Abstract
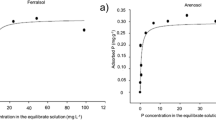
Soil Samples were collected from a field experiment conducted to evaluate the agronomic effectiveness of a reactive phosphate rock (PR), Sechura sand, relative to that of monocalcium phosphate (MCP) at different soil pHs and rates of application. The samples were analysed for P soluble in the soil solution and bicarbonate extractable P. The rate of dissolution of PR was calculated from the data on the fractionation of inorganic P. In MCP plots P in the soil solution decreased sharply with time especially at low pHs and high rates of fertiliser application. In PR plots the concentration remained with time at the same as or a slightly higher level than that was found one month after application. Solution concentration of P was lower at very high rates of PR application than at intermediate rates. In both MCP and PR plots bicarbonate extractable P decreased with increasing pH. Bicarbonate extractable P was linearly related to MCP but not to PR applied. The rate of dissolution and the proportion of PR dissolved decreased with increasing rates of PR application but the amount dissolved increased. Phosphate dissolved at high level of PR application did not seem to enhance proportionately either the concentration of P in soil solution or bicarbonate extractable P.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson GA (1988) Dissolution of rock phosphate in soil, plant and fertiliser systems. PhD Thesis, University of New England, Armidale, Australia
Barrow NJ (1985) Reactions of anions and cations with variable charge soils. Adv. Agron. 38: 183–230
Bolland MDA, Allen DG and Gilkes RJ (1989) The influence of seasonal conditions, plant species and fertiliser type on the prediction of plant yield using the Colwell bicarbonate soil test for phosphate. Fert Res 19: 143–158
Kanabo IAK and Gilkes RJ (1988) The effect of level of phosphate rock application on its dissolution in soil and on bicarbonate-soluble phosphorus. Fert Res 16: 67–85
Kirk GJD and Nye PH (1986) A simple model for predicting the rates of dissolution of sparingly soluble calcium phosphate in soil. II Applications of the model. J Soil Sci 37: 541–554.
Mackay AD, Gregg PEH and Syers JK (1984) Field evaluation of Chatham Rise phosphorite as a phosphatic fertiliser for pasture. NZ J Agric Res 27: 65–82
Murphy J and Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica Chimica Acta 27: 31–36
Olsen SR, Cole CV, Watanabe FS and Dean LA (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. United States Department of Agriculture Circular 939
Rajan SSS (1983) Effect of sulphur content of phosphate rock/sulphur granules on the availability of phosphate to plants. Fert Res 4: 287–296
Rajan SSS (1987) Phosphate rock and phosphate rock/sulphur granules as phosphate fertiliser and their dissolution in soil. Fert Res 11: 43–60
Rajan SSS, Fox RL, Saunders WMH, and Upsdell M (1991) Influence of pH, time and rate of application on phosphate rock dissolution and availability to pastures. I. Agronomic benefits. Fert Res 28: 85–93
Sorn-Srivichai P, Tillman RW, Syers JK and Cornforth IS (1984) The effect of soil pH on Olsen bicarbonate phosphate values. J Sci Food Agric 35: 257–264
Watkinson JH (1969) The kinetics of ion exchange in soil. PhD thesis, Victoria University, Wellington, New Zealand
Williams CH (1980) Soil acidification under clover pasture. Aust J Exp Agric Anim Husb 20: 561–567
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajan, S.S.S., Fox, R.L. & Saunders, W.M.H. Influence of pH, time and rate of application on phosphate rock dissolution and availability to pastures. Fertilizer Research 28, 95–101 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01048860
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01048860