Summary
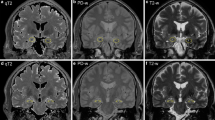
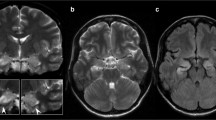
In two patients with limbic encephalitis serial magnetic resonance (MR) imaging showed evolution of abnormal high-signal intensity in both hippocampal formations on T2-weighted images.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brierley JB, Corsellis JA, Hierons R, Nevin S (1960) Subacute encephalitis of later adult life mainly affecting the limbic areas. Brain 83:356–368
Corsellis JAN, Goldberg GJ, Norton AR (1968) “Limbic encephalitis” and its association with carcinoma. Brain 91:481–496
Camara EG, Chelume GJ (1987) Paraneoplastic limbic encephalopathy. Brain Behav Immun 1:349–355
Burton GV, Bullard DE, Walther PJ, Burger PC (1988) Paraneoplastic limbic encephalopathy with testicular carcinoma: a reversible neurological syndrome. Cancer 62:2248–2251
Kohler J, Hufschmidt A, Hermle L, Volk B, Lücking CH (1988) Limbic encephalitis: two cases. J Neuroimmunol 20:177–178
Lacomis D, Khoshbin S, Schick RM (1990) MR imaging of paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis. J Comput Assist Tomogr 14:115–117
Ingenito GG, Berger JR, David NJ, Norenberg MD (1990) Limbic encephalitis associated with thymoma. Neurology 40:382
Newman NJ, Bell JR, MC Kee AC (1990) Paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis: neuropsychiatric presentation. Biol Psychiatry 27: 529–542
Langston JW, Dorfman LJ, Forno LS (1975) “Encephalo-myeloneuritis” in the absence of cancer. Neurology 25:633–637
Case record of the Massachusetts General Hospital (1989) Case 39, 1988. N Engl J Med 319:849–860
McArdle JP, Millingen KS (1988) Limbic encephalitis associated with malignant thymoma. Pathology 20:292–295
Hollander AM den, Hulst AM van, Meerwaldt JD, Haasjes JG (1989) Limbic encephalitis: a rare presentation of small-cell lung carcinoma. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 11:388–392
Heinz ER, Crain BJ, Radtke RA, Berger PC, Friedman AH, Djang WT, Wilkinson WE (1990) MR imaging in patient with temporal lobe seizure: correlation of results with pathologic findings. AJNR 11:827–832
Spagnoli MV, Grossman RI, Packer RJ, Hackney DB, Goldberg HI, Zimmerman RA, Bilaniuk LT (1987) Magnetic resonance imaging determination of gliomatosis cerebri. Neuroradiology 29:15–18
Davidson HD, Steiner RE (1985) Magnetic resonance imaging in infections of the central nervous system. AJNR 6:499–504
Lavi E, Fishman PS, Highkin MK, Weiss SR (1988) Limbic encephalitis after inhalation of a murine coronavirus. Lab Invest 58: 31–36
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kodama, T., Numaguchi, Y., Gellad, F.E. et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of limbic encephalitis. Neuroradiology 33, 520–523 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00588045
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00588045