T.L., Wohlwend, D., Zubler, R.H. Cell surface antigen CD5 is a marker for activated human B cells. Eur J Immunol 1989, 19, 1209–1213.
Casail, P., Notkins, A.L. Probing the human B cell repertoire with EBV, polyreactive antibodies and CD5+ lymphocytes. Ann Rev Immunol 1989, 7, 513–535.
Casaili, P., Burastero, S.E., Balow, J.E., Notkins, A.L. High affinity to ssDNA are produced by CD5- B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. J Immunol 1989, 143, 3476–3483.
Burastero, S.E., Casail, P., Wilder, R.L., Notkins, A.L. Monoreactive high affinity and polyreactive low affinity rheumatoid factor are produced by CD5+ B cells from patients with rhematoid arthritis. J Exp Med 1988, 168, 1979–1992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S.T., Wang, C.R., Liu, M.F. et al. The study of circulating CD5 positive B lymphocytes in Chinese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 15, 250–253 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02229702
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02229702