Summary
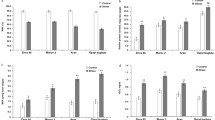
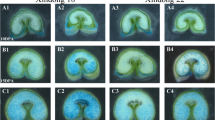
Kernels of Zea mays were subjected to dehydration treatment at various times during germination. Embryos from kernels dehydrated during the first 36 h of germination are resistant to dehydration and subsequently germinate earlier than controls. Dehydration of kernels germinated during 72h leads to an irreversible arrest of growth of the embryos. However, autoradiographic observations showed that these embryos are still able to incorporate [3H] uridine and probably [4-5-3H] lysine. Incorporation of [3H] thymidine does not occur. The effect of dehydration on root ultrastructure was studied. In embryos dehydrated after 24 h and 72 h of germination, condensation of chromatin is seen and association of elements of rough endoplasmic reticulum with vacuoles and glyoxysomes can be noted. These changes are reversible in drought-resistant embryos and irreversible in drought-sensitive embryos. However, more notable changes than those seen after 24 h can be observed in embryos dehydrated after 72 h of germination: mitochondria and proplastids can not be distinguished with certainty, glyoxysomes fuse and preferably dispose at the periphery of the cell. Rehydration of drought-sensitive embryos causes breakdown in plasma and nuclear membranes, which leads to the loss of cellular compartimentalization. Moreover, the chromatin remains definitively condensed and has lost its function of genetic regulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berjak, P., Villiers, T.A.: Ageing in plant embryos. II: age induced damage and its repair during early germination. New Phytol. 71, 135–144 (1972)
Berrie, A.M.M., Drennan, D.S.H.: The effect of hydration-dehydration on seed germination. New Phytol. 70, 135–142 (1971)
Buttrose, M.S.: Ultrastructure of developing wheat endosperm. Austral. J. Biol. Sci. 16, 305–317 (1963)
Chen, D., Sarid, S., Katchalski, E.: The role of the water stress in the inactivation of messenger RNA of germinating wheat embryos. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 61, 1378–1383 (1968)
Dagnelie, P.: Théorie et méthode statistique. Tome II. Ed. J. Duculot. S.A. Gembloux (1970) Presses Agronom. Gembloux
de Barsy, Th., Deltour, R., Bronchart, R.: Study of nucleolar vacuolation and RNA synthesis in embryonic root cells of Zea mays. J. Cell Sci 16, 95–112 (1974)
Deltour, R., Jacqmard, A.: Relation between water stress and DNA synthesis during germination of Zea mays L. Ann. Bot. 38, 529–534 (1974)
Hanson, A.D.: The effects of imbibition drying treatments on wheat seads. New Phytol. 72, 1063–1073 (1973)
Jakob, K.M., Bovey, F.: Early nucleic acid and protein syntheses and mitoses in the primary root tips of germinating Vicia faba. Expl. Cell Res. 54, 118–126 (1969)
Lison, L.: Statistique appliquée à la biologie expérimentale. Paris: Gauthier-Villars 1968
Marinos, N.G., Fife, D.N.: Ultrastructural changes in wheat embryos during a “Presowing drought hardening” treatment. Protoplasma 74, 381–396 (1972)
Miksche, J.P.: DNA synthesis in primary root of Glycine max during germination. Canad. J. Bot. 44, 789–794 (1966)
Monneron, A., Moule, Y.: Critical evaluation of specificity in electron microscopical radioautoradiography in animal tissues. Exptl. Cell Res. 56, 179–193 (1969)
Nir, I., Klein, S., Pojakoff-Mayber, M.: Effect of moisture stress on submicroscopic structure of maize roots. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 22, 17–33 (1969)
Pochon, J., Tardieux, P.: Techniques d'analyse en microbiologie du sol. Edition de la Tourelle (1962)
Rejman, E., Buchowicz, J.: The sequence of initiation of RNA, DNA and protein synthesis in the wheat grains during germination. Phytochemistry 10, 208–212 (1971)
Reynolds, E.S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electronopaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208–212 (1963)
Sen, S., Osborne, D.J.: Germination of rye embryos following hydration-dehydration treatments: enhancement of protein and RNA synthesis and earlier induction of DNA replication. J. Expl. Bot. 25 (89), 1010–1019 (1974)
Van de Walle, C., Bernier, G.: The onset of cellular synthetic activity in roots of germinating corn. Exptl. Cell Res. 55, 378–384 (1964)
Van de Walle C.: Mak column chromatography of the first RNA synthesized during germination of Zea mays embryos. FEBS Letters 16, 219–222 (1971)
Van de Walle, C., Bernier, G., Deltour, R., Bronchart, R.: in Press: Sequence of reactivation of ribonucleic acid synthesis during early germination of the maize embryo. Plant Physiol. 57 (1976)
Yoo, B.Y.: Ultrastructural changes in cells of Pea embryo radicle during germination. J. Cell Biol. 45, 158–171 (1970)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crèvecoeur, M., Deltour, R. & Bronchart, R. Cytological study on water stress during germination of Zea mays . Planta 132, 31–41 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00390328
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00390328