Abstract
Six compounds were identified from gland extracts of the cotton bollworm, Heliothis armigera(Hubner): (Z)-11-hexadecenal (Z11-16:Ald), (Z)-9-hexa-decenal (Z9-16:Ald), hexadecanal, (Z)-11-hexadecenol (Z11-16:OH), (Z)-7-hexadecenal (Z7-16:Ald), and (Z)-9-tetradecenal (Z9-14:Ald). Each of the compounds that were identified was examined for its ability to elicit sexual responses from male moths in a flight tunnel. Males flew upwind to Z11-16:Ald alone, but greater levels of copulatory responses were evoked with the addition of 2.5% Z9-16:Ald to the Z11-16:Ald. Addition of hexadecanal to the binary mixture had no effect in raising the behavioral response of the males in the flight tunnel. The effect of Z7-16:Ald on male flight depended on the loading. The addition of 1% of this component to 2 mg of the binary mixture reduced levels of copulatory response, but the same addition (1 %) to 10 μg of the binary mixture increased copulatory response. The addition of 79-14:Ald or Z11-16:OH to the binary mixture reduced behavioral responses of males. High loadings of the binary mixture (200–2000 μg) were better than a low loading (10 μg) in eliciting response of males.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buser, H. R., Arn, H., Guerin, P., and Rauscher, S. (1983). Determination of double bond position in mono-unsaturated acetates by mass spectrometry of dimethyl disulfide adducts.Anal. Chem. 55: 818–822.
Dunkelblum, E., and Kehat, M. (1989). Female sex pheromone components ofHeliothis peltigera (Lepidoptere: Noctuidae): Chemical identification from gland extracts and male response.J. Chem. Ecol. 15: 2233–2245.
Dunkelblum, E., Gothilf, S., and Kehat, M., (1980). Identification of the sex pheromone of the cotton bollworm,Hetiothis armigera, in Israel.Phytoparasitica 8: 209–211.
Dunkelblum, E., Tan, S. H., and Silk, P. J. (1985). Double-bond location in monounsaturated fatty acids by dimethyl disulfide derivatization and mass spectrometry: Application to analysis of fatty acids in pheromone glands of four Lepidoptera.J. Chem. Ecol. 11: 265–277.
Gothilf, S., Kehat, M., Jacobson, M., and Galun, R. (1978a). Screening pheromone analogues by EAG technique for biological activity on males ofEarias insulana, Heliothis armigera andSpodoptera littoralis.Envir. Entomol. 7: 31–35.
Gothilf, S., Kehat, M., Jacobson, M., and Galun, R. (1978b). Sex attractants for maleHeliothis armigera (Hbn).Experientia 34: 853–854.
Gothilf, S., Kehat, M. Dunkelblum, E., and Jacobson, M. (1979). Efficacy of (Z)-11-hexadecenal and (Z)-11-tetradecenal as sex attractants forHeliothis armigera on two different dispensers.J. Econ. Entomol. 72: 718–720.
Kehat, M., Gothilf, S., Dunkelbum, E., and Greenberg, S. (1980). Field evaluation of female sex pheromone components of the cotton bollworm,Heliothis armigera. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 27: 188–193.
Kehat, M., Gothilf, S., Dunkelblum, E., and Greenberg, S. (1982). Sex pheromone traps as a means of improving control programs for the cotton bollworm,Heliothis armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae).Envir. Entomol. 11: 727–729.
Leonhardt, B. A., and De Vilbiss, E. D. (1985). Separation and double-bond determination on nanogram quantities of aliphatic monounsaturated alcohols, aldehydes and carboxylic acid methyl esters.J. Chromatogr. 322: 484–490.
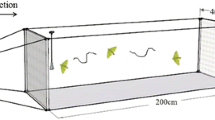
Miller, J. R., and Roelofs, W. L. (1978). Sustained-flight tunnel for measuring insect responses to wind-borne sex pheromones.J. Chem. Ecol. 4: 187–198.
Nesbitt, B. F., Beevor, P. S., Hall, D. R., and Lester, R. (1979). Female sex pheromone components of the cotton Bollworm,Heliothis armigera. J. Insect Physiol. 25: 535–541.
Nesbitt, B. F., Beevor, P. S., Hall, D. R., and Lester, R. (1980). (Z)-9-Hexadecenal: A minor component of the female sex pheromone ofHeliothis armigera.Entomol. Exp. Appl. 27: 306–308.
Piccardi, P., Capizzi, A., Cassani, G., Spinelli, P., Arsura, E., and Massardo, P. (1977). A sex pheromone component of the Old World bollworm,Heliothis armigera. J. Insect Physiol. 23: 1443–1445.
Pope, M. M., Gaston, L. K., and Baker, T. C. (1982). Composition, quantfication, and periodicity of sex pheromone gland volatiles from individualHeliothis virescens females.J. Chem. Ecol. 8: 1043–1055.
Pope, M. M., Gaston, L. K., and Baker, T. C. (1984). Composition, quantification, and periodicity of sex pheromone gland volatiles from individualHeliothis zea females.J. Insect Physiol. 30: 943–945.
Roelofs, W., and Bjostad, L. (1984). Biosynthesis of lepidopteran pheromones.Bioorg. Chem. 12: 279–298.
Rothschild, G. H. L. (1978). Attractants forHeliothis armigera and H. punctigera.J. Aust. Entomol. Soc. 17: 389–390.
Ryan, J. A. (1960). Significance tests for multiple comparison of proportions, variances, and other statistics.Psychol. Bull. 57: 318–328.
Shorey, H. H., and Hale, R. L. (1965). Mass-rearing of the larvae of nine Nocutid species on a simple artificial medium.J. Econ. Entomol. 58: 522–524.
Teal, P. E. A., and Tumlinson, J. H. (1987). The role of alcohols in pheromone biosynthesis by two noctuid moths that use acetate pheromone components.Arch. Insect Biochem. Physol. 4: 261–269.
Teal, P. E. A., Tumlinson, J. H., and Heath, R. R. (1986). Chemical and behavioral analyses of volatile sex pheromone components released by callingHeliothis virescens (F.) females (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae).J. Chem. Ecol. 12: 107–126.
Vetter, R. S., and Baker, T. C. (1984). Behavioral responses of maleHeliothis zea moths in sustained-flight tunnel to combinations of 4 compounds identified from female sex pheromone gland.J. Chem. Ecol. 10: 193–202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Contribution from the Agricultural Research Organization, The Volcani Center, Bet Dagan, Israel. No. 2455-E, 1988 series.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kehat, M., Dunkelblum, E. Behavioral responses of maleHeliothis armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) moths in a flight tunnel to combinations of components identified from female sex pheromone glands. J Insect Behav 3, 75–83 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01049196
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01049196