Summary
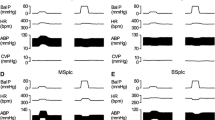
In dogs, anaesthetized with chloralose, fentanyl (5 μg/kg i.v.) augmented the bradycardia produced by electrical stimulation of the carotid sinus nerves. In contrast, the same dose of the drug did not change the bradycardic response to stimulation of the nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) indicating that a central facilitation of baroreceptor impulses occurs within the NTS, probably at the first synapse of baroreceptor reflex fibres.
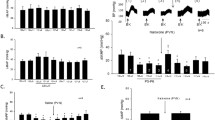
Bilateral destruction of the NTS caused a ful-minating hypertension and tachycardia similar to that after cutting the baroreceptor afferent fibres. After both procedures, fentanyl (20 μg/kg i.v.) produced marked hypotension and bradycardia. The bradycardic effect was abolished by cutting both vagal nerves when the dogs were pretreated with a β-adrenoceptor blocking agent (S 2395, 50 μg/kg i.v.).
The results provide evidence that the NTS is not the main site of action either for the hypotensive effect or for the vagally mediated bradycardia of fentanyl. Since the dorsal nucleus of the vagal nerve was destroyed together with the NTS, this nucleus does also not appear to be a major site of the action of fentanyl.
Blockade of dopamine receptors by haloperidol or pimozide or of serotonin receptors by methysergide did not change the hypotensive, bradycardic and sympathoinhibitory effects of fentanyl.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler, A., Kostowski, W., Rechia, M., Samanin, R.: Anatomical specificity as the critical determinant of the interrelationship between raphe lesions and morphine analgesia. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 32, 39–44 (1975)
Amico, D., Patel, B., Klavans, H.: The effect of methysergide on 5-hydroxytryptamine turnover in whole brain. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 28, 454–456 (1976)
Antonaccio, M. J., Kelly, E., Halley, J.: Centrally mediated hypotension and bradycardia by methysergide in anesthetized dogs. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 33, 107–177 (1975)
Biscoe, T., Sampson, S.: Field potentials evoked in the brain stem of the cat by stimulation of the carotid sinus, glossopharyngeal, aortic and superior laryngeal nerves. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 209, 341–358 (1970)
Contreras, E., Tamayo, L.: Influence of changes in brain 5-hydroxytryptamine on morphine analgesia. Arch. Biol. med. exp. 4, 69–71 (1967)
Cottle, M. K.: Degeneration studies of primary afferents of IXth and Xth cranial nerves in the cat. J. comp. Neurol. 122, 329–345 (1964)
Crill, W., Reis, D.: Distribution of carotid sinus and depressor nerve in cat brainstem. Amer. J. Physiol. 214, 269–276 (1968)
Daskalopoulos, N., Laubie, M., Schmitt, H.: Localization of the central sympatho-inhibitory effect of a narcotic analgesic agent, fentanyl in cats. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 33, 91–97 (1975)
Edis, A. J., Shepherd, J. T.: Selective denervation of aortic baroreceptors and chemoreceptors in dogs. J. appl. Physiol. 30, 294–296 (1971)
Genevese, E., Zonta, N., Mantegazza, P.: Decreased antinociceptive activity of morphine in rats pretreated intraventricularly with 5,6-dihydroxytryptamine, a long lasting selective depletor of brain serotonin. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 32, 359–364 (1973)
Gorlitz, B. D., Frey, H. H.: Central monoamines and antinociceptive drug action. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 20, 171–180 (1972)
Humphrey, D. R.: Neuronal activity in the medulla oblongata of the cat evoked by stimulation of the carotid sinus nerve. In: Baroreceptors and hypertension (P. Kezdi, ed.), pp. 131–168. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1967
Laubie, M., Schmitt, H., Canellas, J., Roquebert, J., Demichel, P.: Action hypotensive et bradycardisante du dextromoramide: origine centrale, role des barorecepteurs et du système nerveux autonome. J. Pharmacol. (Paris) 4, 369–384 (1973a)
Laubie, M., Schmitt, H., Mouille, P., Cheymol, G., Gilbert, J. C.: Effects adrenolytiques beta et hemodynamiques du dl (hydroxy 2′-t butylamino 3′ propyloxy) 8 thiochromane (S 2395). Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. 201, 323–333 (1973b)
Laubie, M., Schmitt, H., Canellas, J., Roquebert, J., Demichel, P.: Centrally mediated bradycardia and hypotension induced by narcotic analgesics: dextromoramide and fentanyl. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 28, 66–75 (1974)
Lipski, J., McAllen, R., Spyer, K.: The sinus nerve and baroreceptor input to the medulla of the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 251, 61–78 (1975)
McAllen, R., Spyer, K.: The location of cardiac vagal preganglionic motoneurones in the medulla of the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 258, 187–204 (1976)
Schmitt, H., Schmitt, H., Boissier, J. R., Guidicelli, J. F., Fichelle, J.: Cardiovascular effects of 2-(2,6-dichlorophenylamino)-2-imidazoline (St 155). Central sympathetic structures. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 2, 340–346 (1968)
Seller, H., Illert, H.: Lokalisation der ersten Umschaltstelle der Karotissinusafferenz und über ihre Funktion in der Reflexverarbeitung. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 300, R 72 (1968)
Seller, H., Illert, H.: The localization of the first synapse in the carotid sinus baroreceptor reflex pathway and its alteration of the afferent input. Pflügers Arch. 306, 1–19 (1969)
Sparkes, C. G., Spencer, P. S.: Antinociceptive activity of morphine after injection of biogenic amines in the cerebral ventricles of the conscious rats. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 42, 230–241 (1971)
Tenen, S. S.: The effects of p-chlorophenylalamine, a serotonin depletor, on avoidance acquisition, pain sensitivity and related behaviour in the rat. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 10, 204–219 (1967)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laubie, M., Schmitt, H. & Drouillat, M. Central sites and mechanisms of the hypotensive and bradycardic effects of the narcotic analgesic agent fentanyl. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 296, 255–261 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00498691
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00498691