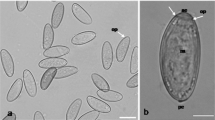
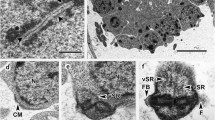
Abstract
Using light and electron microscopy, we studied the ultrastructure ofSpironucleus muris (syn.Hexamita muris) from spontaneously and experimentally infected normal and athymic mice. Kinetosomes and cytoskeletal fibers arranged in two-fold rotational symmetry are similar to the speciesSpironucleus elegans from amphibians. Taxonomic proposals and a possible evolutionary scheme for diplomonad genera accepted at the last International Congress of Parasitology are given. The genusHexamita should be divided into two new genera:Hexamita (usually free-living) andSpironucleus (exclusively parasitic). We consider previous descriptions of hexamitiasis in rodents as dealing with spironucleosis. We distinguish a fresh and an old cyst of the parasite on the basis of structure, light refraction, location in the host, and infectivity. The transition from a fresh to an old cyst paralles the dessication of feces. The trophozoites can damage the microvilli and penetrate into the epithelium. We explain the differences in findings concerning intestinal lesions and forms of the disease (from acute to chronic to latent) by differences in the virulence of different parasite strains and by differences in inherent host resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bingham, A.K., Meyer, E.A.:Giardia excystation can be induced in vitro in acidic solutions. Nature277, 301–302 (1979)
Boorman, G.A., Lina, P.H.C., Zurcher, C., Nieuwerkerk, H.T.M.:Hexamita andGiardia as a cause of mortality in congenitally thymus-less (nude) mice. Clin. Exp. Immunol.15, 623–627 (1973)
Brugerolle, G.: Contribution à l'étude cytologique et phylétique de Diplozoaires (Zoomastigophorea, Diplozoa, Dangeard 19710). III. Etude ultrastructurale du genreHexamita (Dujardin, 1838). Protistologica10, 83–90 (1974)
Brugerolle, G.: Contribution à l'étude cytologique et phylétique des Diplozoaires (Zoomastigophorea, Diplozoa, Dangeard 1910). V. Nouvelle interprétation de l'organisation cellulaire deGiardia. Protistologica11, 99–109 (1975a)
Brugerolle, G.: Contribution à l'étude cytoloqique et phylétique des Diplozoaires (Zoomastigophorea, Diplozoa, Dangeard 1910). VI. Caractères généraux des Diplozoaires. Protistologica11, 111–118 (1975b)
Brugerolle, G.: Etude ultrastructurale du genreEnteromonas da Fonseca (Zoomastigophorea) et révision de l'ordre des Diplomonadida Wenyon. J. Protozool.22, 468–475 (1975c)
Brugerolle, G.: Contribution à l'étude cytologique des Protozoaires Zooflagellés parasites: Proteromonadida, Retortamonadida, Diplomonadida, Oxymonadida, Trichomonadida. Thèse, Université Clermont II, Série E, no 227, 1976
Brugerolle, G.: Cytologic, taxonomic and evolutionary aspects of the diplomonad parasites. Proceedings of the Fourth International Congress of Parasitology, Warsaw, Poland, August 1978. Short Communication Section B, 93 1978 (in press)
Brugerolle, G., Taylor, F.J.R.: Taxonomy, cytology and evolution of the Mastigophora. In: Protozoological actualities. Report of the Fifth International Congress of Protozoology, S.H. Hutner, ed., pp. 14–28. New York: 1977
Brugerolle, G., Joyon, L., Oktem, N.: Contribution à l'étude cytologique et phylétique des Diplozoaires (Zoomastigophorea, Diplozoa Dangeard 1910). I. Etude ultrastructurale du genreTrepomonas (Dujardin). Protistologica9, 339–348 (1973a)
Brugerolle, G., Joyon, L., Oktem, N.: Contribution à l'étude cytologique et phylétique des Diplozoaires (Zoomastigophorea, Diplozoa Dangeard 1910). II. Etude ultrastructurale du genreSpironucleus (Lavier 1936). Protistologica9, 495–502 (1973b)
Brugerolle, G., Joyon, L., Oktem, N.: Contribution à l'etude cytologique et phylétique des Diplozoaires (Zoomastigophorea, Diplozoa Dangeard 1910). IV. Etude ultrastructurale du genreOctomitus (Prowazek 1904). Protistologica10, 457–463 (1974)
Erlandsen, S., Chase, D.G.: Paneth cell function: phagocytosis and intracellular digestion of intestinal organisms. I.Hexamita muris. J. Ultrastruct. Res.41, 296–318 (1972)
