Summary
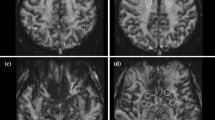
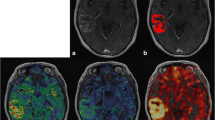
This retrospective study was performed to describe the appearance of intracranial hemorrhagic lesions on magnetic resonance (MR) imaging at 0.35 tesla using the spin-echo technique, and define the present clinical role of MRI in this particular pathology. Forty-eight examinations of forty-three patients with forty-seven intracranial hemorrhagic lesions (39 true hematomas and 8 hemorrhagic lesions mixed with other tissues) were reviewed for this study. Comparative CT studies were available for all the patients. In our limited experience with acute hematomas (less than 3 days old), low or isointense signal was seen with a short TR (0.5 s), but a relative increase in signal intensity was observed with a long TR (2.0 s). This appearance of acute hematoma was not specific. Chronic hematomas (more than 3 days old) were imaged as foci of bright signal intensity on both short and long TR. This pattern was characteristic of chronic hematoma. With a short TR (0.5 s), two hemorrhagic lesions (5 and 7 days old) were displayed as an isointense signal surrounded by a rim of high intensity signal. This peripheral zone most likely represented liquefaction at the clot's periphery and the initial formation of methemoglobin. T1 and T2 relaxation times were found to be very long for acute hematomas (first two days). T1 values of chronic hematomas (more than 3 days old) were compaaatively short and in the same range as T1 of white matter. T2 values of chronic hematomas decreased also but remained very long.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailes DR, Young IR, Thomas DJ, et al. (1982) NMR imaging of the brain using spin-echo sequences. Clin Radiol 33: 395–414
Bydder GM, Steiner RE, Young IR, et al. (1982) Clinical NMR imaging of the brain: 140 cases. AJNR 3: 459–480
Coooks LE, Ortendahl DA, Kaufman L, et al. (1983) Clinical efficiency of nuclear magnetic resonance imaging. Radiology 146: 123–128
Sipponen JT, Sepponen RE, Sivula A (1984) Chronic subdural hematoma: Demonstration by magnetic resonance. Radiology 150: 79–85
Moon KL Jr, Brant-Zawadzki M, Pitts LH, et al. (1984) Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging of CT-isodense subdural hematomas. AJNR 5: 319–322
Sipponen JT, Sepponen RE, Sivula A (1983) Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) imaging of intracerebral hemorrhage in the acute and resolving phases. JCAT 7: 954–959
Han JS, Kaufman B, Alfidi RJ, et al. (1984) Head trauma evaluated by magnetic resonance and computed tomography: A comparison. Radiology 150: 71–77
Da La Paz RL, New PFJ, Buonanno FS, et al. (1984) NMR imaging of intracranial hemorrhage. JCAT 8: 599–607
Crooks L, Arakawa M, Hoenninger J, et al. (1982) Nuclear magnetic resonance whole-body imager operating at 3.5 KGauss. Radiology 143: 169–174
Ehman RL, Kjos BO, Brasch RC, et al. (1984) Spin-echo imaging: Method for correction of systematic errors in calculated T1 and spin density. Presented at the Third Annual Meeting of the Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. New York, August 13–17
Koenig SH, Brown RD III, Lindstrom RT (1981) Interactions of solvent with the heme region of methemoglobin and fluoromethemoglobin. Biophys J 34: 397–408
Bradley WA, Schmidt PG (1984) The changing MRI appearance of subarachnoid hemorrhage: Effect of methemoglobin formation. Presented at the Third Annual Meeting of the Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. New York, August 13–17
Scotti G, Terbrugge K, Melancon D et al. (1977) Evaluation of the age of subdural hematomas by computerized tomography. J Neurosurg 47: 311–315
Wolverton MK, Creeps LF, Sundaram M, et al. (1983) Hyperdensity of recent hemorrhage at body computed tomography: Incidence and morphologic variation. Radiology 148: 779–784
Butzer JF, Cancilla PA, Cornell SH (1976) Computerized axial tomography of intracerebral hematoma. A clinical and neuropathological study. Arch Neurol 33: 206–214
Dolinskas CA, Bilaniuk LT, Zimmerman RA, et al. (1977) Computed tomography of intracerebral hematomas. I. Transmission CT observations on hematoma resolution. AJR 129: 681–688
New PFJ, Aronow S (1976) Attenuation measurements of whole blood and blood fractions in computed tomography. Radiology 121: 635–640
Messina AV, Chernik NL (1975) Computed tomography: The “resolving” intracerebral hemorrhage. Radiology 118: 609–613
Muller HR, Wuthrigh R, Wiggli U, et al. (1975) The contribution of computerized axial tomography to the diagnosis of cerebellar and pontine hematomas. Stroke 6: 467–475
Scott WR, New PFJ, Davis KR, et al. (1974) Computerized axial tomography of intracerebral and intraventricular hemorrhage. Radiology 112: 73–80
Dolinskas CA, Bilaniuk LT, Zimmerman RA et al. (1977) Computed tomography of intracerebral hematomas. II. Radionuclide and transmission CT studies of the perihematoma region. AJR 129: 689–692
Brant-Zawadzki M, Bartkowski HM, Pitts LH et al. (1984) NMR imaging of experimental and clinical cerebral edema. Noninvasive Med Imag 1: 43–47
Young IR, Bydder GM, Hall AS, et al. (1983) Extracerebral collections: Recognition by NMR imaging. AJNR 4: 833–834
Moller A, Ericson K (1979) Computed tomography of isoattenuating subdural hematomas. Radiology 130: 149–152
Amendola M, Ostrum BJ (1977) Diagnosis of isodense subdural hematomas by computed tomography. AJR 129: 693–697
Dooms GC, Hricak H, Sollitto RA, et al. (1985) MR of lipomatous tumors and tumors with fatty component: Comparison with CT
Rosen BR, Carter EA, Pykett IL, et al. (1985) Proton chemical shift imaging: An evaluation of its clinical potential using an in vivo fatty liver model. Radiology 154: 469–472
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dooms, G.C., Uske, A., Brant-Zawadzki, M. et al. Spin-echo MR imaging of intracranial hemorrhage. Neuroradiology 28, 132–138 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00327885
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00327885