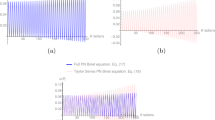
Abstract
A brief description is given of the present state of some aspects of work on the theory of the long-period features of the orbit of Saturn's satellite Hyperion. Expressions resulting from the use of a Lie series transformation, which give a theory of the long-period motion to the second order in the mass of Titan, and also a differential correction process, provide a procedure for the construction of a dynamically consistent set of parameters of the long-period motion, including co-efficients of the long-period terms, using a fit to observationally determined values of such parameters. This is carried out with two sets of data from the reduction of the two main sequences of observations of the satellite, those between 1875 and 1922, and also those between 1967 and 1983.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campbell, J.K. and Anderson, J.D.: 1989,Astron. J.,97, 1485–1495.
Hill, G.W.: 1888,Astron. J.,8, 57–62.
Message, P.J.: 1989,Celest. Mech.,45, 45–53.
Newcomb, S.: 1891,Astron. Papers of the American Ephemeris, III.
Taylor, D.B., Sinclair, A.T., and Message, P.J.: 1987,Astron. & Astrophys.,181, 383–390.
Taylor, D.B.: 1993,Astron. & Astrophys., in press.
Woltjer, J.: 1928,Annalen van de Sterrewacht te Leiden,XVI, Pt.3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Message, P.J. On the second order long-period motion of Hyperion. Celestial Mech Dyn Astr 56, 277–284 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00699738
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00699738