Flatt, R.E., Halvorsen, J.A., Kemp, R.L.: Hexamitiasis in a laboratory mouse colony. Lab. Anim. Sci.28, 62–65 (1978)
Grassé, P.P., ed.: Traité de zoologie. I. Paris: Masson, 1952
Herweg, C., Kunstýř, I.: Effect of intestinal flagellateSpironucleus (Hexamita) muris and of dimetridazole on intestinal microflora in thymus-deficient (nude) mice. Zentralbl. Bakteriol. (Orig. A)245, 262–269 (1979)
Honigberg, B.M., Vickerman, K., Kulda, J., Brugerolle, G.: Cytology and taxonomy of parasitic flagellates: A review. Report of the section B5 of the Fourth International Congress of Parasitology, Warsaw 1978 (in press)
Keast, D., Chesterman, F.C.: Changes in macrophage metabolism in mice heavily infected withHexamita muris. Lab. Anim.6, 33–39 (1972)
Kruiningen, van, H.J., Knibbs, D.R., Burke, C.N.: Hexamitiasis in laboratory mice. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc.173, 1202–1204 (1978)
Kulda, J., Nohýnková, E.: Flagellates of the human intestine and of intestines of other species. In: Parasitic protozoa, J.P. Kreier, ed., vol. II, pp. 1–138. New York: Academic Press 1978
Kunstýř, I.: Infectious form ofSpironucleus (Hexamita) muris: banded cysts. Lab. Anim.11, 185–188 (1977)
Kunstýř, I.:Spironucleus muris und die Spironukleose thymus-defizienter Mäuse. Habilitationsschrift, Medizinische Hochschule Hannover 1978
Kunstýř, I., Ammerpohl, E.: Resistance of faecal cysts ofSpironucleus muris to some physical factors and chemical substances. Lab. Anim.12, 95–97 (1978)
Kunstýř, I., Friedhoff, K.T.: Parasitic and mycotic infections in laboratory animals. In: Proceedings of the VIIth Symposium of the International Committee on Laboratory Animals, S. Erichsen, H.A. Solleveld, A. Spiegel, eds, Stuttgart: Gustav Fischer Verlag (in press)
Kunstýř, I., Ammerpohl, E., Meyer, B.: Experimental spironucleosis (hexamitiasis) in the nude mouse as a model for immunologic and pharmacologic studies. Lab. Anim. Sci.27, 782–788 (1977a)
Kunstýř, I., Meyer, B., Ammerpohl, E.: Spironucleosis in nude mice: an animal model for immunoparasitologic studies. In: Proceedings of the Second International Workshop on Nude Mice, T. Nomura, N. Ohsawa, N. Tamauki, K. Fujiwara, eds., pp. 17–27. Tokyo: University of Tokyo Press, Stuttgart: Gustav Fischer Verlag 1977b
Lavier, G.: Sur la structure des Flagellés du genreHexamita (Dujardin). C.R. Soc. Biol. (Paris)121, 1177–1180 (1936)
Lussier, G., Loew, F.M.: An outbreak of hexamitiasis in laboratory mice. Can. J. Comp. Med.34, 350–353 (1970)
MacDonald, T.T., Ferguson, A.: Small intestinal epithelial cell kinetics and protozoal infection in mice. Gastroenterology74, 496–500 (1978)
Matthiesen, T., Kunstýř, I., Tuch, K.:Hexamita muris-Infektion bei Mäusen und Feldhamstern in einem Versuchstierbestand. Z. Versuchstierkd.18, 113–120 (1976)
Meshorer, A.: Hexamitiasis in laboratory mice. Lab. Anim. Care19, 33–37 (1969)
Nemanic, C., Owen, R.L., Stevens, D.P., Mueller, J.C.: Ultrastructural observations on giardiasis in a mouse model. II. Endosymbiosis and organelle distribution inGiardia muris andGiardia lamblia. J. Infect. Dis.140, 222–228 (1979)
Ruitenberg, E.J., Kruyt, B.C.: Effect of intestinal flagellates on immune response of mice. Parasitology71, 30 (1975)
Sebesteny, A.: Pathogenicity of intestinal flagellates in mice. Lab. Anim.3, 71–77 (1969)
Sheffield, H.G., Bjorvatn, B.: Ultrastructure of the cyst ofGiardia lamblia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg.26, 23–30 (1977)
Thiery, J.P., Rambourg, A.: Cytochimie des polysaccharides. J. Microsc.21, 225–232 (1974)
Wagner, J.E., Doyle, R.E., Ronald, N.C., Garrison, R.G., Schmitz, J.A.: Hexamitiasis in laboratory mice, hamsters and rats. Lab. Anim. Sci.24, 349–354 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brugerolle, G., Kunstýř, I., Senaud, J. et al. Fine structure of trophozoites and cysts of the pathogenic diplomonadSpironucleus muris . Z. Parasitenkd. 62, 47–61 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00925366
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00925366