Abstract
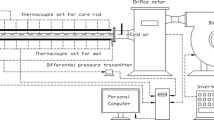
An experimental study was conducted on the heat transfer under the condition of constant heat flux and the flow around a circular cylinder with tripping-wires, which were affixed at ± 65° from the forward stagnation point on the cylinder surface. The testing fluid was air and the Reynolds number Red, based on the cylinder diameter, ranged from 1.2 × 104 to 5.2×104. Especially investigated are the interactions between the heat transfer and the flow in the critical flow state, in relation to the static pressure distribution along the cylinder surface and the mean and turbulent fluctuating velocities in the wake. It is found that the heat transfer from the cylinder to the cross flow is in very close connection with the width of near wake.
Zusammenfassung
Der Wärmeübergang bei konstantem Wärmestrom und die Strömung um einen Kreiszylinder mit Stolperdrähten, die bei ± 65° vom vorderen Staupunkt angebracht werden, wurden in dieser Arbeit untersucht. Das strömende Medium war Luft bei Reynolds-Zahlen, definiert mit dem Zylinderdurchmesser, von 1.2×104 bis 5.2×104. Besonders wurde die Wechselwirkung zwischen Wärmeübergang und Strömung im kritischen Bereich untersucht in Bezug auf die statische Druckverteilung um den Zylinder und die mittlere Schwankungsgeschwindigkeit im Totwasser. Es ergibt sich, daß der Wärmeübergang sehr eng mit der Breite der abgelösten Strömung zusammenhängt.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CD :
-
pressure drag coefficient=\(\mathop \smallint \limits_0^\prod \)Cp cos θ dθ
- Cp :
-
static pressure coefficient=(P−P∞)/1/2 ρU 2∞
- d:
-
cylinder diameter
- f:
-
vortex shedding frequency
- h:
-
heat transfer coefficient
- I:
-
electric current
- k:
-
roughness height
- Nu:
-
Nusselt number
- P:
-
static pressure
- q:
-
heat flux per unit area and unit time
- Red :
-
Reynolds number=U∞d/ν
- S:
-
area of heating surface
- St:
-
Strouhal number=fd/U∞
- T:
-
temperature
- U:
-
time mean velocity
- U∞ :
-
upstream velocity
- u′:
-
turbulent velocity fluctuation along mean flow direction
- V:
-
electric voltage
- W:
-
wake width defined as distance between points of U/U∞= 1.0
- W*:
-
non-dimensional half wake width=W/2d
- x:
-
horizontal distance from cylinder axis
- y:
-
vertical distance normal to wake axis
- ɛ:
-
tripping-wire diameter
- θ:
-
circumferential angle from stagnation point
- λ :
-
thermal conductivity of air
- ν :
-
kinematic viscosity of air
- ρ:
-
density of air
- b:
-
back
- m:
-
mean
- w:
-
wall
- ∞:
-
main flow
References
Achenbach, E.: Distribution of local pressure and skin friction around a circular cylinder in cross-flow up to Re=5 × 106. J. Fluid Mech. 34 (1968) 625–639
Achenbach, E.: Total and local heat transfer from a smooth circular cylinder in cross-flow at high Reynolds number. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 18 (1975) 1387–1396
Achenbach, E.: Influence of surface roughness on the cross-flow around a circular cylinder. J. Fluid Mech. 46 (1971) 321–335
Achenbach, E.: The effect of surface roughness on the heat transfer from a circular cylinder to the cross-flow of air. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 20 (1977) 359–369
Richter, A.; Naudascher, E.: Fluctuating forces on a rigid circular cylinder in confined flow. J. Fluid Mech. 78 (1976) 561–576
Goldstein, S. (ed.): Modern Developments in Fluid Dynamics. Dover: (1965)
Fage, A.; Warsap, J. H.: The effect of turbulence and surface roughness on the drag of a circular cylinder. Aero. Res. Counc. Lond. R & M. No. 1283 (1930)
Aiba, S.; Yamazaki, Y.: An experimental investigation of heat transfer around a tube in a bank. J. Heat Transf. Trans. ASME 98C (1976) 503–508
Giedt, W.H.: Investigation of variation of point unit heat-transfer coefficient around a cylinder normal to an air stream. Trans. ASME 71 (1949) 375–381
Schmidt, E.; Wenner, K.: Wärmeabgabe über den Umfang eines angeblasenen geheizten Zylinders. Forsch. Geb. IngWes. 12 (1941) 65–73
Fujita, H.; Takahama, H.; Yamasita, R.: The forced convective heat transfer on a plate with a cylinder inserted in the boundary layer. Trans. JSME. 42 (1976) 2828–2836
Richardson, P.D.: Heat and mass transfer in turbulent separated flows. Chemical Engng. Sci. 18 (1963) 149–155
Apelt, C.J.; West, G.S.; Szewczyk, A.A.: The effects of wake splitter plates on the flow past a circular cylinder in the range 104 <Re<5x104. J. Fluid Mech. 61 (1973) 187–198
Szechenyi, E.: Supercritical Reynolds number simulation for two-dimensional flow over circular cylinders. J. Fluid Mech. 70 (1975) 529–542
Roshko, A.: On the wake and drag of bluff bodies. J. Aeron. Sci. 22 (1955) 124–132
Wieselsberger, C.: Neuere Feststellungen über die Gesetze des Flüssigkeits- und Luftwiderstands. Phys. Z. 22 (1921) 321–328
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aiba, S., Ota, T. & Tsuchida, H. Heat transfer and flow around a circular cylinder with tripping-wires. Wärme- und Stoffübertragung 12, 221–231 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00997314
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00997314