Abstract
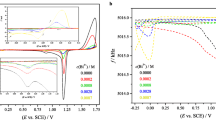
The cyclic voltammetric response of iridium oxide films, grown electrochemically in acidic solutions, can display a notable dependence on the time spent in the reduced state and on other factors such as the carrying out of very slow sweep rate experiments. This is seen primarily as a substantial positive shift of the anodic peaks and in a diminishment, by up to about 50%, in the reaction kinetics. This effect, termed as film ageing, can be reversed, either by long times of cycling over an extended range of potential or by a brief holding period in the oxidized state of the film. Oxide films do not exhibit ageing in alkaline solutions. It is, therefore, suggested that film ageing is associated primarily with the loss of water from the film in acidic solutions at negative potentials, resulting in the inhibition of subsequent ion/solvent transport processes in the film.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Capon and R. Parsons,J. Electroanal. Chem. 39 (1972) 275.
D. N. Buckley and L. D. Burke,J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 171 (1975) 1447.
J. O. Zerbino, N. R. de Tacconi and A. J. Arvia,J. Electrochem. Soc. 125 (1978) 1266.
S. Gottesfeld and S. Srinivasan,J. Electroanal. Chem. 86 (1978) 89.
S. Gottesfeld and J. D. E. McIntyre,J. Electrochem. Soc. 126 (1980) 742.
S. H. Glarum and J. H. Marshall,ibid. 127 (1980) 1457.
J. Mozota and B. E. Conway,ibid. 128 (1981) 2142.
Idem, Electrochim. Acta 28 (1983) 1, 9.
V. I. Birss, R. Meyers, H. Angerstein-Kozlowska and B. E. Conway,J. Electrochem. Soc. 131 (1984) 1502.
L. D. Burke, J. K. Mulcahy and D. P. Whelan,J. Electroanal. Chem. 163 (1984) 117.
L. D. Burke and D. P. Whalen,ibid. 162 (1984) 121.
L. D. Burke and R. A. Scannell,ibid. 175 (1984) 119.
D. A. J. Rand and R. Woods,ibid. 55 (1984) 375.
P. G. Pickup and V. I. Birss,ibid. 220 (1987) 83.
P. G. Pickup and V. I. Birss,J. Electrochem. Soc. 135 (1988) 126.
Idem, J. Electroanal. Chem. 240 (1988) 171.
Idem, J. Electrochem. Soc. 135 (1988) 41.
Idem, J. Electroanal. Chem. 240 (1988) 185.
M. L. Hitchmann and S. Ramanathan,Analyst 113 (1988) 35.
M. Vukovic,J. Appl. Electrochem. 17 (1989) 737.
D. Cukman and M. Vukovic,J. Electroanal. Chem. 279 (1990) 283.
M. Vukovic,J. Appl. Electrochem. 20 (1990) 969.
R. Kotz, C. Barbero and O. Haas,J. Electroanal. Chem. 296 (1990) 37.
V. I. Birss, H. Elzanowska and S. Gottesfeld,ibid. 318 (1991) 327.
L. S. Robblee, J. L. Lefko and S. B. Brummer,J. Electrochem. Soc. 130 (1983) 731.
C. L. Ballestrasse, R. T. Ruggeri and T. Beck,Ann. Biomed. Eng. 13 (1985) 405.
A. H. Schroeder, F. B. Kaufman, V. Patel and E. M. Engler,J. Electroanal. Chem. 113 (1980) 193.
A. H. Schroeder and F. B. Kaufman,ibid. 113 (1980) 209.
Yu-Min Tsou, Hsu-Yang Liu and A. J. Bard,J. Electrochem. Soc. 135 (1988) 1669.
S. Gottesfeld, A. Redondo, I. Rubinstein and S. W. Feldberg,J. Electroanal. Chem. 265 (1989) 15.
P. Daum and R. W. Murray,J. Phys. Chem. 85 (1981) 389.
H. S. White, J. Leddy and A. J. Bard,J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 104 (1982) 481.
K. Lian and V. I. Birss,J. Electroanal. Chem. 319 (1991) 227.
H. Elzanowska, J. Segal and V. I. Birss,J. Electroanal. Chem., submitted.
Idem, J. Electrochem. Soc., submitted.
H. A. Kozlowska and B. E. Conway,J. Electroanal. Chem. 95 (1979) 273.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This paper is dedicated to Professor Brian E. Conway on the occasion of his 65th birthday and in recognition of his outstanding contribution to electrochemistry.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elzanowska, H., Birss, V.I. Reversible ageing of iridium oxide electrodes in acidic solutions. J Appl Electrochem 23, 646–654 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00721957
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00721957