Summary
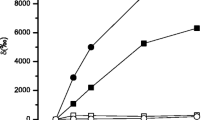
The uptake of phosphate as influenced by sodium and potassium ions was investigated in the light and in the dark. It was found to be a function of the external phosphate concentration. At a low concentration (up to 10−5 mol/l) in the presence of Na+ phosphate is quickly absorbed and hence phosphate is the limiting factor for further labelling. In the presence of K+ phosphate uptake is constant over a long period.
The enhancement of phosphate uptake by Na+ is also found when the external concentration of P is raised up to 10−4 mol/l. Then the gross uptake proceeds over six hours, with the greatest Na+-dependent increase occurring in the label of the TCA-insoluble phosphate fraction (Pu).
The phosphate uptake is strongly dependent on the pH of the reaction mixture. In the presence of Na+ it is highest between pH 5.6 and 7. As the uptake in the presence of K+ parallels the dissociation curve of the dihydrogen form H2PO −4 , the Na+-enhancement is optimal in the alkaline pH range (pH 8).
On the basis of a comparison between the pH-dependence of phosphate uptake and the dependence of the uptake on the external phosphate concentration analysed by a method of enzyme kinetics, it is suggested that Ankistrodesmus metabolically transports H2PO −4 but not HPO =4 . Moreover, it is concluded from the absence of light stimulation and the weak inhibition of the uptake by DCMU or CCCP in the presence of K+ that at low P-concentrations the diffusion is limiting the uptake. Only at higher concentrations is an active phosphate uptake measured.
Furthermore it is concluded that the observed Na+-stimulation of the 32P-labelling of the TCA-soluble and insoluble compounds inside the cell is indirect and depends only on the action of Na+ and K+ ions at the first transport site in the plasmalemma.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Arnon, D. I., Fratzke, W. E., Johnson, C. M.: Hydrogen ion concentration in relation to absorption of inorganic nutrients by higher plants. Plant Physiol. 17, 515–524 (1942).
Avron, M.: Photophosphorylation by swiss-chard chloroplasts. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 40, 257–272 (1960).
Baumeister, W., Conrad, D.: Über Beziehungen zwischen der Natriumversorgung und dem Phosphathaushalt bei Scenedesmus obliquus (Turp.). Kuetz. Ber. dtsch. bot. Ges. 79, 15–26 (1966).
Farr, T. D.: Phosphorus, properties of the element and some of its compounds. Tennessee Valley Authority, Chem. Engineering, Report No 8 (1950).
Gerlach, E., Deuticke, B.: Eine einfache Methode zur Mikrobestimmung von Phosphat in der Papierchromatographie. Biochem. Z. 337, 477–479 (1963).
Goodman, J., Rothstein, A.: The active transport of phosphate into yeast cell. J. gen. Physiol. 40, 915–923 (1957).
Hagen, C. E., Hopkins, H. T.: Ionic species in orthophosphate absorption by barley roots. Plant Physiol. 30, 193–199 (1955).
Hendrix, J. E.: The effect of pH on the uptake and accumulation of phosphate and sulphate ions by bean plants. Amer. J. Bot. 54, 560–563 (1967).
Honert, T. H. Van Den: Over eigenschappen van plantenwortels, welke cen rol spelen bij de opname van voedingszouten. Naturk. T. v. Nederl. Ind. 97, 150–162 (1937).
Jacobson, L., Hannaple, R. J., Moore, D. P.: Non-metabolic uptake of ions by barley roots. Plant Physiol. 33, 278–282 (1958).
Lineweaver, H., Burk, D.: The determination of enzyme dissociation constants. J. Amer. chem. Soc. 56, 658–666 (1934).
MacRobbie, E. A. C.: Ionic relations of Nitella translucens. J. gen. Physiol. 45, 861–878 (1962).
McGeorge, W. T.: Electrodialysis as a measure of phosphate availability in soils and the relation of soil reaction and ionization of phosphates to phosphate assimilation. Ariz. Agr. Exp. Sta. Tech. Bull. 38, 593–630 (1932).
Meszes, G., Erdei, L.: (Mg++−K+−Na+)-activated ATPase activity and its properties in Scenedesmus obtiusculus alga cells. Acta biochim. biophys. Acad. Sci. hung. 4, 131–139 (1969).
Quastel, J. H.: Molecular transport at cell membranes. Proc. roy. Soc. B 163, 169–196 (1965).
Siegenthaler, P. A., Belsky, M. M., Goldstein, S.: Phosphate uptake in an obligately marine fungus: A specific requirement for sodium. Science 155, 93–94 (1967).
Simonis, W., Urbach, W.: Über eine Wirkung von Natrium-Ionen auf die Phosphataufnahme und die lichtabhängige Phosphorylierung von Ankistrodesmus braunii. Arch. Mikrobiol. 46, 265–286 (1963).
Sitte, P.: Biomembranen: Struktur und Funktionen. Ber. dtsch. bot. Ges. 82, 329–383 (1969).
Ulrich-Eberius, C. I., Simonis, W.: Der Einfluß von Natrium- und Kalium-Ionen auf die Photophosphorylierung bei Ankistrodesmus braunii. Planta (Berl.) 92, 358–373 (1970).
Yanagita, T.: Successive determination of the free, acid-labile and residual phosphates in biological systems. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 55, 260–268 (1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ullrich-Eberius, C.I., Simonis, W. Der Einfluß von Natrium- und Kaliumionen auf die Phosphataufnahme bei Ankistrodesmus braunii . Planta 93, 214–226 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00387642
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00387642