Abstract
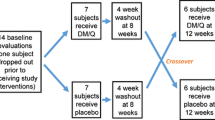
Fifteen autistic individuals were involved in an investigation using fenfluramine and placebo in a double-blind crossover design. Subjects were assessed using IQ tests, the Real Life Rating Scale (RLRS), the Adaptive Behavior Scale-School Edition (ABS-SE), and videotaped play data on 8 of 12 visits, including 2 follow-up visits. Serotonin level in platelet-poor plasma was assessed on all 12 visits. Serotonin levels decreased with the administration of fenfluramine, and increased with the reinstatement of placebo. Statistical tests revealed no significant differences on the IQ scores, the RLRS, or the ABS-SE for the drug versus the placebo conditions. Videotaped data favored the subjects while on placebo. Group and individual data were analyzed over time and indicated no significant improvements due to the drug. The implications of this research make it difficult to recommend fenfluramine as a treatment for autism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Association on Mental Deficiency. (1981).Adaptive Behavior Scale-School Edition. Monterey, CA: McGraw-Hill.
American Psychiatric Association. (1980).Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (3rd ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
August, G. J., Raz, N., & Baird, T. D. (1985). Brief report: Effects of fenfluramine on behavioral, cognitive, and affective disturbances in autistic children.Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 15, 97–107.
August, G. J., Raz, N., & Baird, T. D. (1987). Fenfluramine response in high and low functioning autistic children.Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 26, 342–346.
Beeghly, J. H. L., Kuperman, S., Perry, P. J., Wright, G. J., & Tsai, L. Y. (1987). Fenfluramine treatment of autism: Relationship of treatment response to blood levels of fenfluramine and norfenfluramine.Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 17, 541–548.
Beisler, J. M., Tsai, L. Y., & Stiefel, B. (1986). Brief report: The effects of fenfluramine on communication skills in autistic children.Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 16, 227–233.
Campbell, M., Adams, P., Small, A. M., Curren, E. L., Overall, J. E., Anderson, L. T., Lynch, N., & Perry, R. (1988). Efficacy and safety of fenfluramine in autistic children.Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 27, 434–439.
Coggins, T. E., Morisset, C., Krasney, L., Frederickson, R., Holm, V. A., & Raisys, V. A. (1988). Brief report: Does fenfluramine treatment enhance the cognitive and communicative functioning of autistic children?Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 18, 425–434.
DeMyer, M. K., Hingtgen, J. N., & Jackson, R. K. (1981). Infantile autism reviewed: A decade of research.Schizophrenia Bulletin, 7, 388–451.
Dunn, L., & Dunn, L. (1981).Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test-Revised. Circle Pines, MN: American Guidance Service.
Du Verglas, G., Banks, S. R., & Guyer, K. E. (1988). Clinical effects of fenfluramine on children with autism: A review of the research.Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 18, 297–307.
Freeman, B. J., Ritvo, E. R., Yokota, A., & Ritvo, A. (1986). A scale for rating symptoms of patients with the syndrome of autism in real life settings.Journal of the American Academy of Child Psychiatry.25, 130–136.
Geller, E., Ritvo, E. R., Freeman, B. J., & Yuwiler, A. (1982). Preliminary observations on the effect of fenfluramine on blood serotonin and symptoms in three autistic boys.New England Journal of Medicine, 307, 165–169.
Groden, G., Groden, J., Dondey, M., Zane, T., Pueschel, S. M., & Veliceur, W. (1987). Effects of fenfluramine on the behavior of autistic individuals.Research in Developmental Disabilities, 8, 203–211.
Hendrick, D., Prather, E., & Tobin, A. (1975).Sequenced Inventory of Communication Development. Seattle: University of Washington Press.
Ho, H. H., Lockitch, G., Eaves, L., & Jacobson, B. (1986). Blood serotonin concentrations and fenfluramine therapy in autistic children.Journal of Pediatrics, 108, 465–469.
