Abstract
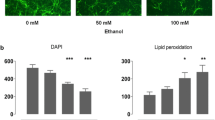
Effects of ethanol on glucose transporter gene expression were examined in cultured rat astrocytes. Exposure to 50 or 100 mM ethanol for 18 hours significantly inhibited hexose uptake and reduced the number of glucose transporters, as indicated by binding studies with cytochalasin B. Indirect immunofluorescence and immunoperoxidase staining showed marked reduction of the GLUT1 glucose transporter by exposure to 100 mM ethanol for 5 or 18 hours, but no obvious change in response to 50 mM ethanol. Western blot analysis showed GLUT1 protein levels to be decreased by 52±12% (p<0.05) after exposure to 100 mM ethanol for 18 hours.In situ hybridization histochemistry indicated an increase in steady-state GLUT1 mRNA in astrocytes exposed to 50 or 100 mM ethanol for 5 or 18 hours. Quantitation of GLUT1 mRNA levels by northern blot analysis showed that GLUT1 mRNA levels were increased by 59 and 112% in cells treated for 5 h with 50 and 100 mM ethanol, respectively. A similar effect was observed after treatment for 18 hours, but ethanol did not alter actin gene expression. Experiments using actinomycin D to block RNA synthesis suggest that this increase in steady-state mRNA level results from increased message stability. These results suggest that ethanol acts on GLUT1 gene expression at the post-transcriptional level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baquer, N.Z., Hothersall, J.S., and McLean, P. (1988). Function and regulation of the pentose phosphate pathway in brain.Current Topics in Cell. Reg. 29:265–289.
Boado, R.J., and Pardridge, W.M. (1993). Glucose deprivation causes posttranscriptional enhancement of brain capillary endothelial glucose transporter gene expression via GLUT1 mRNA stabilization.J. Neurochem. 60:2290–2296.
Carter, B.Z., and Malter, J. (1991). Regulation of mRNA stability and its relevance to disease.Lab. Invest. 65:610–621.
Charness, M.E. (1993). Brain lesions in alcoholics.Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 17:2–11.
Choi, T.B., Boado, R.J., and Pardridge, W.M. (1989). Blood-brain barrier glucose transporter mRNA is increased in experimental diabetes mellitus.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 164:375–380.
Chu, E., Koeller, D.M., Casey, J.L., Drake, J.C., Chabner, B.A., Elwood, P.C., Zinn, S., and Allegra, C.J. (1991). Autoregulation of human thymidylate synthase messenger RNA translation by thymidylate synthase.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 88:8977–8981.
Clarke, D.W., Boyd, F.T. Jr., Kappy, M.S., and Raizada, M.K. (1984). Insulin binds to specific receptors and stimulates 2-deoxy-D-glucose uptake in cultured glial cells from rat brain.J. Biol. Chem. 259:11672–11675.
Davies, D.L., and Vernadakis, A. (1984). Effects of ethanol on cultured glial cells: proliferation and glutamine synthetase activity.Brain Res. 318:27–35.
Eckardt, M.J., Campbell, G.A., Marietta, C.A., Majchrowicz, E., and Weight, F.F. (1988). Acute ethanol administration selectively alters localized cerebral glucose utilization.Brain Res. 444:53–58.
Fletcher, T.L., and Shain, W. (1993). Ethanol-induced changes in astrocytes gene expression during rat central nervous system development.Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 17:993–1001.
Gayer, G.G., Gordon, A., and Miles, M.F. (1991). Ethanol increases tyrosine hydroxylase gene expression in N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells.J. Biol. Chem. 266:22279–22284.
Giordano, T., Kleinsek, D., and Foster, D.N. (1989). Increase in abundance of a transcript hybridizing to elongation factor 1 alpha during cellular senescence and quiescence.Exp. Gerontol. 24:501–513.
Grunwald, F., Schrock, H., Biersack, H.-J., and Kuschinsky, W. (1993). Changes in local cerebral glucose utilization in the awake rat during acute and chronic administration of ethanol.J. Nucl. Med. 34:793–798.
Held, I.R., Sayers, S.T., and McLane, J.A. (1991). Acetylcholine receptor gene expression in skeletal muscle of chronic ethanol-fed rats.Alcohol 8:173–177.
Jacobs, D.B., Mandelin, A.M., II, Giordano, T., Xue, I., Malter, J., Singh, L.D., Snyder, A.K., and Singh, S.P. (1995). AUUUA-specific mRNA binding proteins in astrocytes.Life Sci. 58:2083–2089.
Kennedy, L.A., and Mukerji, S. (1986). Ethanol neurotoxicity. 2. Direct effects on differentiating astrocytes.Neurobehav. Toxicol. Teratol. 8:17–21.
Klausner, R.D., Rouault, T.A., and Harford, J.B. (1993). Regulating the fate of MRNA: the control of cellular iron metabolism.Cell 72:19–28.
Krauss, S.W., Diamond, I., and Gordon, A.S. (1994). Selective inhibition by ethanol of the type 1 facilitative glucose transporter (GLUT1).Mol Pharmacol 45:1281–1286.
