Summary
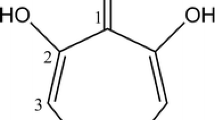
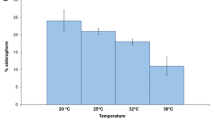
Several strains of the enterobacterial groupErwinia herbicola (Enterobacter agglomerans) were screened for siderophore production. After 3 days of growth in a low-iron medium, all strains studied produced hydroxamate siderophores. The retention values of the main siderophore during thin-layer chromatography on silica gel plates and on HPLC reversed-phase columns were identical with those of an authentic sample of ferrioxamine E (norcardamine). Gas-chromatographic analysis of the HI hydrolyzate yielded succinic acid and 1,5-diaminopentane in equimolar amounts; fast-atom-bombardment (FAB) mass spectroscopy showed a molecular mass of 653 Da. Iron from55Fe-labelled ferrioxamine E was well taken up by iron-starved cells ofE. herbicola (K m=0.1 μM,V max=8 pmol mg−1 min−1). However, besides ferrioxamine E (100%), several exogenous siderophores such as enterobactin (94.5%), ferric citrate (78.5%), coprogen (63.5%) and ferrichrome (17.5%) served as siderophores, suggesting the presence of multiple siderophore receptors in the outer membrane ofE. herbicola.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aydin M, Lucht N, König WA, Lupp R, Jung G, Winkelmann G (1985) Structure elucidation of the peptide antibiotics herbicolin A an B. Liebigs Ann Chem 1985: 2285–2300
Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology (1984) Krieg NR (ed), vol 1. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore/London
Bickel H, Bosshardt R, Gäugmann E, Reusser P, Vischer E, Voser W, Wettstein A, Zähner H (1960) Stoffwechselprodukte von Actinomyceten. Über die Isolierung und Charakterisierung der Ferrioxamine A-F, neuer Wuchsstoffe der Sideramin-Gruppe. Helv Chim Acta 43: 2118–2128
Braun V, Winkelmann G (1981) Stereoselective recognition of ferrichrome by fungi and bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 11:237–241
Braun V, Winkelmann G (1987) Microbial iron transport. Structure and function of siderophores. Prog Clin Biochem Med 5:67–99
Braun V, Hantke K, Eick-Helmerich K, Köster W, Preßler U, Sauer M, Schäffer S, Schöffler H, Staudenmaier H, Zimmermann L (1987) Iron transport systems in Escherichia coli. In: Winkelmann G, van der Helm D, Neilands JB (eds) Iron transport in microbes, plants and animals. VCH Verlagsgesellschaft, Weinheim, pp 35–51
Chatterjee AK, Starr MP (1980) Genetics ofErwinia species. Amin Rev Microbiol 34: 645–676
Colonna B, Nicoletti M, Visca P, Casalino M, Valenti P, Maimone F (1985) Composite IS1 elements encoding hydroxamate-mediated iron uptake in FIme plasmids from epidemicSalmonella spp. J Bacteriol 162:307–316
Dell A, Hider RC, Barber M, Bordoli RS, Sedgwick RD, Tyler AN, Neilands JB (1982) Field desorption and fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry of hydroxamate containing siderophores. Biomed Mass Spectrom 9:158–161
Ewing WH, Fife MA (1972)Enterobactir agglomerans (Beijerinck) com. nov. (the herbicola-lathyri bacteria). Int J Syst Bacteriol 22:4–11
Expert D, Toussaint A (1985) Bacteriocin-resistant mutants ofErwinia chrysanthemi: possible involvement of iron acquisition in pathogenicity. J Bacteriol 163:221–227
Gibson F, Magrath DJ (1969) The isolation and characterization of hydroxamic acid (aerobactin) formed byAerobacter aerogenes 62-I. Biochim Biophys Acta 192:175–184
Keller-Schierlein W, Prelog V (1961) Stoffwechselprodukte von Actinomyceten. 30. Über das Ferrioxamin E; ein Beitrag zur Konstitution des Nocardamins. Helv Chim Acta 44:1981–1985
Konetschny-Rapp S, Huschka H, Winkelmann G, Jung G (1988) High-performance liquid chromatography of siderophores from fungi. Biol Metals 1:9–17
Kotoujansky A (1987) Molecular genetics of pathogenesis by soft-rotErwinias., Annu Rev Phytopathol 25:405–430
Lawlor KM, Payne S (1984) Aerobactin genes inShigella spp. J Bacteriol 160: 266–272
Leong SA, Neilands JB (1982) Siderophore production by phytopathogenic microbial species. Arch Biochem Biophys 218:351–359
Matzanke BF, Müller GI, Raymond KN (1984) Hydroxamate siderophore iron uptake inE. coli: stereospeciflc recognition of ferric rhodotorulic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 121:922–930
Mergaert J, Verdonk L, Kersters K, Swings J, Boeufgras J-M, De Ley J (1984) Numerical taxonomy of Erwinia species using API systems. J Gen Microbiol 130: 1893–1910
Meyer JM, Abdallah MA (1980) The siderochromes of nonfluorescent pseudomonads: production of nocardamine by Pseudomonas stutzeri. J Gen Microbiol 118:125–129
Müller A, Zähner H (1968) Stoffwechselprodukte von Mikroorganismen. 65. Ferrioxamine ausEubacteriales. Arch Mikrobiol 62:257–263
O'Brien IG, Gibson F (1970) The structure of enterochelin and related 2,3-dihydroxy-N-benzoylserine conjugates fromEscherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta 215:393–402
Payne SM (1980) Synthesis and utilization of sidierophores byShigella flexneri. J Bacteriol 143:1420–1424
Pollack JR, Neilands JB (1970) Enterobactin, an iron transport compound from Salmonella typhimurium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 38: 989–992
Slade MB, Tiffln AI (1984) Biochemical and serological characterization of Erwinia. Methods Microbiol 15: 227–293
van der Helm D, Poling M (1976) The crystal structure of ferrioxamine E. J Am Chem Soc 98: 82–86
Warner PJ, Williams PH, Bindereif A, Neilands JB (1981) CoIV plasmid-specified aerobactin synthesis by invasive strains ofEscherichia coli. Infect Immun 33: 540–545
Wiebe C, Winkelmann G (1975) Kinetic studies on the specificity of chelate iron uptake in Aspergillus. J Bacteriol 123:837–842
Yang C, Leong J (1982) Production of desferrioxamines B and E from a ferroverdin-producingStreptomyces species. J Bacteriol 149: 381–383
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berner, I., Konetschny-Rapp, S., Jung, G. et al. Characterization of ferrioxamine E as the principal siderophore ofErwinia herbicola (Enterobacter agglomerans) . Biol Metals 1, 51–56 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01128017
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01128017