Hussain, M. N., & Sole, M. J. (1981). A simple, specific, radioenzymatic assay for picogram quantities of serotonin or acetylserotonin in biological fluids and tissues.Analytical Biochemistry, 111, 105–110.
Klykylo, W. M., Feldis, D., O'Grady, D., Ross, D. L., & Halloran, C. (1985). Brief report: Clinical effects of fenfluramine in ten autistic subjects.Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 15, 417–423.
National Society for Autistic Children. (1981).How they grow: A handbook for parents of young child with autism. Washington, DC: Author.
Piggott, L. R., Gdowski, C. L., Villanueva, D., Fischhoff, J., & Frohman, C. F. (1986). Side effects of fenfluramine in autistic children.Journal of the American Academy of Child Psychiatry, 25, 287–289.
Realmuto, G. M., Jensen, J., Klykylo, W., Piggott, L., Stubbs, G., Yuwiler, E. Freeman, B. J., & Ritvo, E. (1986). Untoward effects of fenfluramine in autistic children.Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology, 6, 350–355.
Ritvo, E. R., Freeman, B. J., Geller, E., & Yuwiler, A. (1983). Effects of fenfluramine on 14 outpatients with the syndrome of autism.Journal of the American Academy of Child Psychiatry, 22, 549–558.
Ritvo, E. R., Freeman, B. J., Yuwiler, A., Geller, E., Schroth, P., Yokota, A., Mason-Brothers, A., August, G. J., Klykylo, W., Leventhal, B., Lewis, K., Piggott, L., Realmuto, G., Stubbs, E. G., & Umansky, R. (1986). Fenfluramine treatment of autism: UCLA collaborative study of 81 patients at nine medical centers.Psychopharmacology Bulletin, 22, 133–140.
Ritvo, E. R., Freeman, B. J., Yuwiler, A., Geller, E., Yokota, A., Schroth, P., & Novak, P. (1984). Study of fenfluramine in outpatients with the syndrome of autism.Journal of Pediatrics, 105, 823–828.
Ritvo, E. R., Yuwiler, A., Geller, E., Kales, A., Rashkis, S., Schicor, A., Plotkin, S., Axelrod, R., & Howard, C. (1971). Effects of L-dopa in autism.Journal of Autism and Childhood Schizophrenia, 1, 190–205.
Siegel, S. (1956).Non-parametrics statistics for the behavioral sciences. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Stubbs, E. G., Budden, S. S., Jackson, R. H., Terdal, L. G., & Ritvo, E. R. (1986). Effects of fenfluramine on eight outpatients with the syndrome of autism.Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 28, 229–235.
Thorndike, R. L. (1972).Manual for Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale. Boston: Houghton-Mifflin.
Wechsler, D. (1974).Manual for the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children-Revised. New York: Psychological Corp.
Yarbrough, E., Santat, U., Perel, I., Weber, C., & Lombardi, R. (1987). Effects of fenfluramine on autistic individuals residing in a state developmental center.Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 17, 303–314.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors thank the classroom staff, outpatient workers, regional managers, and social workers for all their help, cooperation, and support throughout this study. A special thanks goes to the Parent Relief staff, particularly Linda Lipka and Bob Adair. This study could not have been conducted without the help of Steve Cohen, Nancy Freeman, Margaret Howard, Binnie Hyman, Adrienne Perry, Patricia Reid, Don Smith, Robyn Williston, and Dr. Michael Sole and Dr. Nassir Hussain of the Department of Pharmacology, University of Toronto. Additionally we thank Leticia Byrch, R. N., for her invaluable services during this study. The Ontario Society for Autistic Citizens gave its support both financially and otherwise, and for this we thank them. Finally, we thank Robins Drug Co., whose contributions included financial support, the fenfluramine pills, and the placebo pills. It was with the help of the above-named people and more that we were able to carry out this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sherman, J., Factor, D.C., Swinson, R. et al. The effects of fenfluramine (Hydrochloride) on the behaviors of fifteen autistic children. J Autism Dev Disord 19, 533–543 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02212856
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02212856