Summary
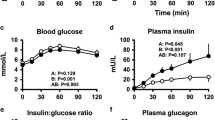
The present study was designed to determine the effect of low dose continuous and oscillatory intraportal insulin infusions upon subsequent glucose-induced insulin release. In overnight-fasted and anesthetized rats with indwelling catheters in the jugular vein, carotic artery, and mesenteric vein insulin was infused intraportally for 3 h via the mesenteric vein catheter at a continuous rate of 45 µU/kg·min, or the same amount of insulin was administered at alternating high (72 µU/kg·min) and low infusion rates (18 µU/kg·min), respectively, in 2-, 4-, 8-, and 16-min cycles (oscillatory infusions). Another group received a continuous infusion of saline. Glucose (0.4 g/kg) was given i.v. 30 min after the end of the insulin or saline infusion. During the 3-h infusion of insulin or saline the peripheral glucose level remained unchanged in all groups. In response to the i.v. glucose load peripheral arterial plasma insulin levels were significantly elevated after preceding oscillatory infusions compared to the continuous insulin infusion. As compared to the group receiving saline the glucose-induced insulin response after continuous insulin infusion was significantly reduced. The plasma glucose responses were not different except for inexplicably elevated glucose levels in the 4-min cycle group. No difference was observed for plasma glucagon levels in all groups. The present data demonstrate an augmented responsiveness of theβ-cell to glucose after a preceding oscillatory infusion of insulin and an impaired responsiveness to glucose after continuous insulin infusion. This indicates that an oscillatory insulin release might be of importance for an adequate regulation ofβ-cell function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goodner CJ, Walike BC, Koerker DJ, Ensinck JW, Brown AC, Chideckel EW, Palmer J, Kalnasy L (1977) Insulin, glucagon, and glucose exhibit synchronous, sustained oscillations in fasting monkeys. Science 195:177–179
Koerker DJ, Goodner CJ, Walike Hansen B, Brown AC, Rubenstein AH (1978) Synchronous sustained oscillation of C-peptide and insulin in the plasma of fasting monkeys. Endocrinology 102:1649–1652
Lang DA, Matthews DR, Peto J, Turner RC (1978) Cyclic oscillations of basal plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in human beings. New Engl J Med 301 (19):1023–1027
Hansen BC, Pek S, Koerker DJ, Goodner CJ, Wolfe RA, Schielke GP (1981) Neural influences on oscillations in basal plasma levels of insulin in monkeys. Am J Physiol 240:E5-E11
Land DA, Matthews DR, Burnett M, Turner RC (1981) Brief, irregular oscillations of basal plasma insulin and glucose concentrations in diabetic man. Diabetes 30:435–439
Lang DA, Matthews DR, Burnett M, Ward GM, Turner RC (1982) Pulsatile, synchronous basal insulin and glucagon secretion in man. Diabetes 31:22–26
Hansen BC, Jen K-LC, Pek SB, Wolfe RA (1982) Rapid oscillations in plasma insulin, glucagon, and glucose in obese and normal weight humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 54:785–792
Goodner GJ, Hom FG, Koerker DJ (1982) Hepatic glucose production oscillates in synchrony with the islet secretory cycle in fasting rhesus monkey. Science 215:1257–1260
Stagner JI, Samols E, Weir GC (1980) Sustained oscillations of insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin from the isolated canine pancreas during exposure to a constant glucose concentration. J Clin Invest 65:939–942
Yalow RS, Berson SA (1960) Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest 30:1157–1175
Faloona GR, Unger RH (1974) Glucagon. In: Jaffe BM, Behrman HR (eds) Methods of hormone radioimmunoassay. Academic Press, New York, pp 317–330
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stapelfeldt, W., Bender, H., Schusdziarra, V. et al. Effect of continuous and oscillatory portal vein insulin infusion upon glucose-induced insulin release in rats. Res. Exp. Med. 184, 67–71 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01852224
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01852224