Summary
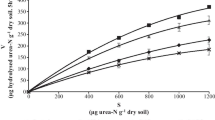
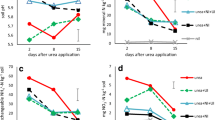
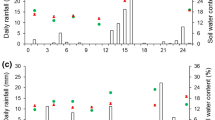
Comparison of the effects of N-(n-butyl) thiophosphoric triamide (NBPT) and phenylphosphorodiamidate (PPD) on hydrolysis of urea by plant (jackbean), microbial (Bacillus pasteurii), and soil urease showed that whereas NBPT was considerably more effective than PPD for inhibiting hydrolysis of urea added to soil, it was much less effective than PPD for inhibiting hydrolysis of urea by plant or microbial urease. Studies to account for this observation indicated that NBPT is rapidly decomposed in soil to a compound that is much more effective than NBPT for inhibition of urease activity and that this compound is N-(n-butyl) phosphoric triamide.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beaton JD (1978) Urea: Its popularity grows as a dry source of nitrogen. Crop Soils 30:11–14
Bremner JM, Chai HS (1986) Evaluation of N-butyl phosphorothioic triamide for retardation of urea hydrolysis in soil. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 17:337–351
Bremner JM, Chai HS (1989) Effects of phosphoroamides on ammonia volatilization and nitrite accumulation in soils treated with urea. Biol Fertil Soils 8, in press
Chai HS, Bremner JM (1987) Evaluation of some phosphoroamides as soil urease inhibitors. Biol Fertil Soils 3:189–194
Douglas LA, Bremner JM (1970) Extraction and colorimetric determination of urea in soils. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 34:859–862
Engelstad OP, Hauck RD (1974) Urea: Will it become the most popular nitrogen carrier? Crop Soils 26:11–14
Harre EA, White WC (1985) Fertilizer market profile. In: Engelstad OP (ed) Fertilizer technology and use. Am Soc Agron, Madison. Wisc, pp 1–24
Hauck RD (1984) Technological approaches to improving the efficiency of nitrogen fertilizer use by crop plants. In: Hauck RD (ed) Nitrogen in crop production. Am Soc Agron, Madison, Wisc, pp 551–560
Gasser JKR (1964) Urea as a fertilizer. Soils Fert 27:175–180
Mulvaney RL, Bremner JM (1979) A modified diacetylmonoxime method for colorimetric determination of urea in soil extracts. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 10:1163–1170
Mulvaney RL, Bremner JM (1981) Control of urea transformations in soils. In: Paul EA, Ladd JN (eds) Soil biochemistry, vol 5. Dekker, New York, pp 153–196
Stangel PJ (1984) World nitrogen situation — trends, outlook and requirements. In: Hauck RD (ed) Nitrogen in crop production. Am Soc Agron, Madison, Wisc, pp 23–54
Tomlinson TE (1970) Urea: Agronomic applications. Proc Fert Soc 113:1–76
Zantua MI, Bremner JM (1975) Comparison of methods of assaying urease activity in soils. Soil Biol Biochem 7:291–295
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCarty, G.W., Bremner, J.M. & Chai, H.S. Effect of N-(n-butyl) thiophosphoric triamide on hydrolysis of urea by plant, microbial, and soil urease. Biol Fert Soils 8, 123–127 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00257755
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00257755