Kwon, Y.K., and Hecht, N.B. (1993). Binding of a phosphoprotein to the 3′ untranslated region of the mouse protamine 2 mRNA temporally represses its translation.Mol. Cel. Biol 13: 6547–6557.
Lancaster, F., Ed, (1994).Alcohol and Glial Cells, Research Monograph No. 27, NIH, Bethesda, MD.
Ledig, M., and Tholey, G. (1994). Fetal alcohol exposure and glial cell development. In (F.E. Lancaster, ed.),Alcohol and Glial Cells, Research Monograph No 27, NIH, Bethesda, MD, pp. 117–132.
Martin, P.R., Rio, D., Adinoff, B., Johnson, J.L., Bisserbe, J.C., Rawlings, P.R., Rohrbaugh, J.W., Stapleton, J.M., and Eckardt, M.J. (1992). Regional cerebral glucose utilization in chronic organic mental disorders associated with alcoholism.J. Neurospychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 4:159–167.
Martin, P.R., McCool, B.A., and Singleton, C.K. (1993). Genetic sensitivity to thiamine deficiency and development of alcoholic organic brain disease.Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res 17:31–37.
Martin, P.R., Adinoff, B., Weingartner, H., Mukerjee, A.B., and Eckardt, M.J. (1986). Alcoholic organic brain disease, nosology and pathophysiologic mechanisms.Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. & Biol. Psychiat. 10:147–164.
Miles, M.F., Diaz, J.E., and DeGuzman, V.S. (1991). Mechanisms of neuronal adaptation to ethanol. Ethanol induces Hsc70 gene transcription in NG108-15 neuroblastoma × glial cells.J. Biol. Chem. 266:2409–2414.
Miles, M.F., Wilke, N., Elliot, M., Tanner, W., and Shah, S. (1994). Ethanol-responsive genes in neural cells include the 78-kilodalton glucose-regulated protein (GRP78) and 94-kilodalton glucose-regulated protein (GRP94) molecular chaperones.Mol. Pharmacol. 46:873–879.
Pessin, J.E., and Bell, G.I. (1992). Mammalian facilitative glucose transporter family: Structure and molecular regulation.Ann. Rev. Physiol. 54:911–930.
Raju, T., Bignami, A., and Dahl, D. (1981).In vivo andin vitro differentiation of neurons and astrocytes in the rat embryo.Dev. Biol. 85:344–357.
Roeder, L.M., Hopkins, I.B., Kaiser, J.R., Hanukoglu, L., and Tildon, J.T. (1988). Thyroid hormone action on glucose transporter activity in astrocytes.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 156:275–281.
Sachs, H., Russell, J.A., Christman, D.R., and Cook, B. (1987). Alteration of regional cerebral glucose metabolic rate in non-Korsakoff chronic alcoholism.Arch. Neurol. 44:1242–1251.
Samson, Y., Baron, J.C., Feline, A., Bories, J., and Crouzel, C. (1986). Local cerebral glucose utilization in chronic alcoholics: a positron tomographic study.J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 49:1165–1170.
Sieber, J.E., and Traystman, R.J. (1992). Special issues: Glucose and the brain.Critical Care Med. 20:104–114, 1992.
Singh, S.P., Snyder, A.K., and Eman, S. (1990). Effects of ethanol on hexose uptake by cultured rat brain cells.Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 14:741–745.
Snyder, A.K., Singh, S.P., and Ehmann, S. (1992). Effects of ethanol on DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis in rat astrocyte cultures.Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 16:295–300.
Tewari, S., Brown, E.C., Gaultier, C.R., and Najarian, P. (1987). Translational regulation in rat brain hemispheres.Neurochem. Res. 12:179–188.
Vina, J.R., Salus, J.E., DeJoseph, M.R., Pallardo, F., Towfighi, J., and Hawkins, R.A. (1991). Brain energy consumption in ethanol-treated Long-Evans rats.J. Nutr. 121:879–886.
Walker, P., Donovan, J.A., Van Ness, B.G., Fellows, R.E., and Pessin, J.E. (1988). Glucose-dependent regulation of glucose transport activity, protein, and mRNA in primary cultures of rat brain glial cells.J. Biol. Chem. 263:15594–15601.
Wardzala, L.J., Cushman, S.W., and Salans, L.B. (1978). Mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell.J. Biol. Chem. 253:8002–8005.
Werner, H., Raizada, M.K., Mudd, L.M., Foyt, H.L., Simpson, I.A., Roberts, C.T. Jr., and Leroith, D. (1989). Regulation of rat brain/HepG2 glucose transporter gene expression by insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 in primary cultures of neuronal and glial cells.Endocrinology 125:314–320.
Williams-Hemby, L., and Porrino, L.J. (1994). Low and moderate doses of ethanol produce distinct patterns of cerebral metabolic changes in rats.Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 18:982–988.A1938001 00005 CS-SPJRNPDF [HEADSUP]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, L.D., Singh, S.P., Handa, R.K. et al. Effects of ethanol on GLUT1 protein and gene expression in rat astrocytes. Metab Brain Dis 11, 343–357 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02029495
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02029495